Your tech stack is growing, and with it, the endless stream of log data from every device, application, and system you manage. It’s a flood—one growing 50 times faster than traditional business data—and hidden within it are the patterns and anomalies that hold the key to the performance of your applications and infrastructure.
But here’s the challenge you know well: with every log, the noise grows louder, and manually sifting through it is no longer sustainable. Miss a critical anomaly, and you’re facing costly downtime or cascading failures.
That’s why log analysis has evolved. AI-powered log intelligence isn’t just a way to keep up—it’s a way to get ahead. By detecting issues early, cutting through the clutter, and surfacing actionable insights, it’s transforming how fast-moving teams operate.
The stakes are high. The question is simple: are you ready to leave outdated log management behind and embrace the future of observability?
Why traditional log analysis falls short
Traditional log analysis methods struggle to keep pace with the complexities of modern IT environments. As organizations scale, outdated approaches relying on manual processes and static rules create major challenges:
- Overwhelming log volumes: Exponential growth in log data makes manual analysis slow and inefficient, delaying issue detection and resolution.
- Inflexible static rules: Predefined rules cannot adapt to dynamic workloads or detect previously unknown anomalies, leading to blind spots.
- Resource-intensive and prone to errors: Manual query matching requires significant time and effort, increasing the likelihood of human error.
These limitations become even more pronounced in multicloud environments, where resources are ephemeral, workloads shift constantly, and IT landscapes evolve rapidly. Traditional tools lack the intelligence to adapt, making it difficult to surface meaningful insights in real time.
How AI transforms log analysis
AI-powered log analysis addresses these shortcomings by leveraging machine learning and automation to process vast amounts of data, detect anomalies proactively, and generate actionable insights. Unlike traditional methods, AI adapts dynamically, ensuring organizations can stay ahead of performance issues, security threats, and operational disruptions.
The challenge of log volume and variety
If you’ve ever tried to make sense of the endless stream of log data pouring in from hundreds of thousands of metrics and data sources, you know how overwhelming it can be. Correlating events and finding anomalies across such a diverse and massive dataset isn’t just challenging—it’s nearly impossible with traditional methods.
As your logs grow exponentially, manual analysis can’t keep up. AI log analysis offers a solution, enabling you to make sense of vast datasets, identify anomalies as they happen, and reveal critical insights buried within the noise of complex log data.
So, what is AI log analysis?
AI log analysis builds on log analysis by using artificial intelligence and automation to simplify and interpret the increasing complexity of log data.
Unlike traditional tools that rely on manual processes or static rules, AI log analysis uses machine learning (ML) algorithms to dynamically learn what constitutes “normal” behavior across systems, proactively surfacing anomalies, pinpointing root causes in real time, and even preventing issues by detecting early warning signs before they escalate.
In today’s dynamic, multicloud environments—where resources are often ephemeral, workloads shift constantly, and SaaS sprawl creates an explosion of log data—AI-powered log analysis has become essential. An AI tool can sift through vast amounts of data, uncover hidden patterns, and find anomalies far faster and more accurately than human teams. And so, AI log analysis not only saves valuable time and resources but also ensures seamless monitoring, enhanced security, and optimized performance.
With AI log analysis, organizations can move from a reactive to a proactive approach, mitigating risks, improving operational efficiency, and staying ahead in an increasingly complex IT landscape.
How does it work? Applying machine learning to log data
The goal of any AI log analysis tool is to upend how organizations manage the overwhelming volume, variety, and velocity of log data, especially in dynamic, multicloud environments.
With AI, log analysis tools can proactively identify trends, detect anomalies, and deliver actionable insights with minimal human intervention. Here’s how machine learning is applied to log analysis tools:
Step 1 – Data collection and learning
AI log analysis begins by collecting vast amounts of log data from across your infrastructure, including applications, network devices, and cloud environments. Unlike manual methods that can only handle limited data sets, machine learning thrives on data volume. The more logs the system ingests, the better it becomes at identifying patterns and predicting potential issues.
To ensure effective training, models rely on real-time log streams to continuously learn and adapt to evolving system behaviors. For large-scale data ingestion, a data lake platform can be particularly useful, enabling schema-on-read analysis and efficient processing for AI models.
Step 2 – Define normal ranges and patterns
With enough log data necessary to see trends over time, the next step in applying machine learning is detecting what would fall in a “normal” range from log data. This means identifying baseline trends across metrics, such as usage patterns, error rates, and response times. The system can then detect deviations from these baselines without requiring manual rule-setting. It’s also important to understand that deviations or anomalies may also be expected or good in nature and not always considered problematic. The key is to establish a baseline and then interpret that baseline.
In multicloud environments, where workloads and architectures are constantly shifting, this step ensures that AI log analysis tools remain adaptive, even when the infrastructure becomes more complex.
Step 3 – Deploy algorithms for proactive alerts
With established baselines, machine learning algorithms can monitor logs in real time, detecting anomalies that could indicate potential configuration issues, system failures, or performance degradation. These anomalies are flagged when logs deviate from expected behavior, such as:
- Unusual spikes in network latency that may signal resource constraints.
- New log patterns appearing for the first time, which may indicate an emerging issue.
- Levels of error conditions in application logs increasing could indicate an outage on the horizon or that performance issues are happening.
- A sudden increase in failed login attempts suggesting a security breach.
Rather than simply reacting to problems after they occur, machine learning enables predictive log analysis, identifying early warning signs and reducing Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR). This proactive approach supports real-time monitoring, less outages by having healthier logs with less errors, capacity planning, and operational efficiency, ensuring that infrastructure remains resilient and optimized.
By continuously refining its understanding of system behaviors, machine learning-based log analysis eliminates the need for static thresholds and manual rule-setting, allowing organizations to efficiently manage log data at scale while uncovering hidden risks and opportunities.
Step 4 – Maintaining Accuracy with Regular Anomaly Profile Resets
Regularly resetting the log anomaly profile is essential for ensuring accurate anomaly detection and maintaining a relevant baseline as system behaviors evolve. If the anomaly profile is not reset there is potential that once seen as negative behavior may never be flagged again for the entire history of that log stream. Resetting machine learning or anomaly algorithms can allow organizations to test new log types or resources, validate alerts with anomalies or “never before seen” conditions, and reset specific resources or groups after a major outage to clear outdated anomalies.
Additional use cases include transitioning from a trial environment to production, scheduled resets to maintain accuracy on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis, and responding to infrastructure changes, new application deployments, or security audits that require a fresh anomaly baseline.
To maximize effectiveness, best practices recommend performing resets at least annually to ensure anomaly detection remains aligned with current system behaviors. Additionally, temporarily disabling alert conditions that rely on “never before seen” triggers during a reset prevents unnecessary alert floods while the system recalibrates. A structured approach to resetting anomaly profiles ensures log analysis remains relevant, minimizes alert fatigue, and enhances proactive anomaly detection in dynamic IT environments.
Benefits of AI for log analysis
Raw log data is meaningless noise until transformed into actionable insights. Modern AI-powered log analysis delivers crucial advantages that fundamentally change how we handle system data:
Immediate impact
- Sort through data faster. AI automatically clusters and categorizes incoming logs, making critical information instantly accessible without manual parsing.
- Detect issues automatically. Unlike static thresholds that can’t keep up with changing environments, AI learns and adjusts in real time. It recognizes shifting network behaviors, so anomalies are detected as they emerge—even when usage patterns evolve.
- Only be alerted to important information. Alerts from logs, like many alerts in IT, are prone to “boy who cried wolf syndrome.” When a log analysis tool creates too many alerts, no single alert stands out as the cause of an issue, if there even is an issue at all. With AI, you can move towards only being alerted when something worth your attention is happening, clearing the clutter and skipping the noise.
- Detect anomalies before they create issues. In most catastrophic events, there’s typically a chain reaction that occurs because an initial anomaly wasn’t addressed. AI allows you to remove the cause, not the symptom.
Strategic benefits
- Know the root cause: AI doesn’t just flag an issue—it understands the context, helping you pinpoint the root cause before small issues escalate into major disruptions.
- Enhance security: Sensitive data is safeguarded with AI-enabled privacy features like anonymization, masking, and encryption. This not only protects your network but also ensures compliance with security standards.
- Allocate resources faster and more efficiently: By automating the heavy lifting of log analysis, AI frees up your team to focus on higher-priority tasks, saving both time and resources.
Measurable results
- Reduce system downtime. Quick identification of error sources leads to faster resolution and improved system reliability.
- Reduce noisy alerts. Regular anomaly reviews result in cleaner logs and more precise monitoring.
- Prevent issues proactively. Early detection of unusual patterns helps prevent minor issues from escalating into major incidents.
Why spend hours drowning in raw data when AI log analysis can do the hard work for you? It’s smarter, faster, and designed to keep up with the ever-changing complexity of modern IT environments. Stop reacting to problems—start preventing them.
How LM Logs uses AI for anomaly detection
When it comes to AI log analysis, one of the most powerful applications is anomaly detection. Real-time detection of unusual events is critical for identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate. LM Logs, a cutting-edge AI-powered log management platform, stands out in this space by offering advanced anomaly detection features that simplify the process and enhance accuracy.
Let’s explore how LM Logs leverages machine learning to uncover critical insights and streamline log analysis.
To start — not every anomaly signals trouble—some simply reflect new or unexpected behavior. However, these deviations from the norm often hold the key to uncovering potential problems or security risks, making it critical to flag and investigate them. LM Logs uses machine learning to make anomaly detection more effective and accessible. Here’s how it works:
- Noise reduction: By filtering out irrelevant log entries, LM Logs minimizes noise, enabling analysts to focus on the events that truly matter.
- Unsupervised learning: Unlike static rule-based systems, LM Logs employs unsupervised learning techniques to uncover patterns and detect anomalies without requiring predefined rules or labeled data. This allows it to adapt dynamically to your environment and identify previously unseen issues.
- Highlighting unusual events: LM Logs pinpoints deviations from normal behavior, helping analysts quickly identify and investigate potential problems or security breaches.
- Contextual analysis: LM Logs combines infrastructure metric alerts and anomalies into a single view. This integrated approach streamlines troubleshooting, allowing operators to focus on abnormalities with just one click.
- Flexible data ingestion: Whether structured or unstructured, LM Logs can ingest logs in nearly any format and apply its anomaly detection analysis, ensuring no data is left out of the process.
By leveraging AI-driven anomaly detection, LM Logs transforms how teams approach log analysis. It not only simplifies the process but also ensures faster, more precise identification of issues, empowering organizations to stay ahead in an ever-evolving IT landscape.
Case Study: How AI log analysis solved the 2024 CrowdStrike incident
In 2024, a faulty update to CrowdStrike’s Falcon security software caused a global outage, crashing millions of Windows machines. Organizations leveraging AI-powered log analysis through LM Logs were able to pinpoint the root cause and respond faster than traditional methods allowed, avoiding the chaos of prolonged outages.
Rapid identification
When the incident began, LM Logs anomaly detection flagged unusual spikes in log activity. The first anomaly—a surge of new, unexpected behavior—was linked directly to the push of the Falcon update. The second, far larger spike occurred as system crashes, reboots, and error logs flooded in, triggering monitoring alerts. By correlating these anomalies in real time, LM Logs immediately highlighted the faulty update as the source of the issue, bypassing lengthy war room discussions and saved IT teams critical time.
Targeted remediation
AI log analysis revealed that the update impacted all Windows servers where it was applied. By drilling into the affected timeslice and filtering logs for “CrowdStrike,” administrators could quickly identify the common denominator in the anomalies. IT teams immediately knew which servers were affected, allowing them to:
- Isolate problematic systems.
- Initiate targeted remediation strategies.
- Avoid finger-pointing between teams and vendors by quickly escalating the issue to CrowdStrike.
This streamlined approach ensured organizations could contain the fallout and focus on mitigating damage while awaiting a fix from CrowdStrike.
Learning in progress
One of the most remarkable aspects of this case was the machine learning in action. For instance:
- LM Logs flagged the first occurrence of the system reboot error—”the system has rebooted without cleanly shutting down first”—as an anomaly.
- Once this behavior became repetitive, the system recognized it as learned behavior and stopped flagging it as an anomaly, allowing teams to focus on new, critical issues instead.
This adaptive capability highlights how AI log analysis evolves alongside incidents, prioritizing the most pressing data in real-time.
Results
Using LM Logs, IT teams quickly:
- Pinpointed the root cause of the outage.
- Determined the scope of the impact across servers.
- Avoided wasting valuable time and resources on misdirected troubleshooting.
In short, AI log analysis put anomaly detection at the forefront, turning what could have been days of confusion into rapid, actionable insights.
AI log analysis is critical for modern IT
In today’s multicloud environments, traditional log analysis simply can’t keep up with the volume and complexity of data. AI solutions have become essential, not optional. They deliver real-time insights, detect anomalies before they become crises, and enable teams to prevent issues rather than just react to them.
The CrowdStrike incident of 2024 demonstrated clearly how AI log analysis can transform crisis response—turning what could have been days of debugging into hours of targeted resolution. As technology stacks grow more complex, AI will continue to evolve, making log analysis more intelligent, automated, and predictive.
Organizations that embrace AI log analysis today aren’t just solving current challenges—they’re preparing for tomorrow’s technological demands. The question isn’t whether to adopt AI for log analysis, but how quickly you can integrate it into your operations.
For years, the term “AIOps” has been tossed around, but for IT teams, it hasn’t really brought the change it promised. Gartner coined the term, promising that machine learning and AI would forever change how we manage IT operations. Yet, the reality has been underwhelming. For most teams, traditional AIOps has amounted to little more than event management with a shiny new label.
The problem isn’t just unmet expectations. IT environments have become increasingly complex, with data sources multiplying exponentially. Today, only a tiny percentage of alerts are critical, but the sheer volume of noncritical alerts has skyrocketed. Teams are drowning in noise, tied to outdated, rules-based systems requiring constant upkeep. The promised automation and efficiency never materialized. Instead, IT teams are left grappling with missed SLAs, delayed resolutions, and burned-out employees.
But this isn’t another story about AIOps falling short. This is about what happens when we take a step back and fundamentally rethink the approach. The future of ITOps isn’t about managing every alert—it’s about regaining control of your IT operations.
With Edwin AI, we’re not just rebranding old ideas; we’re delivering proven results through autonomous operations, intelligent event processing, and comprehensive data integration.
In this article, we’ll explore:
- Why traditional AIOps failed to deliver on its promises
- What makes the next generation of ITOps—agentic AIOps—fundamentally different
- How Edwin AI is transforming IT operations today
- Real results that teams are achieving without the usual overhead
Successful IT operations aren’t about reacting faster—they’re about working smarter. Let’s dive into what that really means.
Why traditional AIOps failed
Traditional AIOps promised to change IT operations forever, but instead, it introduced new complexities while failing to solve the fundamental problems. Let’s break down why these systems aren’t working—and why they never could.
AIOps’ foundation was flawed
At its core, traditional AIOps is built on three fundamentally problematic pillars:
- Rules-based systems demand constant maintenance. Traditional AIOps is like building a house on shifting sand. These systems depend entirely on predefined rules that require constant maintenance. As your IT environment evolves—which it does by the day, hour, and minute—each rule needs manual updates. It’s a never-ending cycle of tweaking and tuning that consumes valuable engineering time.
- CMDB and topology data are unreliable. Traditional AIOps systems are only as good as their Configuration Management Database (CMDB) integration. They rely heavily on topology maps to make correct associations and avoid false alerts. But here’s the situation: CMDBs are notoriously difficult to maintain and often outdated. When your topology data is wrong—which it frequently is—your entire AIOps system breaks down, creating more problems than it solves.
- Alert fatigue is constant and growing. The most visible symptom of traditional AIOps failure is the sheer volume of alerts. When a single tool generates hundreds of “critical” alerts per hour, and only a fraction are critical, you’re not managing operations—you’re drowning in noise. Your teams waste precious time sifting through alerts instead of solving real problems.
The cost of AIOps’ empty promises
Failed AIOps tools are costing your business more than you might realize. This isn’t about theoretical problems—it’s about the real pain your organization feels every day.
Your infrastructure is more complex than ever, but your tools are still stuck in the past. Traditional AIOps sold you a dream of intelligent operations, but delivered nothing more than bloated dashboards and endless alert streams. The impact? It’s hitting your bottom line in ways that executives often miss:
- Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) continues to climb. Your best people—the ones who should be driving innovation—are trapped in a cycle of alert fatigue and manual remediation. Each day brings another flood of notifications, most of them false positives, all of them demanding attention. When you’re spending that vast majority of your time on noise, there’s no room left for signal.
- Top talent isn’t leaving just because of better offers—they’re leaving because they’re exhausted. Every morning brings hundreds of alerts to triage, dozens of rules to tweak, and countless hours spent maintaining a system that was supposed to maintain itself. The promise of automation has become just another layer of manual work.
- Every minute of downtime has a ripple effect. While your teams are busy managing their alert queues, real incidents are slipping through the cracks. SLAs aren’t just numbers on a report—they’re promises to your customers. Broken promises mean missed SLAs, which can translate into financial penalties, damaged relationships, and lost revenue. And right now, those promises are being broken by systems that were meant to help keep them.
The cost isn’t just operational—it’s strategic. While your competitors are innovating, you’re investing in:
- Endless tool customization and integration
- Training teams on systems that don’t deliver
- Maintaining rules that are outdated before they’re even implemented
- Validating topology data
- Investigating non-critical alerts
- Firefighting issues that should have been prevented
The failure of AIOps is a business survival problem. The market won’t wait while you struggle with systems that were outdated before they were implemented. It’s time to stop patching over the problems of traditional AIOps and start embracing a fundamentally different approach.
Agentic AIOps is the next generation of ITOps
If, like many organizations, your IT operations have been bogged down by alert fatigue, unmanageable tool sprawl, and failed promises from traditional AIOps, it’s time for a change. The challenges posed by legacy systems have left many organizations scrambling, but there’s a new way forward: agentic AIOps.
Agentic AIOps represents a complete departure from the limitations of old AIOps tools. It’s not about just detecting issues—it’s about actively solving them. By combining agentic AI with AIOps, agentic AIOps provides an autonomous, self-maintaining approach to IT operations that proactively detects, diagnoses, and resolves issues across your entire infrastructure. It’s built to eliminate noise, provide actionable insights, and remove the burden of constant maintenance, all while learning and adapting in real time.
This is the shift your IT operations need. Here’s how agentic AIOps is setting the new standard for IT management:
No maintenance, no rules, no topology
No more rules-based systems. Agentic AIOps doesn’t need your topology maps or your CMDB to function. It learns your environment organically, adapts to changes automatically, and maintains itself. No more spending weekends updating correlation rules or mapping dependencies. The system evolves with your infrastructure, not against it.
Comprehensive data integration
Traditional tools see your IT environment as a collection of metrics and logs. Agentic AIOps sees the whole story. It pulls in everything—from your standard observability data to the Slack message where Diana mentioned that weird database behavior last month. It’s not just collecting data; it’s building context from:
- Team communications across channels
- Historical incident records in your ITSM
- Documentation buried in some internal database
- Tribal knowledge scattered across your organization
Beyond alert reduction—true IT event intelligence
This isn’t about filtering alerts—it’s about understanding them. When something goes wrong, agentic AIOps doesn’t just tell you what happened. It tells you why it matters, what it’s connected to, and most importantly—what you should do about it. We’re talking about:
- 80%+ reduction in noise (and no, that’s not a typo)
- Automatic correlation of related events across your entire stack
- Predictive insights that help you prevent issues, not just react to them
A generative AI interface built for real work
With a generative interface powered by Large Language Models (LLMs), agentic AIOps makes complex problem-solving accessible to everyone on your team. Junior engineers can tap into years of institutional knowledge. Senior engineers can focus on strategy instead of firefighting. It’s like having an AI-powered expert system that:
- Provides contextual summaries of incidents
- Offers intelligent troubleshooting guidance
- Learns from every interaction to get smarter over time
The bottom line? Agentic AIOps gives you control without constant attention
Agentic AIOps isn’t about replacing your team—it’s about amplifying their capabilities. It’s about shifting left, from reactive firefighting to proactive control. No rules to maintain, no topologies to update, no alert fatigue to manage. Just intelligent, autonomous operations that let your team focus on what matters: driving your business forward.
This isn’t just a better way to manage IT operations—it’s the only way to scale operations in today’s complex, dynamic environments. And the best part? It’s not a future promise. It’s delivering results today.
The Edwin AI advantage: Agentic AIOps that delivers on its promises
We built Edwin AI specifically to solve the challenges that traditional AIOps have failed to address.Traditional tools often result in bloated dashboards, excessive noise, and little actionable insight. Edwin AI is here to close that gap by leveraging agentic AI, a powerful engine that empowers IT teams to solve problems faster and more effectively.
Agentic AI enables Edwin AI to act not just as a passive tool, but as an active, intelligent assistant that reduces noise, automates resolution, and ensures the right information reaches the right person at the right time. By utilizing agentic AI, Edwin AI allows Level 1 support staff to resolve issues typically reserved for Level 2 or 3 engineers, without needing to escalate them, enabling teams to resolve problems smarter, not harder.
Here’s what this looks like in practice:
- Your newer team members can handle advanced issues because a generative AI agent provides them with instant access to your organization’s collective troubleshooting knowledge, built directly into Edwin AI.
- Your seasoned engineers spend less time managing routine incidents, as Edwin AI’s Event Intelligence enables them to focus on high-value, strategic work instead of triaging alerts.
- Issues are resolved more quickly, as Edwin AI delivers the right information immediately—no more searching through documentation or relying on tribal knowledge. Agentic AI makes these insights actionable, right when you need them.
- Unlike traditional AIOps tools that overwhelm teams with noise, Edwin AI manages this automatically. AI correlates alerts, reduces false positives, and proactively remediates issues before they reach your team. Your IT operations run smoother, and your team isn’t buried under unnecessary alerts.
Perhaps most importantly, Edwin AI prevents the all-too-familiar scenario of your team working late nights and weekends to keep up with an endless stream of incidents. By empowering every team member with the tools they need to resolve complex issues independently, you get better coverage and support, without the risk of burnout. Agentic AI ensures that issues are handled with context, knowledge, and automation, which means your IT team spends less time managing incidents and more time solving the right problems.
Edwin AI isn’t just another dashboard—it’s a real-world solution already in use today, helping teams in production environments solve complex problems, reduce MTTR, and improve overall IT efficiency. It’s driven by agentic AI, which actively drives improvements, automates processes, and resolves issues faster.
Sure, we could talk about impressive metrics like MTTR improvement and alert noise reduction (for that, we welcome you to read at least one of our case studies.). But at the end of the day, what really matters is this: Edwin AI helps your team spend less time triaging alerts and more time on meaningful work. Problems get solved faster. Your team can go home on time. And your IT operations finally deliver on the promises that traditional AIOps tools couldn’t.
Agentic AIOps is setting us up for the future, today.
As we move from reactive to predictive operations, businesses face new challenges that demand more than just traditional tools. Scaling for tomorrow’s demands requires not just efficiency, but smart, adaptive systems that evolve with your organization. Edwin AI offers real, actionable results today, laying the foundation for long-term success.
With Edwin AI, you’re not just solving today’s problems—you’re positioning your organization to thrive in a future where IT operations are proactive, agentic, and seamlessly integrated. The burden of firefighting and missed SLAs is a thing of the past. Edwin AI empowers your team with the tools and intelligence they need to take control, solve complex problems, and drive innovation.
The future of AIOps is here, and it’s faster, smarter, and more proactive than ever before. Don’t wait for the next wave of disruption—take the first step toward transforming your IT operations today.
Every minute of system downtime costs enterprises a minimum of $5,000. With IT infrastructure growing more complex by the day, companies are put at risk of even greater losses.
Adding insult to injury, traditional operations tools are woefully out of date. They can’t predict failures fast enough. They can’t scale with growing infrastructure. And they certainly can’t prevent that inevitable 3 AM crisis—the one where 47 engineers and product managers flood the war room, scrambling through calls and documentation to resolve a critical production issue.
Agentic AIOps flips the script. Unlike passive monitoring tools, it actively hunts down potential failures before they impact your business. It learns. It adapts. And most importantly, it acts—without waiting for human intervention.
This blog will show you how agentic AIOps transforms IT from reactive to predictive, why delaying implementation could cost millions, and how platforms like LogicMonitor Envision—the core observability platform—and Edwin AI can facilitate this transformation.
You’ll learn:
- What agentic AIOps is
- The core components driving agentic AIOps
- How agentic AIOps works
- A step-by-step guide to implementing agentic AIOps
- How agentic AIOps compares to traditional AIOps and related concepts
- Real-world use cases where agentic AIOps delivers measurable value
- The key benefits of agentic AIOps
- How LogicMonitor enables agentic AIOps success
What is agentic AIOps?
Agentic AIOps redefines IT operations by combining generative AI and agentic AI with cross-domain observability to autonomously detect, diagnose, and resolve infrastructure issues.
For IT teams floundering in alerts, juggling tools, and scrambling during incidents, this shift is transformative. Unlike traditional tools that merely detect issues, agentic AIOps understands them. It doesn’t just send alerts—it actively hunts down root causes across your entire IT ecosystem, learning and adapting to your environment in real time.
Agentic AIOps is more than a monitoring tool; it’s a paradigm shift. It unifies observability, resolves routine issues automatically, and surfaces strategic insights your team would otherwise miss. This is achieved through:
- Operating autonomously, learning and adapting in real time.
- Unifying observability across the entire infrastructure, minimizing blind spots.
- Automatically resolving routine issues, while surfacing critical insights.
With its zero-maintenance architecture, there’s no need for constant rule updates or alert tuning. The generative interface simplifies troubleshooting by transforming complex issues into actionable steps and clear summaries.
Agentic AIOps isn’t just a tool—it’s essential for the future of IT operations.
Why is agentic AIOps important?
As IT systems grow more complex—spanning hybrid environments, cloud, on-premises, and third-party services—the challenges of managing them multiply. Data gets scattered across platforms, causing fragmentation and alert overload.
Traditional AIOps can’t keep up. Static rules and predefined thresholds fail to handle the dynamic nature of modern IT. These systems:
- Require constant manual tuning
- Struggle to connect disparate data
- Are reactive, not proactive
As a result, IT teams waste time piecing together data, hunting down issues, and scrambling to prevent cascading failures. Every minute spent is costly.
Agentic AIOps changes that. By shifting to a proactive approach, it automatically detects and resolves issues before they escalate. This not only reduces downtime but also cuts operational costs.
With agentic AIOps, IT teams are freed from routine firefighting and can focus on driving innovation. By unifying observability and automating resolutions, it removes the noise, enhances efficiency, and supports smarter decision-making.
| Traditional AIOps | Agentic AIOps |
| Relies on static rules | Learns and adapts in real time |
| Requires constant updates to rules and thresholds | Zero-maintenance |
| Data is often siloed and hard to connect | Comprehensive view across all systems |
| Reactive | Proactive |
| Time-consuming troubleshooting | Actionable, clear next steps |
| Teams are overwhelmed with alerts and firefighting | Automates routine issue resolution, freeing teams for higher-value tasks. |
| Struggles with cross-functional visibility | Cross-tool integration |
| Noisy alerts | Filters out noise |
Key components of agentic AIOps
Enterprise IT operations are trapped in a costly paradox: despite pouring resources into monitoring tools, outages continue to drain millions, and digital transformation often falls short. The key to breaking this cycle lies in two game-changing components that power agentic AIOps:
Generative AI and agentic AI power autonomous decision-making
Agentic AIOps is powered by the complementary strengths of generative AI and agentic AI.
While generative AI creates insights, content, and recommendations, agentic AI takes the critical step of making autonomous decisions and executing actions in real-time. Together, they enable a level of proactive IT management previously beyond reach.
Here’s how the two technologies work in tandem:
- Generative AI: This component generates meaningful content from raw data, such as plain-language summaries, root cause analyses, and step-by-step guides for remediation. It transforms complex technical data into easily digestible insights and recommendations. In short, generative AI clarifies the situation, offering valuable context and potential solutions.
- Agentic AI: Once insights are generated by the system, agentic AI takes over. It doesn’t simply offer suggestions; it actively makes decisions and implements them based on real-time data. This allows the system to autonomously resolve issues, such as rolling back configurations, scaling resources, or initiating failovers without human intervention.
By combining the strengths of both, agentic AIOps transcends traditional IT monitoring. It enables the system to shift from a reactive stance—where IT teams only respond to problems—to a proactive approach where it can predict and prevent issues before they affect operations.
Why this matters
Instead of simply alerting IT teams when something goes wrong, generative AI sifts through data to uncover the underlying cause, offering clear, actionable insights. For example, if an application begins to slow down, generative AI might pinpoint the bottleneck, suggest the next steps, and even generate a root cause analysis.
But it’s agentic AI that takes the reins from there, autonomously deciding how to respond—whether by rolling back a recent update, reallocating resources, or triggering a failover to ensure continuity.
This ability to not only detect but also act, reduces downtime, cuts operational costs, and enhances system reliability. IT teams are freed from the constant cycle of fire-fighting, instead managing and preventing issues before they impact business operations.
Cross-domain observability provides complete operational visibility
Fragmented visibility creates significant business risks, but cross-domain observability mitigates these by integrating data across all IT environments—cloud, on-prem, and containerized—while breaking down silos and providing real-time, actionable insights. This capability is essential for agentic AIOps, transforming IT from a reactive cost center to a proactive business driver.
Here’s how it works:
- Data integration: Cross-domain observability connects structured data (like metrics and logs) with unstructured data (such as team conversations and incident reports) into a unified stream, ensuring no critical data is missed. This complete integration empowers agentic AIOps to detect and resolve issues across your entire IT ecosystem without human intervention.
- Dynamic response: Unlike traditional systems that wait for manual adjustments, agentic AIOps continually adapts to evolving conditions in real-time. Through intelligent event correlation and predictive modeling, it autonomously adjusts operations to mitigate risks as they arise.
With agentic AIOps, you gain what traditional IT operations can’t offer: autonomous, intelligent operations that scale with your business, delivering both speed and efficiency.
Why this matters
Cross-domain observability is essential to unlocking the full potential of agentic AIOps. It goes beyond data collection by providing real-time insights into the entire IT landscape, integrating both structured and unstructured data into a unified platform. This gives agentic AIOps the context it needs to make swift, autonomous decisions and resolve issues without manual oversight.
By minimizing blind spots, offering real-time system mapping, and providing critical context for decision-making, it enables agentic AIOps to act proactively, preventing disruptions before they escalate. This shift from reactive to intelligent, autonomous management creates a resilient and scalable IT environment, driving both speed and efficiency.
How does agentic AIOps work?
Agentic AIOps simplifies complex IT environments by processing data across the entire infrastructure. It uses AI to detect, diagnose, and predict issues, enabling faster, smarter decisions and proactive management to optimize performance and reduce downtime.
Comprehensive data integration
Modern IT infrastructures generate an overwhelming amount of data, from application logs to network metrics and security alerts. Agentic AIOps captures and integrates both structured (metrics, logs, traces) and unstructured data (like incident reports and team communications) across all operational domains. This unified, cross-domain visibility ensures no area is overlooked, eliminating blind spots and offering a comprehensive, real-time view of your entire infrastructure.
Real-time intelligent analysis
While traditional systems bombard IT teams with alerts, agentic AIOps uses generative and agentic AI to go beyond simply detecting patterns. It processes millions of data points per second, predicting disruptions before they occur. With continuous, autonomous learning, it adapts to changes without needing manual rule adjustments, offering smarter insights and more precise solutions.
Actionable intelligence generation
Unlike standard monitoring tools, agentic AIOps doesn’t just flag problems—it generates actionable, AI-powered recommendations. Using large language models (LLMs), it provides clear, contextual resolutions in plain language, easily digestible by both technical and non-technical users. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) ensures these insights are drawn from the most up-to-date and relevant data.
Autonomous resolution
This is where agentic AIOps stands apart: when it detects an issue, it takes action. Whether it’s scaling resources, rerouting traffic, or rolling back configurations, the system acts autonomously to prevent business disruption. This eliminates the need for manual intervention, allowing IT teams to focus on higher-level strategy.
Now—imagine during a product launch, the agentic AIOps system detects a 2% degradation in database performance. It could immediately correlate the issue with a recent change, analyze the potential impact—$27,000 per minute—and autonomously roll back the change. The system would then document the incident for future prevention. In just seconds, the problem would be resolved with minimal business impact.
Agentic AIOps stands out by shifting IT operations from constant firefighting to proactive, intelligent management. By improving efficiency, reducing downtime, and bridging the IT skills gap, it ensures your IT infrastructure stays ahead of disruptions and scales seamlessly with your evolving business needs.
Implementing agentic AIOps
Implementing agentic AIOps requires a strategic approach to ensure that your IT operations become more efficient, autonomous, and proactive.
Here’s a step-by-step framework for getting started:
- Assess your current IT infrastructure: Begin by understanding the complexity and gaps in your existing systems. Identify the areas where you’re struggling with scalability, visibility, or reliability. This will help you pinpoint where agentic AIOps can drive the most impact.
- Identify pain points: Take a deep dive into the challenges your IT team faces daily. Whether it’s alert fatigue, delayed incident resolution, or inadequate cross-domain visibility, recognize where agentic AIOps can make the biggest difference. The goal is to streamline processes and reduce friction in areas that are stalling progress.
- Choose the right tools and platforms: Select a platform that integrates observability and AIOps. For example, LogicMonitor Envision offers an all-in-one solution to bring together cross-domain observability with intelligent operations. Additionally, consider tools like Edwin AI for AI-powered incident management to automate and prioritize issues based on business impact.
- Plan a phased implementation strategy: Start with a pilot project to test the solution in a controlled environment. Use this phase to refine processes, iron out any issues, and collect feedback. Then, roll out the solution in stages across different parts of the organization. This phased approach reduces risk and ensures smooth adoption.
- Monitor and refine processes: Once your solution is live, continuously monitor its impact on IT efficiency and business outcomes. Track key metrics such as incident resolution time, alert volume, and downtime reduction. Be prepared to adjust processes as needed to ensure maximum effectiveness.
- Foster a culture of innovation and agility: For agentic AIOps to succeed, it’s important to build a culture that values continuous improvement and agility. Encourage your team to embrace new technologies and adapt quickly to evolving needs. This mindset will optimize the value of agentic AIOps, ensuring your IT operations stay ahead of disruptions.
We all know this part — getting started is often the hardest step, especially when you’re tackling something as transformative as agentic AIOps. But here’s the thing: you can’t afford to ignore the “why” behind the change. Without a clear plan, these innovations are just shiny tools that won’t stick. Your approach matters, because how you introduce agentic AIOps to your IT infrastructure is the difference between success and just another attempt at change that doesn’t stick.
Comparing agentic AIOps to related concepts
When you’re diving into the world of IT operations, it’s easy to get lost in the sea of buzzwords. Terms like AIOps, DevOps, and ITSM can blur together, but understanding the distinctions is crucial for making informed decisions about your IT strategy. Let’s break down agentic AIOps and see how it compares to some of the most common concepts in the space.
Agentic AIOps vs. traditional AIOps
Traditional AIOps typically relies on predefined rules and static thresholds to detect anomalies or failures. When these thresholds are crossed, human intervention is often required to adjust or respond. It’s reactive at its core, often requiring manual adjustments to keep the system running smoothly.
On the other hand, agentic AIOps takes autonomy to the next level. It learns from past incidents and adapts automatically to changes in the IT environment. This means it can not only detect problems in real time but also act proactively, providing insights and recommendations without the need for manual intervention. It’s the difference between being reactive and staying ahead of potential issues before they become full-blown problems.
Agentic AIOps vs. DevOps
DevOps is all about breaking down silos between development and operations teams to speed up software delivery and improve collaboration. It focuses on automating processes in the development lifecycle, making it easier to release updates and maintain systems.
Agentic AIOps, while complementary to DevOps, adds another layer to the IT operations landscape. It enhances DevOps by automating and optimizing IT operations, providing real-time, intelligent insights that can drive more informed decision-making. Instead of just focusing on collaboration, agentic AIOps automates responses to incidents and continuously improves systems, allowing DevOps teams to focus more on innovation and less on firefighting.
Agentic AIOps vs. MLOps
MLOps focuses on managing the lifecycle of machine learning models, from training to deployment and monitoring. It’s designed to streamline machine learning processes and ensure that models perform as expected in real-world environments.
Agentic AIOps also uses machine learning but applies it in a different context. It doesn’t just manage models; it’s geared toward optimizing IT operations. By leveraging AI, agentic AIOps can automatically detect, respond to, and prevent incidents in your IT infrastructure. While MLOps focuses on the performance of individual models, agentic AIOps focuses on the larger picture—improving the overall IT environment through AI-driven automation.
Agentic AIOps vs. ITSM
ITSM (IT Service Management) is about ensuring that IT services are aligned with business needs. It focuses on managing and delivering IT services efficiently, from incident management to change control, and typically relies on human intervention to resolve issues and improve service delivery.
Agentic AIOps enhances ITSM by bringing automation and intelligence into the equation. While ITSM handles service management, agentic AIOps can automate the detection and resolution of incidents, improving efficiency and dramatically reducing resolution times. It makes IT operations smarter by predicting problems and addressing them before they impact users or business outcomes.
By comparing agentic AIOps to these related concepts, it becomes clear that it stands out as a transformative force in IT operations. While other systems may focus on specific aspects of IT management or software development, agentic AIOps brings automation, intelligence, and proactive management across the entire IT ecosystem—making it a game-changer for businesses looking to stay ahead in the digital age.
Agentic AIOps use cases
When it comes to implementing agentic AIOps, the possibilities are vast. From reducing downtime to driving proactive infrastructure management, agentic AIOps has the potential to transform IT operations across industries. Let’s dive into some specific use cases where this technology shines, showcasing how it can solve real-world problems and drive value for businesses.
Incident response and downtime reduction
One of the core strengths of agentic AIOps is its ability to detect performance degradation in real-time. When an issue arises, agentic AIOps doesn’t wait for a human to notice the problem. It immediately analyzes the situation, correlates relevant data, and generates a root cause analysis. The system can then recommend solutions to restore performance before end users are affected. In cases where downtime is minimized, the system works swiftly, ensuring minimal disruption to the business.
Predictive maintenance and asset management
Asset management can be a challenge when it comes to proactively monitoring IT infrastructure. Agentic AIOps addresses this by analyzing performance data and detecting early signs of degradation in hardware or software. By identifying these issues before they become critical, the system can suggest optimal maintenance schedules or even recommend parts replacements to prevent failures. This predictive capability helps reduce unplanned downtime and ensures smooth operations.
Security incident management
In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity is more important than ever. Agentic AIOps plays a vital role in enhancing security by identifying unusual network activity that may indicate a potential threat. It can match this activity to known threats, isolate the affected areas, and provide step-by-step guides for IT teams to contain the threat. The system’s proactive approach reduces the likelihood of security breaches and accelerates the response time when incidents occur.
Digital transformation and IT modernization
As organizations modernize their IT infrastructure and embrace digital transformation, cloud migration becomes a key challenge. Agentic AIOps streamlines this process by analyzing dependencies, identifying migration issues, and even automating parts of the data migration process. By ensuring a smooth transition to the cloud, businesses can maintain operational continuity and achieve greater flexibility in their infrastructure.
Better customer experience
The customer experience often hinges on the reliability and performance of the underlying IT systems. Agentic AIOps monitors infrastructure to ensure optimal performance, identifying and resolving bottlenecks before they affect users. By optimizing resources and automating issue resolution, businesses can ensure a seamless user experience that builds customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Proactive infrastructure optimization
As organizations scale, managing cloud resources efficiently becomes more critical. Agentic AIOps continuously monitors cloud resource usage, identifying underutilized instances and recommending adjustments to workloads. By optimizing infrastructure usage, businesses can reduce costs, improve resource allocation, and ensure that their IT environment is always running at peak efficiency.
H3: Hybrid and multi-cloud management
For companies using hybrid or multi-cloud environments, managing a complex IT ecosystem can be overwhelming. A hybrid observability platform can gathers real-time data from on-premises systems and cloud environments, while agentic AIOps analyzes patterns, detects anomalies, and automates responses—together delivering a unified, intelligent view of the entire infrastructure. With this comprehensive visibility, organizations can optimize resources across their IT landscape and ensure that security policies remain consistent, regardless of where their data or workloads reside.
Data-driven decision making
Agentic AIOps empowers IT teams with data-driven insights by aggregating and analyzing large volumes of performance data. This intelligence can then be used for informed decision-making, helping businesses with capacity planning, resource allocation, and even forecasting future infrastructure needs. By providing actionable insights, agentic AIOps helps organizations make smarter, more strategic decisions that drive long-term success.
These use cases illustrate just a fraction of what agentic AIOps can do. From improving operational efficiency to enhancing security, this technology can bring measurable benefits across many aspects of IT management. By proactively addressing issues, optimizing resources, and providing intelligent insights, agentic AIOps empowers organizations to stay ahead of disruptions and position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly complex IT landscape.
Benefits of agentic AIOps
Let’s face it: there’s no time for fluff when it comes to business decisions. If your IT operations aren’t running efficiently, it’s not just a minor inconvenience—it’s a drain on resources, a threat to your bottom line, and a barrier to growth. Agentic AIOps isn’t just about solving problems—it’s about preventing them, optimizing resources, and driving smarter business decisions. Here’s how agentic AIOps transforms your IT landscape and delivers measurable benefits.
Improved efficiency and productivity
In an age where time is money, agentic AIOps excels at cutting down the noise. By filtering alerts and reducing unnecessary notifications, the system helps IT teams focus on what truly matters, saving valuable time and resources. It also automates root cause analysis, enabling teams to resolve issues faster and boosting overall productivity. With agentic AIOps, your IT operations become leaner and more efficient, empowering teams to act with precision.
Reduced incident risks
Every minute spent resolving critical incidents costs your business. Agentic AIOps significantly reduces response times for high-priority incidents (P0 and P1), ensuring that issues are identified, analyzed, and addressed swiftly. By preventing service disruptions and reducing downtime, agentic AIOps helps you maintain business continuity and minimize the impact of incidents on your operations.
Reduced war room time
When disaster strikes, teams often scramble into “war rooms” to fix the problem. These high-stress environments can drain energy and focus. Agentic AIOps streamlines this process by quickly diagnosing issues and providing actionable insights, reducing the need for lengthy, high-pressure meetings. With less time spent managing crises, your IT teams can redirect their focus to strategic, value-driving tasks that move the business forward.
Bridging the IT skills gap
The demand for specialized IT skills often exceeds supply, leaving organizations scrambling to fill critical positions. Agentic AIOps alleviates this challenge by automating complex tasks that once required deep expertise. With this level of automation, even teams with limited specialized skills can handle sophisticated IT operations and manage more with less. This ultimately reduces reliance on niche talent and ensures your IT team can operate at full capacity.
Cost savings
Cost control is always top of mind for any organization, and agentic AIOps delivers on this front. By automating routine tasks and improving response times, the platform helps reduce labor costs and increase overall productivity. Additionally, its ability to prevent costly outages and minimize downtime contributes to a more cost-effective IT operation, offering significant savings in the long run.
In short, agentic AIOps doesn’t just make IT operations more efficient—it transforms them into a proactive, intelligent force that drives productivity, reduces risks, and delivers lasting cost savings. In a world where the competition is fierce, this level of optimization gives organizations the edge they need to stay ahead and scale effortlessly.
How LogicMonitor enables agentic AIOps success
Let’s be honest for a moment: the path to operational excellence isn’t paved with half-measures. It’s paved with the right tools—tools that not only keep the lights on but that proactively prevent the lights from ever flickering.
LogicMonitor is one such tool that enables agentic AIOps to thrive. By integrating observability with intelligence, LogicMonitor creates the foundation for successful AIOps implementation, making your IT operations smarter, more agile, and more efficient.
LM Envision: Comprehensive observability across hybrid environments
When it comes to achieving true agentic AIOps success, visibility is everything. LM Envision provides comprehensive, end-to-end observability across your entire hybrid IT environment. It delivers real-time data collection and analysis, empowering proactive insights that help you stay ahead of issues before they escalate. As the foundation of your agentic AIOps strategy, LM Envision enables seamless integration, providing the visibility and insights needed to optimize system performance and reduce downtime.
The scalability and flexibility of LM Envision ensures that as your business grows and IT complexity increases, your ability to monitor and manage your infrastructure does as well. Whether you’re operating on-premises, in the cloud, or in hybrid environments, LM Envision adapts, feeding your agentic AIOps system with the critical data it needs to function at peak performance. With LM Envision, you’re always a step ahead, shifting from reactive to proactive IT management and making smarter decisions based on real-time data.
Edwin AI: AI-powered incident management
In the world of agentic AIOps, speed and accuracy are paramount when it comes to incident management. That’s where Edwin AI comes in. As an AI-powered incident management tool, Edwin AI makes agentic AIOps possible by streamlining event intelligence, troubleshooting, and incident response. It automates critical processes, consolidating data from multiple sources to offer real-time incident summaries, auto-correlation of related events, and actionable insights—all while cutting through the noise.
With Edwin AI, teams no longer waste time dealing with irrelevant alerts. By filtering out the noise and presenting the most pertinent information, it speeds up incident resolution and minimizes downtime. One of its standout features is its ability to integrate with a variety of other tools, creating cross-functional visibility and enabling smarter decision-making.
Moreover, Edwin AI offers customizable models, ensuring that its insights are tailored to the unique needs of your organization. It simplifies complex technical details into plain language, enabling all team members—regardless of technical expertise—to understand the situation and take swift action. With Edwin AI, your teams can move faster, more confidently, and with greater precision, all while minimizing the risk of service disruption.
Together, LM Envision and Edwin AI form the ultimate platform for driving agentic AIOps success. By pairing observability with intelligent, autonomous incident management, these tools enable businesses to optimize operations, improve efficiency, and ultimately ensure a more proactive and resilient IT infrastructure.
Why enterprises must act now
Here’s the hard truth: if you don’t act now, you’ll fall behind. The future of IT operations is here, and it’s powered by agentic AIOps. The age of AI (GenAI) is reshaping everything, and companies that don’t harness its power risk being left in the dust.
Early adopters have the chance to redefine performance and cost efficiency. Agentic AIOps isn’t just about keeping up—it’s about staying ahead. Those who implement it today will not only meet the demands of tomorrow, they’ll shape them.
No more chasing buzzwords or empty promises. Organizations are looking for practical, scalable solutions that work. Agentic AI automates the routine so your teams can focus on what truly matters: innovation and strategic impact.
IT leaders know this: the future isn’t waiting. Adapt now or risk being irrelevant.
The traditional data center is undergoing a dramatic transformation. As artificial intelligence reshapes industries from healthcare to financial services, it’s not just the applications that are changing—the very infrastructure powering these innovations requires a fundamental rethinking.
Today’s data center bears little resemblance to the server rooms of the past. The world is seeing a convergence of high-density computing, specialized networks, and hybrid architectures designed specifically to handle the demands of AI workloads.
Source: Gartner (November 2024)
This transformation comes at a critical time. With analyst projections indicating that over 90% of organizations will adopt hybrid cloud by 2027, CIOs face mounting pressure to balance innovation with operational stability. AI workloads demand unprecedented computing power, driving a surge in data center capacity requirements and forcing organizations to rethink their approach to sustainability, cost management, and infrastructure design.
The New Data Center Architecture
At the heart of this evolution is a more complex and distributed infrastructure. Modern data centers span public clouds, private environments, edge locations, and on-premises hardware–all orchestrated to support increasingly sophisticated AI applications.
The technical requirements are substantial. High-density GPU clusters, previously the domain of scientific computing, are becoming standard components. These systems require specialized cooling solutions and power distribution units to manage thermal output effectively. Storage systems must deliver microsecond-level access to massive datasets, while networks need to handle the increased traffic between distributed components.
This distributed architecture necessarily creates hybrid environments where workloads and resources are spread across multiple locations and platforms. While this hybrid approach provides the flexibility and scale needed for AI operations, it introduces inherent challenges in resource orchestration, performance monitoring, and maintaining consistent service levels across different environments. Organizations must now manage not just individual components but the complex interactions between on-premises infrastructure, cloud services, and edge computing resources.
The Kubernetes Factor in Modern Data Centers
Container orchestration, particularly through Kubernetes (K8s), has emerged as a crucial element in managing AI workloads. Containerization provides the agility needed to scale AI applications effectively, but it also introduces new monitoring challenges as containers spin up and down rapidly across different environments.
The dynamic nature of containerized AI workloads adds complexity to resource management. Organizations must track GPU allocation, memory usage, and compute resources across multiple clusters while ensuring optimal performance. This complexity multiplies in hybrid environments, where containers may run on-premises one day and in the cloud the next, making maintaining visibility across the entire container ecosystem critical.
As containerized AI applications become central to business operations, organizations need granular insights into both performance and cost implications. Understanding the resource consumption of specific AI workloads helps teams optimize container placement and resource allocation, directly impacting both operational costs and energy efficiency.
Balancing Cost and Sustainability
Perhaps the most pressing challenge for CIOs is managing the environmental and financial impact of these high-powered environments. Data centers (with cryptocurrencies and AI) consumed about 460 TWh of electricity worldwide in 2022, almost 2% of total global electricity demand. This consumption could more than double by 2026, largely driven by increasing AI workloads.
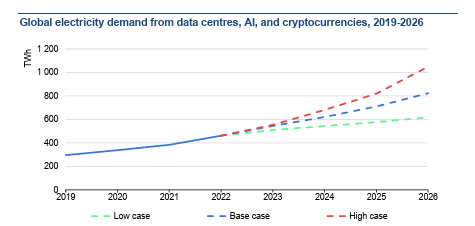
Sources: Joule (2023), de Vries, The growing energy footprint of AI; CCRI Indices (carbon-ratings.com); The Guardian, Use of AI to reduce data centre energy use; Motors in data centres; The Royal Society, The future of computing beyond Moore’s Law; Ireland Central Statistics Office, Data Centres electricity consumption 2022; and Danish Energy Agency, Denmark’s energy and climate outlook 2018.
Leading organizations are adopting sophisticated approaches to resource optimization. This includes:
- Dynamic workload distribution between on-premises and cloud environments
- Automated resource scaling based on actual usage patterns
- Implementation of energy-efficient cooling solutions
- Real-time monitoring of power usage effectiveness
These optimization strategies, while essential, require comprehensive visibility across the entire infrastructure stack to be truly effective.
Hybrid Observability in the Age of the Modern Data Center
As AI workloads become more complex, the next frontier in data center evolution is comprehensive, hybrid observability. Traditional monitoring approaches struggle to provide visibility across hybrid environments, especially when managing resource-intensive AI applications.
Leading enterprises are increasingly turning to AI-powered observability platforms that can integrate data from thousands of sources across on-premises, cloud, and containerized environments.
LogicMonitor Envision is one platform that has proven its value in this new reality. Syngenta, a global agricultural technology company, reduced alert noise by 90% after implementing LM Envision and Edwin AI, the first agentic AI built for IT. The platform allowed their IT teams to shift from reactive troubleshooting to strategic initiatives. This transformation is becoming essential as organizations balance multiple priorities:
- Managing AI workload performance across hybrid environments
- Optimizing resource allocation to control costs
- Meeting sustainability goals through efficient resource utilization
- Supporting continuous innovation while maintaining reliability
These interconnected challenges demand more than traditional monitoring capabilities—they require a comprehensive approach to infrastructure visibility and control.
The Strategic Imperative for Modern Data Centers
The message for CIOs is clear: as data centers evolve to support AI initiatives, full-stack observability becomes more than a monitoring tool. It’s a strategic imperative. Organizations need a partner who can deliver actionable insights at scale, helping them navigate the complexity of modern infrastructure while accelerating their digital transformation journey.
Think about running a city without a traffic control system—chaos, delays, and gridlock everywhere. That’s basically what happens to IT infrastructure without network monitoring. It’s the control center that keeps everything running smoothly, securely, and efficiently.
Network monitoring is all about keeping an eye on data flow, device performance, and system security to ensure everything works seamlessly. But as hybrid networks and cloud-based services become the norm, IT environments are getting more complicated. That’s why network monitoring has gone from being a “nice to have” to a must-have for keeping operations on track.
Without it, businesses risk blind spots that lead to slow performance, disruptions, and security threats, all of which can create bigger problems.
How Network Monitoring Works
Network monitoring works through a simple cycle of data collection, analysis, reporting, and alerting. Each step is key to keeping your network running smoothly and securely:
- Data Collection: Monitoring begins with capturing real-time metrics from devices and endpoints using standardized protocols. This gives you the raw information you need to get a clear picture of what’s happening across your network.
- Analysis: Raw data gets turned into valuable insights by spotting trends, identifying anomalies, and using advanced analytics. These insights help you track performance and catch potential security threats before they become bigger problems.
- Reporting: Clear, actionable reports make complex data easy to understand and use. Whether it’s a simple dashboard or detailed performance metrics, these reports help teams evaluate strategies and make smarter decisions.
- Alerting: Automated alerts catch issues early, so they don’t turn into larger issues. With integrations like email and SMS, monitoring tools make it easy for teams to respond quickly, keep things running smoothly, and avoid unnecessary downtime.
When everything works together, you get the visibility and insights you need to keep your IT environment running smoothly.
Different Types of Networks and Devices
Networks come in many forms, each with its own purpose and infrastructure. Whether you’re dealing with a small local setup or a massive global system, it’s important to know the different types of networks and the devices that make them work. That’s the key to keeping everything running smoothly.
Network types
| Component | Definition | Function |
| Local Area Network (LAN) | A computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area, such as a residence, school, or office building | • Enables resource sharing within a local environment • Provides high-speed data transfer between connected devices • Facilitates centralized management of resources |
| Wide Area Network (WAN) | A telecommunications network that extends over a large geographical area | • Connects multiple LANs across different locations • Enables long-distance communication • Supports global business operations |
| Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) | A wireless computer network that links devices within a limited area using wireless communication | • Provides mobile connectivity • Enables flexible device placement • Supports multiple concurrent users |
| Cloud networks | Networks that leverage cloud computing resources and infrastructure | • Offers scalable networking resources • Enables global accessibility • Provides on-demand services |
| Software-defined Networks (SDN) | An approach to network management that enables dynamic, programmatically efficient network configuration | • Centralizes network control • Enables network programmability • Simplifies network management |
| Data center networks | Designed for high-speed data processing in data centers | Support: • Storage • Computing • Application hosting for enterprise and cloud operations. |
| Industrial networks | Built for industrial automation and control systems | Ensures communication between: • Machinery • Sensors • Systems |
| Edge networks | Located at the periphery of centralized data centers | • Process data closer to the source • Reduces latency and bandwidth use for time-sensitive applications |
| Voice and video networks | Optimized for transmitting voice and video data | Reliable, low-latency communication for real-time interactions |
Core networking devices
| Component | Definition | Function |
| Routers | Network devices that forward data packets between computer networks | • Determines optimal path for data transmission • Connects different networks • Manages traffic between networks |
| Switches | Networking hardware that connects devices within a network | • Forwards data between devices on same network • Manages local network traffic • Creates collision domains |
| Firewalls | Network security devices that monitor and filter incoming and outgoing network traffic | • Enforces security policies • Blocks unauthorized access • Monitors network traffic |
| Servers | Computers that provide resources, services, or applications to clients in a network | • Data processing • Application hosting • Resource distribution |
| Network load balancers | Devices that distribute traffic across multiple servers | • Prevent overload on individual servers • Improves availability and reliability |
Wireless infrastructure
| Component | Definition | Function |
| Access points | Devices that create a wireless local area network | • Broadcasts wireless signals • Connects wireless devices to network • Manages wireless traffic |
| Wireless controllers | Centralized systems for managing wireless access points | • Simplify configuration • Monitoring of wireless networks |
Servers
| Component | Definition | Function |
| Physical servers | Hardware-based computers that provide services to other computers in a network | • Hosts applications and services • Stores and processes data • Manages network resources |
| Virtual servers | Software-based emulation of physical computers | • Provides flexible resource allocation • Enables server consolidation • Supports multiple operating systems |
Storage systems
| Component | Definition | Function |
| SAN/NAS devices | Storage Area Networks (SAN) and Network-Attached Storage (NAS) devices for shared storage | • Provide centralized data storage • High-speed access to data storage for multiple systems |
| Cloud storage gateways | Interfaces that connect on-premises systems to cloud storage solutions | • Enable hybrid cloud strategies • Link local infrastructure with cloud resources |
Security devices
| Component | Definition | Function |
| IDS/IPS | Systems that monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and security policy violations | • Detects security threats • Prevents unauthorized access • Logs security events |
| VPN gateway | A network node that connects two networks using different protocols | • Encrypts network traffic • Enables secure remote access • Maintains private network connectivity |
Voice and video communication devices
| Component | Definition | Function |
| VoIP phones | Phones that use Voice over IP (VoIP) technology for calls | • Deliver cost-effective communication • Flexible use over IP networks |
| Voice conferencing equipment | Systems enabling group audio and video communication | • Provide high-quality audio • Reliable conferencing solution for teams |
Power and environmental monitoring systems
| Component | Definition | Function |
| UPS System | Uninterruptible Power Supply system that provides emergency power | • Maintains power during outages • Protects equipment from power surges • Enables graceful shutdown |
| HVAC Units | Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning systems for environmental control | • Maintains optimal temperature • Controls humidity levels • Ensures proper air circulation |
Miscellaneous
| Component | Definition | Function |
| Application delivery controllers | Devices that optimize and secure the delivery of applications over a network | Enhance: • Performance • Reliability • Security for application delivery to end-users |
| IoT and edge devices | Smart devices located at the edge of a network, such as sensors and gateways | • Collect and process data closer to its source • Enables real-time analytics • Reduced latency |
| Network performance tools | Tools and systems designed to monitor and analyze network efficiency | • Provide metrics and diagnostics • Optimize network performance • Resolve issues |
| End-user devices | Devices used directly by individuals, such as computers and mobile phones | Access and interact with: • Network resources • Applications • Services |
10 Challenges in Network Monitoring
As IT environments grow more complex, network monitoring faces its own set of hurdles. Here are 10 key challenges that teams encounter:
- Scaling monitoring tools: As networks expand with more devices, traffic, and endpoints, traditional monitoring solutions often struggle to scale efficiently without impacting performance.
- Managing alert noise: Excessive alerts, including false positives, lead to alert fatigue, making it harder for teams to identify and prioritize critical incidents.
- Integrating diverse systems: Hybrid IT environments require monitoring tools to integrate seamlessly with on-premises systems, cloud platforms, and third-party applications, increasing configuration complexity.
- Observing hybrid environments: Monitoring distributed infrastructure—spanning physical, virtual, and cloud systems—often lacks consistency, creating gaps in visibility.
- Blind spots in visibility: Encrypted traffic, containerized applications, and microservices can obscure insights, leaving network teams without a complete picture of performance.
- Dynamic infrastructure monitoring: Virtualized resources, containers, and dynamic workloads are constantly spinning up and down, making it challenging to maintain accurate and up-to-date monitoring configurations.
- Budget and resource constraints: Limited budgets and understaffed teams often struggle to implement, manage, and optimize advanced monitoring tools effectively.
- Security of monitoring systems: Poorly secured monitoring platforms can become attack vectors themselves, compromising critical systems and data.
- Delayed incident detection: Latency in identifying and responding to performance degradations or outages increases downtime, often breaching SLAs and impacting end-users.
- Keeping up with emerging technologies: Rapid adoption of new technologies, like IoT, SD-WAN, and 5G, frequently outpaces the capabilities of monitoring tools, requiring constant updates and reconfiguration.
Addressing these challenges requires more than traditional monitoring tools. It demands solutions that are scalable, AI-driven, and designed for the complexities of modern IT.
10 Key Benefits of Network Monitoring
Modern IT environments demand more than just reactive troubleshooting. That’s where advanced monitoring and observability solutions come in, providing a strategic advantage and offering capabilities that go well beyond traditional setups. Here are ten critical benefits that modern monitoring brings to the table:
1. Scaling Monitoring Tools
Use cloud-based, scalable platforms like LogicMonitor, which adapt to growing networks and support the auto-discovery of new devices. Implement distributed collectors to handle high data volumes without overloading central systems.
- Handles growing device counts and traffic seamlessly
- Reduces manual overhead with auto-discovery
- Maintains consistent performance without additional hardware investments
2. Managing Alert Noise
Set dynamic thresholds to reduce false positives and tune alert sensitivity based on historical baselines. Leverage dependency mapping to suppress redundant alerts and focus only on root causes.
- Reduces fatigue caused by excessive alerts
- Helps teams focus on critical issues
- Improves mean time to resolution (MTTR) by addressing root causes directly
3. Integrating Diverse Systems
Choose monitoring platforms with out-of-the-box integrations for cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) and third-party tools like ServiceNow, PagerDuty, or Slack. Use APIs and custom scripts for unsupported tools.
- Provides a single source of truth for hybrid systems
- Speeds up incident response through automated workflows
- Enhances collaboration by integrating monitoring with ticketing and communication tools
4. Observing Hybrid Environments
Deploy unified monitoring solutions that provide visibility into both on-premises and cloud environments. Utilize tools with multi-cloud compatibility and containerized application insights.
- Simplifies managing hybrid IT infrastructure
- Prevents blind spots across distributed systems
- Improves alignment with modern, cloud-driven architectures
5. Blind Spots in Visibility
Use encrypted traffic analytics to inspect metadata without violating privacy. Implement container and microservice-aware monitoring to track service-level performance.
- Provides deeper insights into encrypted traffic and containerized workloads
- Ensures compliance with privacy and regulatory requirements
- Reduces risks associated with undetected performance issues
6. Dynamic Infrastructure Monitoring
Automate device discovery and configuration updates for virtualized environments. Deploy auto-scaling collectors to monitor ephemeral resources like containers and VMs.
- Keeps monitoring configurations accurate in real time
- Prevents lapses in monitoring for short-lived resources
- Enhances agility in dynamic IT environments
7. Budget and Resource Constraints
Focus on cost-effective SaaS-based platforms to reduce capital expenses and hardware requirements. Automate repetitive monitoring tasks to save operational effort.
- Reduces total cost of ownership (TCO) with SaaS solutions
- Frees up IT teams for higher-value tasks
- Scales cost-effectively without requiring additional hardware
8. Security of Monitoring Systems
Secure monitoring platforms with strong access controls, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and encryption for data in transit and at rest. Isolate monitoring tools in dedicated network zones.
- Protects monitoring systems from being exploited as attack vectors
- Ensures compliance with security regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA)
- Builds trust in monitoring data for decision-making
9. Delayed Incident Detection
Implement real-time alerting with anomaly detection powered by machine learning. Use pre-configured dashboards and service-level overviews to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) in real time.
- Shortens response times and reduces downtime
- Detects subtle anomalies before they escalate
- Maintains SLAs by providing proactive incident management
10. Keeping Up With Emerging Technologies
Choose monitoring tools with built-in support for IoT, SD-WAN, and 5G, or ensure extensibility for new technologies. Stay informed about platform updates and industry trends.
- Avoids gaps in monitoring for new technologies
- Enables seamless adoption of modern IT initiatives
- Future-proofs monitoring strategies to align with business growth
Essential monitoring tool features
Choosing the right monitoring solution is critical to managing modern IT environments. The best platforms do more than just cover the basics—they provide tools that give you real insights, simplify your operations, and keep up with your network’s changing needs. Here’s what to look for:
- Unified monitoring for hybrid environments: Monitor on-premises, cloud, and hybrid infrastructures all in one place to ensure complete visibility.
- AI-powered insights: Let AI and machine learning do the heavy lifting: detecting anomalies, predicting issues, and automating repetitive tasks.
- Network device monitoring: Maintain the health and performance of all devices in real time.
- Encrypted traffic visibility: Analyze encrypted data without compromising security or compliance requirements.
- Dynamic topology mapping: Watch your network change and grow with clear visual maps, making it easier to spot issues and understand dependencies.
- Automated device discovery: Automatically identify and onboard new devices as they’re added to the network.
- Pre-built and customizable integrations: Connect your monitoring solution to existing tools and workflows for a streamlined experience.
- Real-time alerting and event correlation: Respond quickly to incidents with automated notifications and detailed event analysis.
- Edge and IoT monitoring: Keep an eye on devices at the edge of your network to ensure reliable performance in distributed environments.
- Security and compliance: Meet regulatory compliance and requirements while also monitoring for threats.
- Multi-cloud observability: Monitor services and applications across multiple cloud environments with consistent insights.
- Scalable architecture: Ensure your monitoring system can grow with your network’s needs, handling increased traffic, devices, and users effortlessly.
- Intuitive user interface: Simplify navigation and data analysis with a platform designed for usability and clarity.
- Cost transparency and predictability: Avoid surprises with clear, scalable pricing that aligns with your organization’s growth.
Modern network monitoring platforms, like LogicMonitor Envision, combine these features to deliver comprehensive visibility and actionable insights. With the right solution, your team can reduce downtime, enhance performance, and stay ahead of potential issues.
Wrapping up
Network monitoring is no longer a supporting player in IT operations—it’s the backbone for ensuring performance, security, and reliability across increasingly complex environments. From hybrid networks to IoT devices, the demands on your infrastructure are growing, and having modern monitoring solutions to stay on top of it all is more important than ever.
Whether you’re troubleshooting issues in real time, proactively identifying vulnerabilities, or optimizing resources for future growth, the right monitoring platform empowers your team to operate with confidence. Solutions like LM Envision combine comprehensive visibility, AI-driven insights, and scalable architectures to meet the challenges of today’s IT landscapes.
Explore more in our network monitoring series to dive deeper into key concepts and best practices including:
- The benefits of network monitoring
- Network monitoring use cases by industry
- 5 key concepts of network monitoring
- Network performance metrics and protocols
- The 3 pillars of network monitoring
- Alert fatigue in network monitoring
With the rapid growth of data, sprawling hybrid cloud environments, and ongoing business demands, today’s IT landscape demands more than troubleshooting. Successful IT leaders are proactive, aligning technology with business objectives to transform their IT departments into growth engines.
At our recent LogicMonitor Analyst Council in Austin, TX, Chief Customer Officer Julie Solliday led a fireside chat with IT leaders across healthcare, finance, and entertainment. Their insights highlight strategies any organization can adopt to turn IT complexity into business value. Here are five key takeaways:
1. Business value first: Align IT with core organizational goals
Rafik Hanna, SVP at Topgolf, emphasizes, “The number one thing is business value.” For Hanna, every tool, and every process, must directly enhance the player experience. As an entertainment destination, Topgolf’s success depends on delivering superior experiences that differentiate them from competitors and drive continued business growth. This focus on outcomes serves as a reminder for IT leaders to ask:
- How does this initiative impact our core business objectives? Every IT action should enhance the end-user experience, whether it’s for customers, clients, or internal users. At Topgolf, Hanna translates IT decisions directly to their “player experience,” ensuring every technology choice meets customer satisfaction and engagement goals.
- Are we measuring what matters? Key performance indicators (KPIs) should reflect business value, not just technical outputs. Hanna’s team, for instance, closely monitors engagement metrics to directly connect IT performance to customer satisfaction.
- Is the ROI on IT investments clear? Clear metrics and ROI assessments make the case for IT spending. For Hanna, measurable gains in customer satisfaction justify the IT budget, shifting it from a cost center to a driver of business value.
Executive insight: Aligning IT goals with organizational objectives not only secures executive buy-in but also positions IT as a strategic partner, essential to achieving broader company success.
2. Streamline your toolset: Consolidate for clarity and efficiency
Andrea Curry, a former Marine and Director of Observability at McKesson, inherited a landscape of 22 monitoring and management tools—each with overlapping functions and costs. Her CTO asked, “Why do we have so many tools?” she recalls. This sparked a consolidation effort from 22 to 5 essential solutions. Curry’s team reduced both complexity and redundancy, ultimately enhancing visibility and response time. Key lessons include:
- Inventory first: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of all current solutions and their roles. Curry’s team mapped out each tool’s purpose and cost, laying the groundwork for informed decisions.
- Eliminate redundancies: Challenge the necessity of every tool. Can one solution handle multiple functions? Curry found that eliminating overlapping tools streamlined support needs and freed resources for higher-value projects.
- Prioritize high-impact solutions: Retain tools that directly contribute to organizational goals. With fewer, more powerful tools, her team reduced noise and gained clearer insights into their environments.
Executive insight: Consolidating tools isn’t just about saving costs; it’s about building a lean, focused IT function that empowers staff to tackle higher-priority tasks, strengthening operational resilience.
3. Embrace predictive power: Harness AI for enhanced observability
With 13,000 daily alerts, Shawn Landreth, VP of Networking and NetDevOps at Capital Group, faced an overwhelming workload for this team. Implementing AI-powered monitoring leveraging LogicMonitor Edwin AI, Capital Group’s IT team cut alerts by 89% and saved $1 million annually. Landreth’s experience underscores:
- AI is a necessity: Advanced AI tools are no longer a luxury but a necessity for managing complex IT environments. For Landreth, Edwin AI is transforming monitoring from reactive to proactive by detecting potential issues early.
- Proactive monitoring matters: AI-driven insights allow teams to maintain uptime and reduce costly incidents by identifying and addressing potential failures before they escalate. This predictive capability saves time and empowers the team to focus on innovation.
- Reduce alert fatigue: AI filters out low-priority alerts, ensuring the team focuses on the critical few. In Capital Group’s case, reducing daily alerts freed up resources for high-value projects, enabling the team to be more strategic.
Executive insight: Embracing AI-powered observability can streamline operations, enhance service quality, and lead to significant cost savings, driving IT’s value beyond technical performance to real business outcomes.
4. Stay ahead: Adopt new technology proactively
When Curry took on her role at McKesson, she transitioned from traditional monitoring to a comprehensive observability model. This strategic shift from a reactive approach to proactive observability reflects the adaptive mindset required for modern IT leadership. Leaders aiming to stay competitive should consider:
- Continuously upskill: Keep pace with evolving technologies to ensure the team’s relevance and competitiveness. Curry regularly brings in training on emerging trends to ensure her team stays at the leading edge of technology.
- Experiment strategically: Curry pilots promising new technologies to assess their value before large-scale deployment. This experimental approach enables a data-backed strategy for technology adoption.
- Cultivate a culture of innovation: Foster an environment where team members feel encouraged to explore and embrace new ideas. Curry’s team has adopted a mindset of continual improvement, prioritizing innovation in their daily workflows.
Executive insight: Proactive technology adoption positions IT teams as innovators, empowering them to drive digital transformation and contribute to competitive advantage.
5. Strategic partnerships: Choose vendors invested in your success
Across the board, our panelists emphasized the importance of strong relationships. Landreth puts it simply, “Who’s going to roll their sleeves up with us? Who’s going to jump in for us?” The right partnerships can transform IT operations by aligning vendors with organizational success. When evaluating partners, consider:
- Shared goals: A successful vendor relationship aligns with your organizational vision, whether for scalability, cost-efficiency, or innovation. Landreth’s team prioritizes vendors that actively support Capital Group’s long-term objectives.
- Proactive support: A valuable partner offers prompt, ongoing support, not just periodic check-ins. For example, Curry’s vendors provide tailored, in-depth support that addresses her team’s specific needs.
- Ongoing collaboration: Partnerships that prioritize long-term success over quick wins foster collaborative innovation. Vendors who integrate their solutions with internal processes build stronger, more effective alliances.
Executive insight: Building partnerships with committed vendors drives success, enabling IT teams to achieve complex objectives with external expertise and support.
Wrapping up
Our panelists’ strategies—from tool consolidation to AI-powered monitoring and strategic partnerships—all enable IT teams to move beyond reactive firefighting into a proactive, value-driven approach.
By implementing these approaches, you can transform your IT organization from a cost center into a true driver of business value, turning the complexity of modern IT into an opportunity for growth and innovation.
LogicMonitor is pleased to have been recognized as a Customers’ Choice vendor for 2024 in the Observability Platforms category on Gartner Peer Insights™. This distinction is based on feedback and ratings as of December 30, 2024. LogicMonitor reviewers gave us a 4.7 (out of 5) overall rating in the report, with 94% saying they would recommend the LogicMonitor platform and 83% coming from companies with over $50 million in revenue based on 49 reviews submitted as of October 2024.
This recognition is particularly meaningful because it comes directly from our customers. Customer Obsession is in our DNA, and a core value our team lives daily here at LogicMonitor. We put customers at the heart of everything we do, because we understand that their success is our success.
“We believe being recognized as a Customers’ Choice represents LogicMonitor’s dedication to being a trusted partner to CIOs, IT operations teams, and organizations on their hybrid observability journeys,” said Julie Solliday, Chief Customer Officer at LogicMonitor. “We’re excited to celebrate this news and thank our visionary customers for sharing their experience on Gartner Peer Insights and helping us achieve this recognition.”
Here are just a few of the comments in the “voice of the customer” that contributed to this distinction:
The Gartner Peer Insights Customers’ Choice designation recognizes vendors in this market based on reviews from verified end users. The Customers’ Choice distinction takes into account both the number of reviews and the overall user ratings. Gartner® maintains rigorous criteria to ensure fair evaluation and recognize vendors with a high customer satisfaction rate.
To all of our customers who submitted reviews, thank you! Your feedback helps us create better products to fit your needs, and we look forward to earning the trust and confidence reflected in this distinction.
If you have a LogicMonitor story to share, we encourage you to join the Gartner® Peer Insights™ crowd and weigh in.
Gartner, Voice of the Customer for Observability Platforms, Peer Contributors, 24 December 2024
Gartner® and Peer Insights™ are trademarks of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Gartner Peer Insights content consists of the opinions of individual end users based on their own experiences, and should not be construed as statements of fact, nor do they represent the views of Gartner or its affiliates. Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in this content nor makes any warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this content, about its accuracy or completeness, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
The cloud has revolutionized the way businesses operate. It allows organizations to access computing resources and data storage over the internet instead of relying on on-premises servers and infrastructure. While this flexibility is one of the main benefits of using the cloud, it can also create security and compliance challenges for organizations. That’s where cloud governance comes in.
Cloud governance establishes policies, procedures, and controls to ensure cloud security, compliance, and cost management. In contrast, cloud management focuses on operational tasks like optimizing resources, monitoring performance, and maintaining cloud services.
Here, we’ll compare cloud governance vs. cloud management and discuss how you can use them to improve your organization’s cybersecurity posture.
What is cloud governance?
Cloud governance is managing and regulating how an organization uses cloud computing technology. It includes developing policies and procedures related to cloud services and defining roles and responsibilities for those using them.
Cloud governance aims to ensure that an organization can realize the benefits of cloud computing while minimizing risks. This includes ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, protecting data privacy, and maintaining security.
Organizations should also develop policies and procedures related to cloud services. These should be designed to meet the organization’s specific needs and be reviewed regularly.
Why is cloud governance important?
Cloud governance is important because it provides a framework for setting and enforcing standards for cloud resources. This helps ensure that data is adequately secured and service levels are met. Additionally, cloud governance can help to prevent or resolve disputes between different departments or business units within an organization.
When developing a cloud governance strategy, organizations should consider the following:
- The types of data that will be stored in the cloud and the sensitivity of that data
- The regulations that apply to the data and the organization’s compliance obligations
- The security risks associated with storing data in the cloud
- The organization’s overall security strategy
- The costs associated with using cloud services
An effective cloud governance strategy will address all of these factors and more. It should be tailored to the organization’s specific needs and reviewed regularly. Additionally, the strategy should be updated as new technologies and regulations emerge.
Organizations without a cloud governance strategy are at risk of data breaches, regulatory non-compliance, and disruptions to their business operations. A well-designed cloud governance strategy can help mitigate these risks and keep an organization’s data safe and secure.
What are the principles of cloud governance?
Cloud governance is built on principles essential for ensuring that cloud resources are used securely, efficiently, and according to business objectives. Sticking to these principles lets your organization lay out clear expectations, streamline processes, and minimize several risks associated with cloud computing. By implementing these guidelines, you can establish a robust governance framework for secure and effective cloud operations:
- Defining roles and responsibilities: Clearly define who is responsible for managing cloud services and their roles and responsibilities.
- Establishing policies and procedures: Develop policies and procedures for using cloud services, including how to provision and de-provision them, how to monitor and audit usage, and how to handle data security.
- Ensuring compliance: Make sure their cloud services comply with all relevant laws and regulations.
- Managing risk: Identify and assess risks associated with using cloud services and put controls in place to mitigate those risks.
- Monitoring and auditing: Monitor their use of cloud services and audit them regularly to ensure compliance with policies and procedures.
What is the framework for cloud governance?
A framework for cloud governance provides guidelines and best practices for managing data and applications in the cloud. It can help ensure your data is secure, compliant, and aligned with your business goals.
When choosing a framework for cloud governance, consider a few key factors:
- First, you must decide what control you want over your data and applications. Do you want complete control, or will you delegate some responsibility to a third-party provider?
- Next, you need to consider the size and complexity of your environment. A smaller organization may only need a few simple rules around data storage and access, while a larger enterprise may require a more comprehensive approach.
- Finally, you need to consider your budget. Many different cloud governance frameworks are available, so it’s essential to find one that fits within your budget.
How do you implement a cloud governance framework?
Implementing a cloud governance framework can be challenging, but it’s essential to have one in place to ensure the success of your cloud computing initiative. Here are a few tips to help you get started:
Define your goals and objectives
Before implementing a cloud governance framework, you need to know what you want to achieve. Do you want to improve compliance? Reduce costs? Both? Defining your goals will help you determine which policies and procedures need to be implemented.
Involve all stakeholders
Cloud governance affects everyone in an organization, so it’s crucial to involve all stakeholders, including upper management, IT staff, and business users. Getting buy-in from all parties will make implementing and following the governance framework easier.
Keep it simple
Don’t try to do too much with your cloud governance framework. Start small and gradually add more policies and procedures as needed. Doing too much at once will only lead to confusion and frustration.
Automate where possible
Many cloud governance tools can automate tasks such as compliance checks and cost reporting. These tools can reduce the burden on your staff and make it easier to enforce the governance framework.
What are the benefits of implementing cloud governance?
Implementing cloud governance gives organizations a structured approach to managing cloud resources, keeping cloud management aligned with business goals, and reducing risks. Using this framework, you can gain better control over your cloud environments so they operate more efficiently while safeguarding sensitive data. Cloud governance offers the following advantages for navigating the complexities of modern cloud computing.
- Improved security: One of the main concerns businesses have regarding cloud computing is security. By implementing governance structures, companies can ensure their data is safe and secure. Cloud governance can help prevent data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Increased transparency: Cloud governance can help increase transparency within an organization. Clear policies and procedures help ensure that everyone knows what is happening with their data, reducing the risk of fraud and corruption.
- Better resource management: Cloud governance can help businesses manage their resources better. Establishing structured guidelines allows companies to use their resources efficiently and improve overall organizational efficiency. This can help save money and improve the organization’s overall efficiency.
What is cloud management?
Cloud management is the process of governing and organizing cloud resources within an enterprise IT infrastructure. It includes the policies, procedures, processes, and tools used to manage the cloud environment.
Cloud management is the process of governing and organizing cloud resources within an enterprise IT infrastructure. It includes the policies, procedures, processes, and tools used to manage the cloud environment.
Cloud management aims to provide a centralized platform for provisioning, monitoring, and managing cloud resources. This helps ensure that all resources are utilized efficiently and that the environment complies with corporate governance policies.
Why is cloud management important?
Cloud management is critical for businesses because it helps them optimize their cloud resources, control costs, and facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements. Cloud management tools help companies automate the provisioning, monitoring, and maintenance of their cloud infrastructure and applications.
How does cloud management work?
Organizations increasingly turn to cloud-based solutions to help them run their businesses, so it’s crucial to understand how cloud management works. By definition, cloud management is administering and organizing cloud computing resources. It includes everything from provisioning and monitoring to security and compliance.
Several different tools and technologies can be used for cloud management, but they all share a common goal: to help organizations maximize their investment in cloud computing.
The first step in effective cloud management is understanding the different types of clouds and how they can be used to meet your organization’s needs. There are three main types of clouds: public, private, and hybrid.
- Public clouds are owned and operated by a third-party service provider. They’re the most popular cloud type, typically used for applications that don’t require a high level of security or performance.
- Private clouds are owned and operated by a single organization. They offer more control and security than public clouds but are also more expensive. Private clouds are often used for mission-critical applications.
- Hybrid clouds are a mix of public and private clouds. They offer the benefits of both clouds, but they can be more challenging to manage. Organizations often use hybrid clouds to store data in both a public and a private cloud.
What is a cloud management platform?
A cloud management platform (CMP) is software that enables an enterprise to monitor and control all aspects of its cloud computing infrastructure and resources. A CMP typically provides a unified, web-based interface through which an administrator can provision, configure, and manage public and private cloud resources.
Benefits of a cloud management platform
A cloud management platform (CMP) gives you centralized control over your cloud resources, helping to optimize operations while maintaining flexibility and security. Through a combination of cloud processes and tools in a single interface, CMPs help simplify management tasks and make the platform worth the investment. Here are some key benefits that make cloud management platforms ideal for organizations that rely on modern cloud environments:
- Cost savings: By moving your business processes and functions to the cloud, you can avoid investing in expensive on-premise software and hardware.
- Increased efficiency: With all your business processes and functions in one place, you can streamline and automate many tasks, freeing up time for you and your team to focus on other areas of the business.
- Improved collaboration: By sharing data and information in the cloud, you’ll provide greater transparency and visibility, allowing your team to work together more effectively.
- Greater flexibility: With a cloud-based solution, you can access your data and applications from anywhere in the world, giving you the freedom to work from anywhere.
What are the differences between cloud governance vs. cloud management?
Cloud governance is the set of processes, policies, and controls an organization uses to manage its cloud services. Cloud management is the day-to-day operational tasks involved in managing a cloud environment, such as provisioning and configuring resources, monitoring usage and performance, and ensuring security.
The two concepts are closely related, but there are some important differences. Cloud governance is primarily concerned with setting and enforcing standards for how the cloud is used within an organization. It defines who can access which resources, what they can use them for, and how they can be configured. Cloud management, on the other hand, is focused on actually carrying out those standards on a day-to-day basis.
How do cloud governance and cloud management work together?
Organizations need both cloud governance and management to ensure that their use of cloud resources is safe, compliant, and efficient. Cloud governance provides the framework for decision-making and sets the expectations for how cloud resources will be used. Cloud management ensures that those decisions are carried out properly and resources are used as intended.
For instance, a retail company experiencing seasonal spikes in demand might develop a cloud governance framework with policies for increasing available IT resources during peak shopping periods. These policies could also help facilitate compliance with data privacy laws like GDPR and define access controls to protect sensitive customer information. Meanwhile, cloud management tools would implement these policies by allocating additional computing resources during Black Friday, monitoring usage to prevent performance issues, and decommissioning unused resources afterward to avoid unnecessary costs.
In another case, a financial institution might rely on cloud governance to establish policies that restrict access to customer financial data to authorized personnel only through multi-factor authentication mechanisms. Governance policies might also require regular compliance audits to ensure systems meet industry regulations and standards. Cloud management tools enforce these rules using automated monitoring to detect and alert administrators of unusual activity, such as unauthorized access attempts or data anomalies.
Best practices for implementing cloud governance and cloud management
Implementing effective cloud governance and management takes careful planning and execution. By adopting best practices, you can be confident your cloud environments are secure and efficient and support your business objectives. By following these best practices, your organization can create a cloud governance and management strategy that builds long-term success in your cloud initiatives:
1. Start with a clear governance framework
Develop a comprehensive cloud governance framework that aligns with your organization’s goals and regulatory requirements. Define data storage, access control, compliance, and risk management policies. Ensure the framework addresses key areas like resource provisioning, decommissioning, and cost monitoring.
2. Prioritize stakeholder involvement
Include stakeholders in creating a strategy that balances efficiency with risk management for all operations, such as IT, legal, compliance, and business administration. Collaboration ensures alignment, avoids siloed approaches, and encourages continued communication across all departments.
3. Leverage automation
Implement tools that automate routine management tasks like resource provisioning, performance monitoring, and compliance checks. Automation reduces human error and helps to ensure the consistent application of policies, freeing up IT teams for higher-value tasks.
4. Regularly monitor performance and costs
Use cloud management platforms to monitor resource utilization, performance metrics, and costs in real-time. Identify underutilized resources or unnecessary expenditures and optimize configurations to reduce waste.
5. Enforce robust security controls
Integrate security measures such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and regular vulnerability assessments into your cloud management practices. Security should be a cornerstone of your governance policies, especially if your organization handles sensitive information like health or financial data.
6. Conduct regular audits
Routinely audit your cloud environment to make sure your system remains compliant with governance policies and industry regulations. Use these audits to identify gaps, improve policies, and validate that your management practices meet organizational goals.
7. Document and communicate policies
Maintain up-to-date documentation of governance and management policies, and keep them easily accessible to all relevant personnel. Conduct training sessions to train teams on these policies to keep everyone up-to-speed on current practices and requirements.
8. Plan for growth
Design strategies that can accommodate organizational growth. Whether you’re adding new applications or transitioning to a hybrid cloud model, ensure your framework is adaptable to future needs.
9. Establish metrics for success
Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of your governance and management efforts. Example KPIs might include cost savings, compliance audit results, or system uptime metrics.
10. Continuously review and improve
The cloud landscape evolves rapidly — your governance and management strategies should, too. Regularly evaluate and update existing policies to keep up with emerging technologies or regulations. Incorporate lessons learned from audits or incidents into your new policies and practices.
Use cases for cloud governance and management
Cloud governance and management are critical for maintaining secure, efficient, cost-effective cloud environments. Together, they provide the oversight and operational structure necessary to address key challenges organizations face when using the cloud. From managing costs to enhancing performance, the right governance and management strategies align cloud resources with business objectives while minimizing risks. Here are some core use cases where cloud governance and management prove to be indispensable:
- Cost control and optimization: To keep cloud costs under control, IT organizations must continuously monitor usage patterns and optimize resource utilization. They also need to identify and track wasteful spending to take corrective action. Cloud governance solutions can help by providing visibility into cost center performance, resource utilization, and spending patterns.
- Security and compliance: To ensure that data stored in the cloud is secure, IT organizations need to implement comprehensive security controls. They also need to be able to track and monitor compliance with internal policies and external regulations. Cloud governance and management solutions can help by providing visibility into security posture and vulnerabilities.
- Performance and availability: To ensure that applications running in the cloud are performing optimally, IT organizations must constantly monitor key metrics. They also need the ability to quickly identify and resolve performance issues. Cloud governance and management solutions can help by providing visibility into performance metrics and SLAs.
Real-world applications of cloud governance and management
Cloud governance and management tackle the distinct challenges of operating in cloud environments. From controlling costs to optimizing performance, these strategies work together to create an efficient and adaptable cloud ecosystem. By combining cloud governance and management, organizations in these industries can address their unique challenges, stay compliant, and enhance reliability:
Healthcare compliance and data protection
A healthcare provider implementing a cloud-based patient records system must meet stringent compliance requirements like HIPAA. Cloud governance establishes policies for access controls, data encryption, and compliance audits to protect patient data. Cloud management tools enforce these policies, automatically flagging unauthorized access attempts and keeping system configurations compliant with the most current regulatory standards.
Retail cost optimization during peak seasons
A retail company preparing for holiday sales uses cloud governance to set policies for scaling resources during peak demand while controlling costs. Governance frameworks dictate thresholds for provisioning additional servers or storage based on projected traffic. Cloud management tools automatically scale resources up or down, monitor performance, and decommission unused resources once demand subsides.
Financial services security and performance
A financial institution using cloud-hosted trading platforms depends on real-time data accuracy, real-time observability, and high availability. Cloud governance ensures robust policies for disaster recovery and data replication. At the same time, cloud management tools monitor system performance and uptime, sending alerts if performance metrics fall below SLA-defined thresholds.
Education sector availability and scalability
An online learning platform sees a surge in users during enrollment periods. Cloud governance defines policies to maintain application availability and enforce data privacy regulations like FERPA. Cloud management tools dynamically allocate computing power to optimize user experiences, even during high-demand periods.
The role of governance and management in the cloud
Cloud governance and cloud management are two important aspects of working with the cloud. Each has its own benefits and importance, and it is essential to understand both before deciding to move to the cloud.
The framework for cloud governance provides guidelines for working with the cloud safely and efficiently. The principles of cloud governance ensure that data security and privacy are always considered. Cloud management platforms provide an easy way to manage all your clouds from one central location, giving you more control over your data.
Maximize your cloud potential with the right strategies
Understanding cloud governance and cloud management is key to building a secure, efficient, and scalable cloud environment. These complementary strategies will help your organization balance oversight and operations, keeping cloud resources aligned with business goals while reducing risks. Whatever your main focus, having a robust framework in place ensures you’re getting the most out of your move to the cloud.
By recognizing the differences between these two concepts, businesses can ensure they are getting the most out of their move to the cloud. If you’re considering cloud management and governance strategies for your organization, contact us today to learn more about what this process entails and some of its benefits.
PostgreSQL and MySQL are two of the most popular open-source databases available today. They both provide the database backend for many web applications, enterprise software packages, and data science projects. The two databases share some similarities in that they both adhere to the SQL standard.
However, some key differences might influence your decision to choose one over the other. PostgreSQL is known for its advanced features, impressive durability, and scalability. MySQL is well-known for its ease of use and speed in read/write operations.
Here’s an overview of their similarities and differences, including their architectures, data types, indexing schemes, security, and performance.
PostgreSQL and MySQL similarities
Both PostgreSQL (also known as “Postgres”) and MySQL are Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS). That means both store data in rows and tables, have a mechanism to define the relationships between the data in the tables and provide the Structured Query Language (SQL) to access the data via standardized queries.
Both database systems are ACID-compliant. ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) compliance ensures data consistency and integrity, even in the face of system errors, hardware failures, and power outages. Both support replication for adding more servers to host data with fault tolerance and a distributed workload.
MySQL and PostgreSQL are both free and open source, meaning that anyone can obtain the source code, install the software, and modify it how they see fit. Both offer tight integration with web servers like Apache and programming languages like PHP and Python.
Architectural differences and data types
While both MySQL and PostgreSQL are examples of an RDBMS, PostgreSQL also qualifies as an Object-Relational Database Management System or ORDBMS. This means that Postgres has the typical characteristics of a relational database, and it’s also capable of storing data as objects.
At a high level, objects in software development are models with attributes and properties that can be accessed with forms of code known as procedures and methods.
To see the difference, look at the supported data types in both systems. MySQL supports a set of standard data types, including VARCHAR (text fields limited to a certain length), TEXT (free-form text), INTEGER (an integer number), BOOLEAN (a true/false field), and DATE (a timestamp). Meanwhile, PostgreSQL supports the standard data types and a wide range of more complex data types not seen in a traditional RDBMS. This includes MONEY (a currency amount), INET (IP addresses), MACADDR (a network device’s MAC address), and many other specialized objects.
Perhaps most importantly, Postgres supports the JSON and JSONB data types, which are JSON text and binary JSON data. As most REST web service APIs today transfer data in JSON format, PostgreSQL is a favorite among app developers and system administrators. While MySQL can be made to store JSON text, the ability to natively query stored JSON data is a major advantage of PostgreSQL.
MySQL and PostgreSQL query languages
PostgreSQL supports creating custom data models with its PL/pgSQL query language, which is substantially more full-featured than MySQL’s standard SQL implementation.
PL/pgSQL can be seen as both a query language and a procedural programming language. PL/pgSQL supports programming constructs like loops, conditional statements, variables, and error handling. The language also makes it easy to implement user-defined functions and stored procedures in queries and scripts.
MySQL’s SQL implementation lacks these features and is best suited for simple queries, data sorting, and exporting.
Even though PL/pgSQL is unique to PostgreSQL, it actually has a stricter adherence to SQL standards than MySQL’s SQL implementation. Advanced SQL features like window functions and common table expressions (CTEs) are available in PostgreSQL but not MySQL.
Database ecosystem and tools
Both PostgreSQL and MySQL boast robust ecosystems supported by various tools and integrations that enhance their functionality and streamline database management.
PostgreSQL’s ecosystem is enriched by an extensive range of open-source and commercial tools designed for automation, scaling, sharding, and migration. Tools like pgAdmin and DBeaver provide intuitive interfaces for database management, while PgBouncer and Patroni simplify connection pooling and high-availability setups. For scaling, Citus offers advanced sharding capabilities, enabling horizontal scaling for large datasets and high traffic. Migration tools like pg_upgrade ensure seamless upgrades between PostgreSQL versions, while Ora2Pg facilitates migration from Oracle databases.
MySQL’s ecosystem is equally expansive, with tools catering to various database management needs. MySQL Workbench provides a comprehensive graphical interface for database design, administration, and performance tuning. For scaling, MySQL supports sharding through ProxySQL and Vitess, which allow for horizontal scaling and improved database performance. Percona Toolkit and AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) streamline migrations, making it easier for enterprises to transition to or from MySQL.
Both ecosystems support automation tools like Ansible and Terraform for infrastructure management, ensuring smoother deployment and scaling of database instances. Whether you choose PostgreSQL or MySQL, the ecosystems offer many tools to optimize database performance and simplify complex operations.
Indexing Methods
Indexes are crucial for database performance, speeding up data retrieval and optimizing queries. PostgreSQL and MySQL offer various indexing methods to suit different use cases:
- B-Tree Indexing: The default method in both databases, ideal for efficient data retrieval in large datasets.
- GiN & GiST Indexing: PostgreSQL-specific, designed for complex data types like arrays, JSON, and full-text search.
- R-Tree Indexing: Suitable for spatial data (points, lines, polygons), enabling faster geospatial queries.
- Hash Indexing: MySQL-specific, uses hash tables for efficient equality-based lookups but not range queries.
- Full-Text Indexing: Supports advanced text searches with keywords and phrases in both databases.
Choosing the right index type boosts query performance and ensures your database meets application demands.
PostgreSQL vs MySQL performance and scalability
Both PostgreSQL and MySQL are capable of scaling to handle large amounts of data and high levels of traffic and to support complex applications. However, scaling MySQL typically involves adding more hardware and database instances, while PostgreSQL has some advanced features that naturally support scaling.
PostgreSQL uses a system called MVCC (Multiversion Concurrency Control) that allows multiple users to access and modify data simultaneously without locking out or slowing down each other’s queries like MySQL. This is particularly helpful for applications requiring high read/write activity levels.
When adding additional servers, MySQL uses binary log-based replications, which is fast but can lead to data inconsistencies when network hiccups interrupt replication activities. PostgreSQL uses the “log-shipping” approach, which is more reliable but can be slower than binary log replication. However, PostgreSQL also supports table partitioning, which allows a single table to be spread across multiple smaller tables. This tends to improve performance because smaller amounts of data are queried simultaneously.
PostgreSQL also has a more advanced query optimizer than MySQL, which helps execute queries more efficiently. PostgreSQL also sports a larger maximum table size than MySQL, making it better suited for applications with large datasets.
Security
PostgreSQL and MySQL take different approaches to security. Both have mechanisms for granting access to schemas and tables to defined users, but PostgreSQL offers more advanced features.
PostgreSQL has a fine-grained approach to user privileges, allowing administrators to assign more specific user privileges and roles. MySQL, however, uses a broader and more basic authorization system with a combination of user accounts and global or database-specific privileges. PostgreSQL supports many authentication methods beyond the simple username and password combination. This includes authenticating against an LDAP server or Active Directory and certificate-based authentication.
Both systems support encryption, with PostgreSQL offering more options. In particular, PostgreSQL supports column-level encryption and a feature known as Transparent Data Encryption (TDE). With TDE, all data in a schema is encrypted using a symmetric encryption key. This key, in turn, is protected by a master key that can be stored in a software key management system or a hardware-based security module.
MySQL uses SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to help ensure data integrity, which makes it a popular database for web applications. Beyond that, MySQL doesn’t offer as many security and encryption features as PostgreSQL. But that doesn’t mean it’s insecure. A MySQL installation can be secured well enough to meet enterprise standards through the judicious use of strong passwords and network-level security.
Transactions
An RDBMS’s transaction methodology ensures data consistency and integrity while playing a large part in the database’s overall performance. The speed at which transactions are performed defines whether a database system suits a particular task.
Since both PostgreSQL and MySQL are ACID-compliant, both support transaction rollbacks and commits. However, MySQL does not enable transactions by default, opting for “auto-commit” mode out of the box. This means each SQL statement is automatically committed or rolled back unless this setting is changed.
MySQL uses a locking mechanism optimized for performance but can lead to inconsistencies in some cases. PostgreSQL uses a strict locking mechanism for a higher level of consistency.
Community support
MySQL first gained popularity in Web 1.0 days, partly because it’s open source and works well with other free and open-source software such as the PHP language and operating systems built on the Linux kernel. A strong community has built around MySQL over time, making it one of the most popular open-source packages ever.
The well-known acronym LAMP—for Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP (or Perl, or Python)—came from this community in honor of the free software packages that have powered many dynamic websites for decades.
MySQL was created by Swedish developers Michael Widenius and David Axmark in 1995. A year later, the two founded the company MySQL AB to provide commercial support and consulting services for the database as it grew in popularity. In 2008, Sun Microsystems acquired MySQL AB for $1 billion. Two years later, Sun was acquired by Oracle Corporation, which means the tech giant owns MySQL.
This raised concerns in the open-source community that Oracle would prioritize its own proprietary RDBMS solutions over MySQL. These fears have mostly been unfounded, as Oracle continues to develop MySQL and offer it under the GNU General Public License (GPL), making it free for personal and non-commercial use. However, the GPL allows Oracle to charge for commercial uses of MySQL, which makes some in the community no longer consider MySQL to truly be “free and open source.”
In response to these concerns, a community-supported version of MySQL has emerged called MariaDB. While identical to MySQL in basic form and function, MariaDB lacks some of MySQL’s advanced features.
PostgreSQL is released under a modified version of the MIT license known as the PostgreSQL License. This is a permissive free and open-source license, allowing users a great deal of flexibility in how they can use and modify the software.
As a result, PostgreSQL remains one of the most popular open-source databases in the world, with a large community support base of many users, enterprise admins, and application developers. However, there are more community contributions to the MySQL and MariaDB ecosystems.
Recent developments
Both PostgreSQL and MySQL have introduced notable updates in recent versions, keeping them at the forefront of open-source database innovation.
The release of PostgreSQL 17 in September 2024 brought several advancements. A new memory management system for the VACUUM process reduces memory consumption and improves overall performance. SQL/JSON capabilities were expanded with functions like JSON_TABLE(), enabling seamless transformation of JSON data into table formats. Logical replication has seen enhancements, such as failover control and incremental backup support via pg_basebackup. Query performance improvements include optimized handling of sequential reads and high-concurrency write operations. PostgreSQL 17 also introduced a COPY command option, ON_ERROR ignore, which enhances data ingestion workflows by continuing operations even when encountering errors.
MySQL 8.0.40, released in October 2024, continues to refine database performance and compliance. Enhancements to the InnoDB storage engine improve adaptive hash indexing and parallel query performance. Security has been bolstered with updates to OpenSSL 3.0.15 integration, ensuring compliance with modern encryption standards. The introduction of the –system-command option allows for finer control over client commands, and a revamped sys schema improves the performance of key views like innodb_lock_waits. MySQL also focuses on developer flexibility with improved error handling and broader compatibility for tools and libraries.
These ongoing developments highlight the commitment of both database communities to addressing evolving performance, scalability, and security needs, ensuring their continued relevance in diverse application environments.
Use cases
MySQL is utilized by an untold number of websites thanks in part to the database being free and open source, as well as its out-of-the-box support for the PHP language. The combination of PHP and MySQL helped create a rush of dynamic websites that didn’t have their HTML code manually updated.
Early on, Google used MySQL for its search engine. Over time, as the search giant’s dataset grew, it moved to different database technologies optimized for unstructured data and fuzzy searches. (Today, Google search is powered by Google’s own distributed data storage system, Bigtable.)
MySQL is still widely used for many small- to medium-sized web applications. Content management systems and specialized web apps like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) almost always support MySQL as a database backend.
Many enterprises also use it as the data backend for their internal applications and data warehouses. PostgreSQL is used in many of the same scenarios. Most web apps that support MySQL will also support PostgreSQL, making the choice a matter of preference for sysadmins and database administrators.
PostgreSQL pros and cons
Here are some of the pros of choosing PostgreSQL:
- Performance and scalability that matches commercial RDBMS products.
- Concurrency support for multiple write operations and reads at the same time.
- The PL/pgSQL language and support for other programming languages, such as Java, JavaScript, C++, Python, and Ruby.
- Support for high availability of services and a reputation for durability.
Some of the cons of PostgreSQL include:
- It can be complex to set up and manage, particularly for newcomers.
- Reliability comes at a performance cost.
- Large databases used in complex applications can be memory intensive.
- Less community support than MySQL/MariaDB.
MySQL pros and cons
The pros of MySQL include:
- MySQL’s storage engines enable fast performance.
- A small footprint and an easy-to-use replication system make it easy to grow and scale.
- Open-source solid community support.
- Nearly all web applications and enterprise systems support MySQL.
Here are some cons of choosing MySQL:
- Not as scalable as PostgreSQL or newer database systems.
- Lack of advanced features like full-text search and complex data types.
- Less resilience when processing complex queries.
- There is no built-in support for backups, requiring third-party backup software.
PostgreSQL and MySQL: Which to choose?
Both PostgreSQL and MySQL are extremely capable RDBMS packages. While PostgreSQL clearly supports more advanced features and has a greater reputation for reliability, that doesn’t mean MySQL is a bad choice.
MySQL’s relative simplicity makes it a great choice for smaller and medium-sized web applications. Those new to SQL and RDBMS applications, in general, can pick up the basics of MySQL quickly, making it a great choice for enterprises with limited IT resources. MySQL also has a strong community, with decades of apps supporting MySQL.
If you will be dealing with a larger dataset or developing complex custom applications, PostgreSQL is an excellent choice. Its support for custom data types and the PL/pgSQL language make Postgres a favorite of sysadmins, web developers, and database administrators worldwide.
PostgreSQL vs MySQL: A side-by-side comparison
| Category | PostgreSQL | MySQL |
| Architecture | ORDBMS; advanced features like inheritance | RDBMS; simple and lightweight |
| Data Types | JSON/JSONB, arrays, custom types | Standard SQL types; basic JSON text support |
| Performance | Optimized for complex queries and writes | Fast for simple, read-heavy workloads |
| Scalability | Partitioning, logical replication, tools | Binary log replication; vertical scaling |
| Query Language | PL/pgSQL; advanced SQL features | Standard SQL; fewer advanced features |
| Security | Fine-grained access, encryption options | Basic privileges; SSL encryption |
| Community Support | Large, enterprise-focused | Widespread, beginner-friendly |
| Use Cases | Complex apps, analytics, REST APIs | Small-medium apps, LAMP stack |
| Licensing | Permissive, unrestricted | GPL; some paid features |
| Notable Features | Advanced indexing, full-text search | Lightweight, multiple storage engines |
Choose the right database, monitor with ease
Selecting between a PostgreSQL and MySQL database ultimately depends on your specific project requirements. PostgreSQL excels in handling complex queries, large datasets, and enterprise-grade features, making it ideal for analytics, REST APIs, and custom applications. MySQL, on the other hand, shines in simplicity, speed, and compatibility, making it perfect for small-to-medium-sized applications and high-traffic web platforms.
Whatever database you choose, ensuring its performance and reliability is critical to your IT infrastructure’s success. That’s where LogicMonitor’s database monitoring capabilities come in.
Comprehensively monitor all your databases in minutes with LogicMonitor. With autodiscovery, there’s no need for scripts, libraries, or complex configurations. LogicMonitor provides everything you need to monitor database performance and health alongside your entire infrastructure—whether on-premises or in the cloud.
Why LogicMonitor for Database Monitoring?
- Turn-key integrations: Monitor MySQL, PostgreSQL, and other databases effortlessly.
- Deep insights: Track query performance, active connections, cache hit rates, and more.
- Auto-discovery: Instantly discover database instances, jobs, and dependencies.
- Customizable alerts: Eliminate noise with thresholds and anomaly detection.
- Comprehensive dashboards: Gain visibility into database and infrastructure metrics in one platform.
Ready to optimize and simplify your database management? Try LogicMonitor for Free and ensure your databases deliver peak performance every day.
Once upon a time, the prospect of an organization letting another organization manage its IT infrastructure seemed either inconceivable or incredibly dangerous. It was like someone handing their house keys to a stranger. Times have changed.
Remote Infrastructure Management (RIM) — when Company X lets Company Y, or a piece of software, monitor and manage its infrastructure remotely — has become the standard in some industries. It’s sometimes the de facto method for IT security, storage, and support.
When did this happen? When organizations started working remotely.
When the COVID-19 pandemic spiraled and governments issued social distancing and stay-at-home orders, companies rolled down the blinds and closed the doors. When remote IT management was a business need, not a request, CIOs came around to the idea. There was no other choice. It was that or nothing.
The C-suite discovered what IT leaders had known for years: RIM is safe, cheap, and just as effective as in-house management.
RIM is not perfect. There are challenges. Problems persist. So, IT leaders need to iron out the kinks before RIM becomes the standard across all industries.
In this guide, learn the current state of RIM, then discover what the future holds.
What is remote infrastructure management?
RIM is the monitoring and management of IT infrastructure from a remote location. Company X outsources infrastructure management to Company Y, for example. Alternatively, super-smart software handles all this monitoring and management, and organizations can view management processes in real time from their devices. An administrator might need to visit the organization’s physical location (or, post-COVID, a home location) to repair broken hardware, but that should be a rare occurrence.
The term “IT infrastructure” — the thing or things that RIM monitors and manages — has different definitions but might include one or all of the below:
- Software
- Hardware
- Data centers
- Networks
- Devices
- Servers
- Databases
- Apps
- Emails
- Telephony
- IT services
- Customer relationship management (CRP) systems
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems
The list goes on.
What is the current state of remote infrastructure management?
The IT infrastructure management landscape looks completely different from 18 months ago. Back then, most IT teams took care of monitoring and management. But then the pandemic hit. Suddenly, organizations required RIM solutions for several reasons:
- IT teams, now working from home, could no longer manage IT infrastructure on-site effectively.
- Work-from-home models presented unique security challenges that required a more scalable infrastructure management solution. Employees accessed different software on different devices at different locations, and only RIM could solve these challenges.
- As the economy stuttered, many organizations reduced IT spending, and RIM provided a cheaper solution than conventional in-house IT.
- New technologies like teleconferencing provided additional security challenges. Hence, there is a demand for a more comprehensive infrastructure management solution.
Recent research from LogicMonitor reveals the collective concerns of IT leaders who monitor and manage the IT infrastructure of at-home employees:
- 49% worry about dealing with internet outrages and other technical issues remotely.
- 49% think too many employees logging into systems remotely will cripple networks.
- 38% worry about employees logging into systems through virtual private networks (VPNs).
- 33% don’t have access to the hardware they need to do their jobs.
- 28% don’t think teleconferencing software is secure enough.
It’s no wonder, then, that so many of these IT leaders are looking for RIM solutions.
Read more fascinating insights from LogicMonitor’s Evolution of IT Research Report.
How much infrastructure management is currently ‘remote’?
The great thing about RIM is its flexibility. Organizations can choose what they want a service provider or software to monitor and manage depending on variables such as internal capabilities and cost. Company X might want to manage its networks remotely but not its software, for example. Research shows database and storage system management are the most popular infrastructure ‘types’ monitored and managed remotely.
Remote infrastructure management challenges
Not all RIMs are the same. CIOs and other IT leaders need to invest in a service provider or software that troubleshoots and solves these challenges:
Challenge 1: Growth and scalability
Only 39% of IT decision-makers feel ‘confident’ their organization can maintain continuous uptime in a crisis, while 54% feel ‘somewhat confident,’ according to LogicMonitor’s report. These professionals should seek an RIM solution that scales at the same rate as their organization.
There are other growth solutions for IT leaders concerned about uptime in a crisis. Streamlining infrastructure by investing in storage solutions such as cloud services reduces the need for hardware, software, and other equipment. With more IT virtualization, fewer problems will persist in a crisis, improving business continuity.
Challenge 2: Security
Security is an enormous concern for organizations in almost every sector. The pandemic has exasperated the problem, with the work-from-home model presenting security challenges for CIOs. There were nearly 800,000 incidents of suspected internet crime in 2020 — up 300,000 from the previous year — with reported losses of over $4 billion. Phishing remains the No.1 cybercrime.
CIOs need a RIM solution that improves data security without affecting employee productivity and performance. However, this continues to be a challenge. IT virtualization doesn’t eliminate cybercrime, and not all service providers and software provide adequate levels of security for data-driven teams.
There are several security frameworks to consider. IT leaders require a RIM solution that, at the least, adheres to SOC2 and ISO standards, preferably ISO 27001:2013 and ISO 27017:2015 — the gold standards of IT security. Other security must-haves include data encryption, authentication controls, and access controls.
Then there’s the problem of data governance. When moving data to a remote location, data-driven organizations must adhere to frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. Otherwise, they could face expensive penalties for non-compliance.
Challenge 3: Costs
The cost of RIM remains a bugbear for many CIOs. As RIM is still a relatively new technology, some service providers charge larger organizations hundreds of thousands to manage and monitor hardware, software, networks, and servers.
Investing in monitoring software provides more value for money. These programs do nearly everything a RIM services provider does but without the expensive price tag. Service providers use software to automate monitoring and management, so organizations won’t notice a big difference.
Regardless of whether organizations choose a service provider or monitoring software, the costs of both methods should provide an investment return. Research shows the average cost of a data breach in the U.S. is $8.46 million, so if remote monitoring and management prevent a breach, it’s well worth it.
Challenge 4: Automation
As mentioned above, software automates much of remote monitoring. However, some monitoring and management tools are better at executing this process than others. That’s because RIM is still a new technology, and some vendors are working out the fine details. Regardless, monitoring tools are becoming more sophisticated daily, automating nearly all the manual processes associated with infrastructure management, such as network performance updates and security patch installation.
Challenge 5: AI/Machine learning
RIM has struggled with AI and machine learning, but this is changing fast. The best tools take advantage of these technologies by providing end-users with invaluable insights into every aspect of their IT infrastructure, from server uptime to network memory.
AI-driven tools leverage predictive analytics to analyze historical data, identify patterns, and predict potential failures before they occur, enabling IT teams to take proactive measures and prevent incidents. Machine learning enhances intelligent automation by optimizing tasks such as resource allocation and network performance, reducing the need for manual intervention and increasing overall efficiency.
AI-powered algorithms will continuously monitor your systems, detecting unusual behaviors or anomalies that could indicate security threats or performance issues, allowing for a swift response. Capacity planning is also improved as AI tools analyze infrastructure usage trends and provide recommendations for resource optimization, ensuring scalability while avoiding unnecessary costs.
Finally, machine learning models correlate data across diverse systems to generate actionable insights, helping CIOs make informed decisions, prioritize tasks, and allocate resources more effectively. These advancements are transforming RIM into a smarter, more efficient approach to infrastructure management.
Not all remote management tools use these technologies, so CIOs and software procurement teams should research the market and find the best platforms and RIM service providers.
Challenge 6: Cloud
RIM and the cloud are a match made in technological heaven. With IT virtualization, CIOs can manage much of their infrastructure (and data) in a cloud environment, which provides these remarkable benefits:
- The cloud reduces the amount of physical hardware (on-premise hardware) in an organization.
- It safeguards data for security and governance purposes.
- Team members can access data remotely wherever they are in the world.
- It protects the environment.
- It improves energy efficiency.
- It scales better.
- It provides cost savings.
The move to full virtualization won’t happen anytime soon, with many business leaders still skeptical about the cloud. 74% of IT leaders think 95% of public, private, and hybrid workloads will run in the cloud in the next five years, according to LogicMonitor’s report. 22% think it will take six years or more; 2% don’t believe it will ever happen. Still, more organizations are using the cloud than ever before.
The cloud brings security challenges for IT teams, but the right tools will ease any concerns.
How to implement remote infrastructure management services effectively
Implementing RIM successfully requires a structured approach that aligns with your organization’s needs, infrastructure, and goals. Below are actionable steps to ensure effective adoption:
1. Assess organizational needs
Before implementing RIM, identify what infrastructure components need to be managed remotely. This might include:
- Networks and servers for real-time monitoring
- Applications requiring frequent updates
- Critical data is subject to compliance regulations
Consider existing IT capabilities and pinpoint areas where RIM can add the most value, such as improving uptime or reducing costs.
2. Choose the right tools and providers
Select tools or service providers that match your infrastructure’s complexity and scalability requirements. Look for:
- Automation and AI capabilities to reduce manual effort
- Compliance with SOC2, ISO 27001, and other relevant standards
- Flexible pricing models that suit your organization’s budget
Ensure your chosen solution integrates seamlessly with existing systems, including hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
3. Prioritize security
Cybersecurity is a critical consideration for any RIM strategy. Implement:
- Data encryption to protect sensitive information
- Role-based access controls to minimize security risks
- Regular audits to ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR or CCPA
Security protocols should safeguard data without hampering employee productivity
4. Leverage automation and AI
Automating routine tasks such as performance monitoring and incident detection streamlines IT and business operations. Use tools that:
- Offer predictive analytics for proactive maintenance
- Automatically apply security patches and updates
This reduces downtime and frees up IT resources for strategic initiatives.
5. Plan for scalability
As your organization grows, your RIM strategy should scale accordingly. Opt for solutions that support:
- Increasing workloads without impacting performance
- Flexible infrastructure that adapts to changing needs, such as expanding cloud storage
Scalability ensures your IT operations remain efficient during growth.
6. Train your IT teams
Equip IT staff with the skills needed to manage RIM tools effectively. Training ensures:
- Seamless tool adoption
- Improved collaboration between teams managing on-premises and remote infrastructure
A well-trained team is critical for realizing the full benefits of RIM.
7. Monitor and optimize continuously
RIM implementation doesn’t end after setup. Continuously track key performance metrics, such as:
- System uptime and availability
- Incident response times
- Infrastructure costs
Use these insights to refine your strategy and improve efficiency.
RIM vs DCIM software
While RIM and Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) software share overlapping goals, they are distinct in their approach and scope. Both focus on improving visibility and control over IT infrastructure, but each caters to different operational needs.
What is DCIM software?
DCIM software specializes in managing the physical components of data centers, such as power, cooling, and space utilization. It provides insights into infrastructure efficiency and helps data center operators optimize performance, reduce energy costs, and plan for future capacity needs.
How RIM differs from DCIM
- Scope of management
- RIM: Broadly encompasses remote monitoring and management of IT infrastructure, including software, hardware, servers, and networks, often across multiple geographic locations.
- DCIM: Primarily focuses on the physical aspects of a data center, such as racks, power distribution, and environmental conditions.
- Location
- RIM: Extends management capabilities beyond the data center, making it ideal for hybrid, remote, and multi-cloud environments.
- DCIM: Typically operates within the confines of a physical data center, offering on-premises insights.
- Key technologies
- RIM: Leverages automation, AI, and cloud-based tools to provide real-time monitoring and incident management.
- DCIM: Relies on sensors, physical monitoring tools, and predictive analytics for maintaining data center health and efficiency.
- Use cases
- RIM: Ideal for organizations with distributed infrastructure needing centralized, remote oversight.
- DCIM: Suited for enterprises managing large-scale, on-premises data centers requiring detailed physical infrastructure management.
When to use RIM or DCIM
Organizations that rely heavily on hybrid IT environments or need to support remote operations benefit from RIM’s flexibility. However, for businesses with significant investments in physical data centers, DCIM provides unparalleled insights into physical infrastructure performance.
Can RIM and DCIM work together?
Yes. These solutions complement one another, with RIM focusing on the IT layer and DCIM ensuring optimal physical conditions in the data center. Together, they provide a holistic view of infrastructure performance and health.
What is the future for remote infrastructure management?
More organizations are investing in RIM. Experts predict the global RIM market will be worth $54.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 9.7% from now until then. Meanwhile, database management and storage system management will grow at CAGR rates of 10.4% and 10% over the next seven years. The two countries that will invest the most money in RIM during this same period will be China and the United States.
With such explosive growth, expect more RIM innovations in the next few years. The software will become smarter. Service providers will offer more infrastructure services. Full cloud monitoring may exist if all infrastructure moves to the cloud.
RIM could also trickle down to smaller businesses that still rely on manual processes for monitoring and management — or don’t carry out these critical tasks at all. As the costs of data centers, servers, and resources rise, small business owners will keep a closer eye on monitoring tools that provide them with insights such as network and bandwidth usage and infrastructure dependencies.
Take control of your IT infrastructure today
RIM has existed, in one form or another, for several years. However, the growing demands of work-from-home have brought remote monitoring and management into the spotlight. Whether it comes from software or a service provider, RIM takes care of software, hardware, server, and network tasks organizations don’t have the time for or don’t want to complete. Despite some challenges, the future of RIM looks bright, providing busy teams with bespoke monitoring and management benefits they can’t find anywhere else.
LogicMonitor is the cloud-based remote monitoring platform for CIOs and IT leaders everywhere. Users get full-stack visibility, world-class security, and network, cloud, and server management tools from one unified view. Welcome to the future of remote monitoring. Learn more or try LogicMonitor for free.
