You can use the OpenTelemetry Collector Installation wizard in LogicMonitor to install an OpenTelemetry Collector. This wizard guides you through choosing a platform for installation, allows you to customize the configuration file (For example, you can configure your Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) policy by specifying the domains the collector is allowed to receive requests from), and provides the command for installing the Collector. If you are installing the Collector in a container, you can edit this command to include optional parameters that allow you to further customize the installation of the Collector.
For more information about CORS, see Mozilla’s Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) documentation.
Installing an OpenTelemetry Collector on Linux
You can install the OpenTelemetry Collector on Linux as a root or non-root user. For root users, lmotel runs as a service; and for non-root users, lmotel runs as a process.
- Navigate to Traces >
 (Onboarding), and select Install OpenTelemetry Collector.
(Onboarding), and select Install OpenTelemetry Collector. - Enter a name for the Collector, and select Linux for the platform.
- Select the version of the Collector you want to install.
- At the Review Configuration step of the wizard, make changes to the configuration file as necessary to customize the Processors in the OpenTelemetry Collector settings. For more information about the modifications you can make, see Configurations for OpenTelemetry Collector Processors.
You can configure CORS by specifying the origins to allow requests. For more information, see CORS (Cross-origin resource sharing) from OpenTelemetry. - At the Commands step of the wizard, modify the cURL command as needed, and then copy the command.
Note: The cURL command to download the Collector binary is only valid for two hours after it is made available.
After you download the installer, you must make it executable (chmod +x installer_file) and then run the executable (./installer_file).
In addition, the installation path for the non-root user is the following:
# installation_path=/home# status check:
$ ps -ef | grep lmotelInstalling an OpenTelemetry Collector in Docker
The wizard provides you with a preconfigured Docker run command for running a container with LogicMonitor’s OpenTelemetry Collector Docker image.
- Navigate to Traces >
 (Onboarding), and select Install OpenTelemetry Collector.
(Onboarding), and select Install OpenTelemetry Collector. - Enter a name for the OpenTelemetry Collector, and select Docker for the platform.
- Select the version of the Collector you want to install.
- At the Review Configuration step of the wizard, make changes to the configuration file as necessary to customize the Processors in the OpenTelemetry Collector settings. For more information about the modifications you can make, see Configurations for OpenTelemetry Collector Processors.
You can configure CORS by specifying the origins to allow requests. For more information, see CORS (Cross-origin resource sharing) from OpenTelemetry. - At the Commands step of the wizard, do the following:
- Enter the username for the user with the minimum privileges. This is the API-only user you created for installing the OpenTelemetry Collector.
An Access ID and Access Key are automatically created for this user. This is required to authenticate to Docker when you install the OpenTelemetry Collector in your Docker container. - Copy the Run command to use for installing the Collector.
You can modify this command as needed by entering optional parameters in the command. For more information, see Configurations for OpenTelemetry Collector Container Installation.
- Enter the username for the user with the minimum privileges. This is the API-only user you created for installing the OpenTelemetry Collector.
- Click Finish.
Use the command from the wizard to install the OpenTelemetry Collector in Docker.
Note: If using Microsoft Azure App Service, you can deploy the OpenTelemetry Collector to an Azure Container Instance after you install it in Docker. For more information, see Configurations for OpenTelemetry Collector Deployment in Microsoft Azure Container Instance.
Installing an OpenTelemetry Collector in Kubernetes
LogicMonitor provides Helm Charts to install an OpenTelemetry Collector in a Kubernetes cluster. These Helm Charts run the OpenTelemetry Collector as a replicaset. The wizard provides preconfigured Helm commands for adding LogicMonitor charts and installing the OpenTelemetry Collector.
In addition, you can leverage an Ingress resource for use with the OpenTelemetry Collector by specifying the Ingress Endpoint. This allows the OpenTelemetry Collector to communicate in a hybrid environment if only some of your resources or services are hosted in Kubernetes, and you need these resources to communicate with resources not hosted in Kubernetes.
- Navigate to Traces >
 (Onboarding), and select Install OpenTelemetry Collector.
(Onboarding), and select Install OpenTelemetry Collector. - Enter a name for the OpenTelemetry Collector, and select Kubernetes for the platform.
- Select the version of the Collector you want to install.
- At the Review Configuration step of the wizard, make changes to the configuration file as necessary to customize the Processors in the OpenTelemetry Collector settings. For more information about the modifications you can make, see Configurations for OpenTelemetry Collector Processors.
You can configure CORS by specifying the origins to allow requests. For more information, see CORS (Cross-origin resource sharing) from OpenTelemetry. - At the Commands step of the wizard, do the following:
- Enter the username for the user with the minimum privileges. This is the API-only user you created for installing the OpenTelemetry Collector.
An Access ID and Access Key are automatically created for this user. This is required to authenticate to Kubernetes when you install the OpenTelemetry Collector in your Kubernetes container. - If you want to leverage an Ingress resource, enter the Ingress Endpoint on which the Ingress Controller listens for incoming spans.
- Copy the Helm Chart command to use for installing the Collector.
You can modify this command as needed by entering the following:- Optional parameters
For more information, see Configurations for OpenTelemetry Collector Container Installation. - Additional properties for leveraging an Ingress resource
For more information, see Configuration for Ingress Resource for OpenTelemetry Kubernetes Installation.
- Optional parameters
- Enter the username for the user with the minimum privileges. This is the API-only user you created for installing the OpenTelemetry Collector.
- Click Finish.
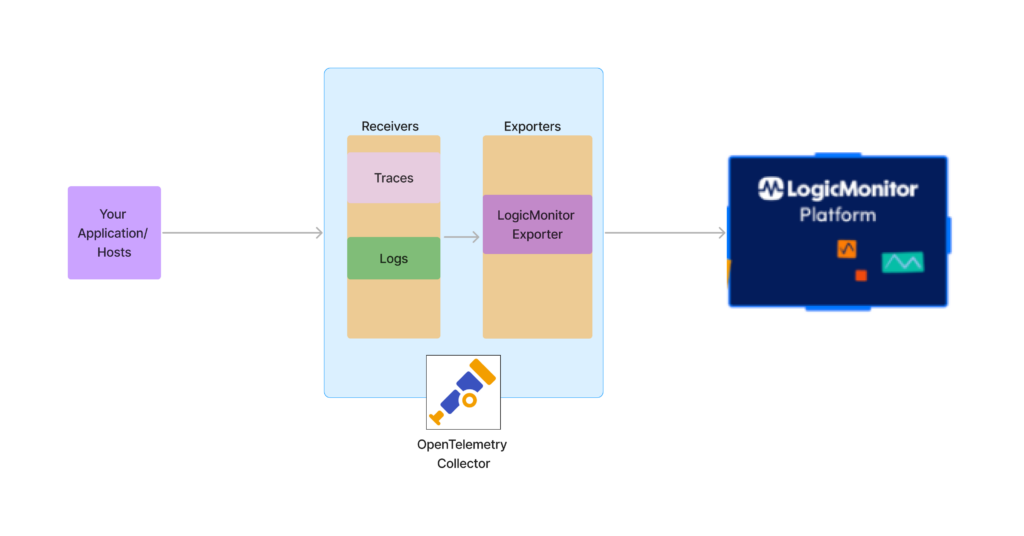
The OpenTelemetry Contrib distribution is a repository for OpenTelemetry Collector components that are not a part of the core repository and distribution of the collector. LogicMonitor Exporter is a part of the OpenTelemetry Contrib distribution.
The OpenTelemetry Collector allows you to collect OpenTelemetry-supported telemetry data from your environment to the LogicMonitor platform. LogicMonitor associates the traces and logs telemetry data from the single OpenTelemetry Collector through the LogicMonitor Exporter to simplify your application’s operations and troubleshoot issues. For more information, see LogicMonitor Exporter from OpenTelemetry.
The OpenTelemetry Contrib distribution offers you the following:
- Broad coverage of traces and log receivers from different sources—Different receivers from the OpenTelemetry Collector can be used to collect traces and log data from different traces and log sources. For example, you can export traces and logs to the LogicMonitor platform from multiple trace providers like Azure and AWS X-Ray and log providers like CloudWatch, Kafka, and Syslog.
- OpenTelemetry distribution management—You can create different distributions of OpenTelemetry Collectors as needed. OpenTelemetry Collector also supports creating builds for other operating systems and creating container images with different architectures.
- Various deployments—Using the helm chart, you can deploy in different modes like a sidecar, daemon sets, and deployment.
- Telemetry interoperability—Receivers for different trace providers can be used to convert the traces from vendor-specific format to OpenTelemetry format. You can then ingest data into the LogicMonitor platform.
Important: You are responsible for upgrading and configuring of OpenTelemetry Collectors. Contact Support if you need assistance.
The following image illustrates the traces and logs ingestion process using a single LogicMonitor Exporter in the OpenTelemetry Collector:
Installing OpenTelemetry Collector from Contrib
Before starting the installation, see “General Requirements and Considerations” for installing the OpenTelemetry Collector. For more information, see OpenTelemetry Collector Installation.
Downloading and Installing OpenTelemetry Collector
Depending on your environment, you can download and install OpenTelemetry Collector on Linux, Windows, Docker, or Kubernetes. For more information, see Getting Started from OpenTelemetry.
For more information on viewing the different releases, see OpenTelemetry Collector Releases from OpenTelemetry.
Note: LogicMonitor Exporter is available with OpenTelemetry Collector Contrib v0.72.0 or later.
Configuring LogicMonitor Exporter
To configure LogicMonitor Exporter, you need to create a configuration file:
receivers:
windowseventlog:
channel: application
syslog:
tcp:
listen_address: "0.0.0.0:54526"
protocol: rfc5424
jaeger:
protocols:
grpc:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
processors:
batch:
exporters:
logicmonitor:
endpoint: https://<company_name>.logicmonitor.com/rest
api_token:
access_id: "<access_id of logicmonitor>"
access_key: "<access_key of logicmonitor>"
extensions:
health_check:
service:
extensions: [health_check]
pipelines:
logs:
receivers : [ windowseventlog, syslog ]
processors: [ batch ]
exporters : [ logicmonitor ]
traces:
receivers : [ otlp, jaeger ]
processors: [ batch ]
exporters : [ logicmonitor ]Exporting Telemetry Data from OpenTelemetry Collector
The OpenTelemetry Collector automatically starts exporting telemetry data to LogicMonitor after you add the LogicMonitor Exporter to your OpenTelemetry Collector configuration file.
While you can view the trace data in different widgets, select View Data to view the details for the selected namespace along with the time period.
Important: You can view span data by selecting Spans from the drop-down list above the graph. The span data options are similar to the traces data.
The Traces page displays the trace data using the following visual components:
- Traces Graph—Displays trace data allowing you to visualize the performance of the traces.
- Traces Table—Lists the spans from your trace data, sorted by time.
You can use filters to narrow your trace data. When you apply the filter to the trace data, the Traces Graph and Traces Table update based on the options selected in the filters. From the Traces Table, you can access the end-to-end trace detail screen.
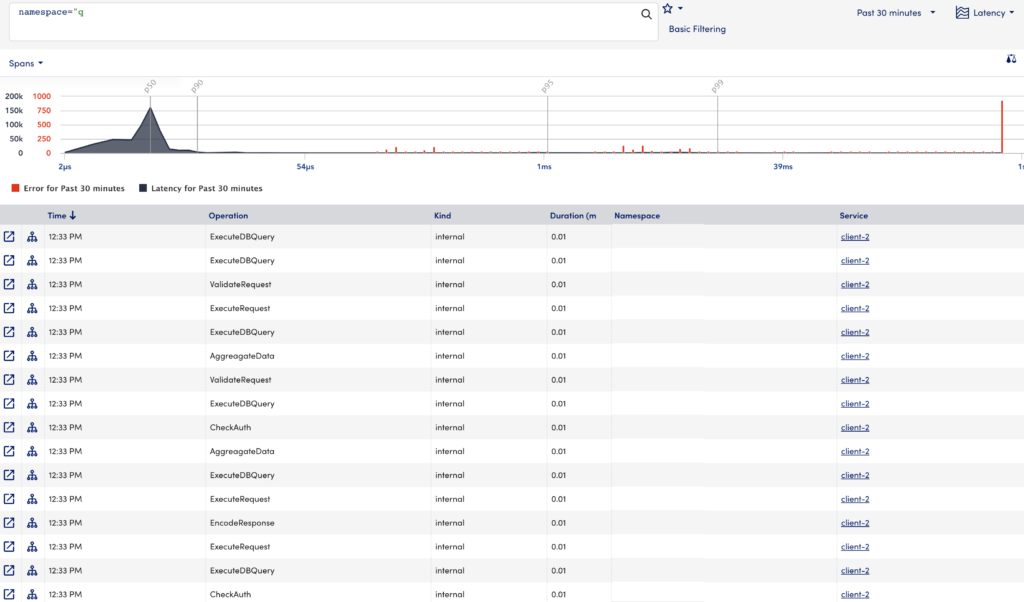
Traces Graph
The Traces Graph allows you to visualize how your traces are performing over time using the following:
- Latency—The Traces Graph displays the operations plotted by latency.
- Time Series—The Traces Graph displays spans and errors ingested over time.
You can select “Latency” or “Time Series” to view the trace data in the Traces Graph for the operation you select.
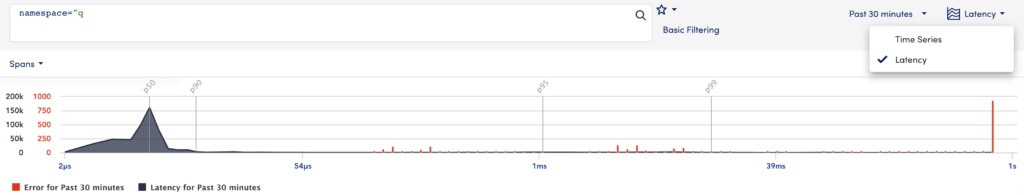
You can narrow the data in the graph by clicking and dragging your cursor over the desired data. The graph zooms in on the selected data.
Comparing Spans Data on Latency Graph
You can visually compare a single span’s data for two different time ranges on the latency graph. To display these details on the latency graph follow the steps:
- Select
 to open the Compare Spans modal.
to open the Compare Spans modal. - On the Time tab, select your required time period from the Second Time Period drop-down.
- (Optional) On the Tags tab, specify any tags as required.
- Select Go.
Two overlay graphs display for the specified time ranges.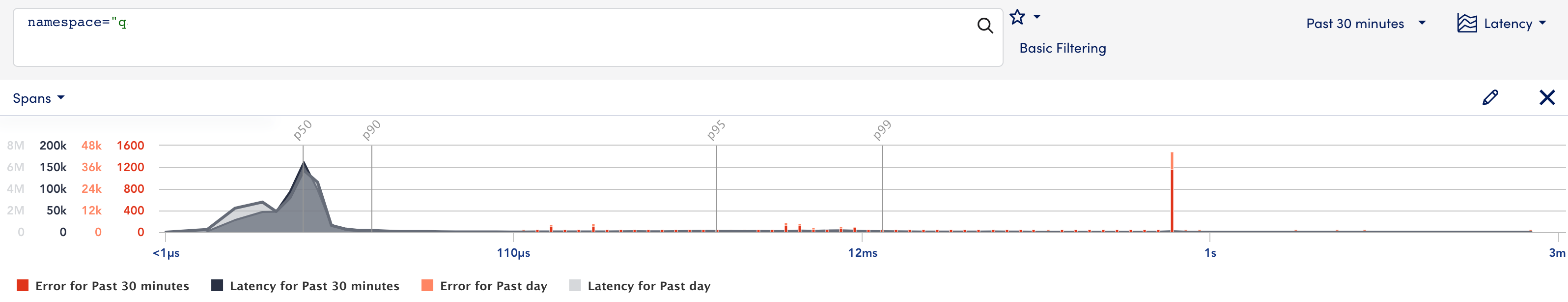
In addition, you can perform the following:
 —edits the compare spans details.
—edits the compare spans details. —closes the overlay compare spans graph.
—closes the overlay compare spans graph.
Traces Table
The Traces Table displays the specific operations within a trace using the following details:
| Field | Description |
| Time | The time that the operation occurred. You can sort the table in ascending or descending time order. |
| Operation | The name of the operation, which is set during instrumentation. |
| Kind | The kind or type of operation (internal, client, servers). |
| Duration (ms) | The duration of the operation in milliseconds. You can sort the table in ascending or descending time order. |
| Namespace | The namespace (application) to which the trace belongs. |
| Service | The service where the operation originated. If there are errors associated with the service, you will see an icon to indicate the severity. |
| Resource | The resource associated with the operation. If there are errors associated with the resource, you will see an icon to indicate the severity. |
In addition to the specific operations of a trace, the traces table also provides the following features:
 —opens the end-to-end trace view for the selected operation, along with other operations in the trace in a new tab.
—opens the end-to-end trace view for the selected operation, along with other operations in the trace in a new tab. —opens a topology map that describes conceptual information about the application. For more information, see Application Topology Overview.
—opens a topology map that describes conceptual information about the application. For more information, see Application Topology Overview.
End-to-End Trace View
Selecting a specific operation displays the end-to-end trace that operation participates in along with other operations in the trace. The end-to-end view focuses on the operation you select, but you will also see the operations before and after it in the timeline.
For each operation, this view displays the Service name and Operation name followed by the duration and error status of the operation. The length of the bar indicates its duration, while the color of the bar indicates the error status of the operation.
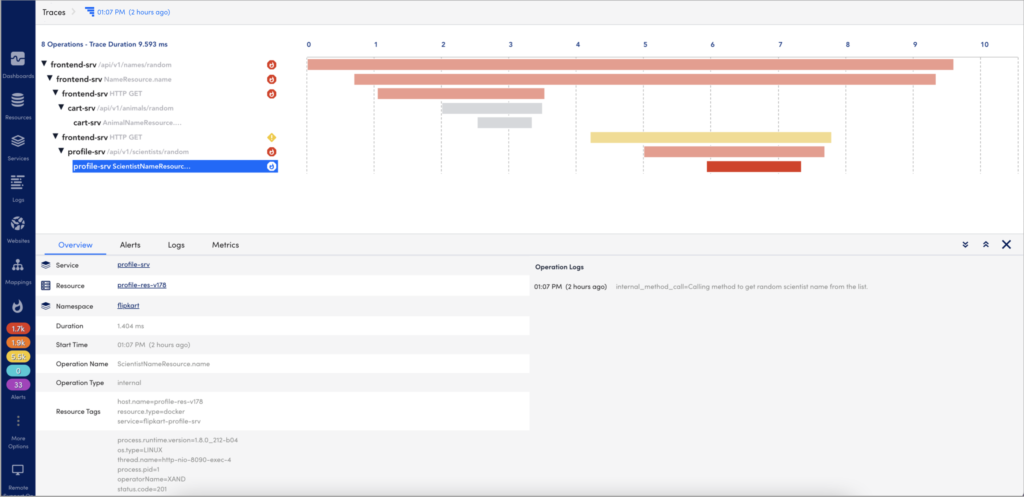
Selecting an operation opens the detail panel for that operation. This detail panel shows the following:
- Overview— Displays basic metadata for the operation (such as tags and logs), the resource the operation is associated with, and the service where the operation started.
- Alerts— Displays a list of any active alerts for the resource that the operation is associated with.
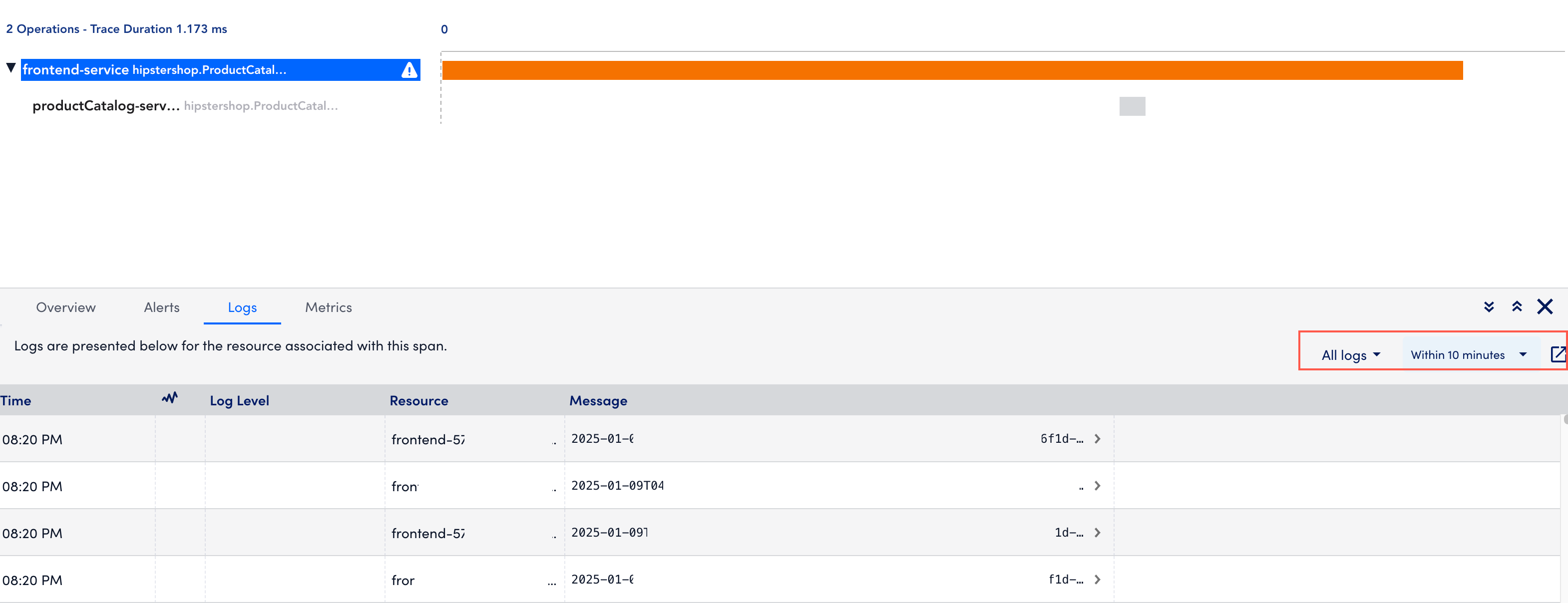
- Logs— Displays operation logs (such as application logs) sent via manual instrumentation, and resources logs (such as infrastructure and application logs) sent from LM Logs. For more information, see LM Logs for more information. In addition, you can filter logs based on the trace ID and also for a specific time range. You can also open the Logs page.
- Metrics— Displays the metrics (Duration, OperationCount, ErrorOperationCount) of the operations associated to the service namely in a graph. The metrics displays for a time range (+/- 15 minutes) of the ingested span. You can zoom in on each graph.
You can use this contextual information to troubleshoot issues identified by the traces (using duration or error status).
The following table lists the supported OpenTelemetry versions:
Important: Use the latest OpenTelemetry Collector version as the previous versions will be deprecated.
| Version | Release Date | Highlights |
| 5.2.00 (Recommended) | 22 May 2025 |
|
| 5.1.00 | 19 March 2025 | LogicMonitor now supports monitoring for Generative AI apps such as Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI chatbots using the LogicMonitor OpenTelemetry Collector (OTEL), with metrics and traces from OpenLIT and Traceloop. |
| 5.0.01 | 7 November 2024 | LogicMonitor now allows you to filter logs when created from a LogSource in the Modules page. |
| 5.0.00 | 13 August 2024 | LogicMonitor now supports the upgrade of the OpenTelemetry collector. |
| 4.0.00 | 11 June 2024 |
|
| 3.0.00 | 9 October 2023 |
|
Deprecated OpenTelemetry Collectors
| Version | Release Date | Highlights |
| 2.0.10 | 16 January 2023 |
|
| 2.0.00 | 29 June 2022 | LogicMonitor now uses OpenTelemetry Collector Contrib version 0.50.0. For more information, see releases from OpenTelemetry. |
| 1.0.06 | 21 April 2022 |
|
For more information on how to manage OpenTelemetry collectors, see Manage OpenTelemetry Collectors.
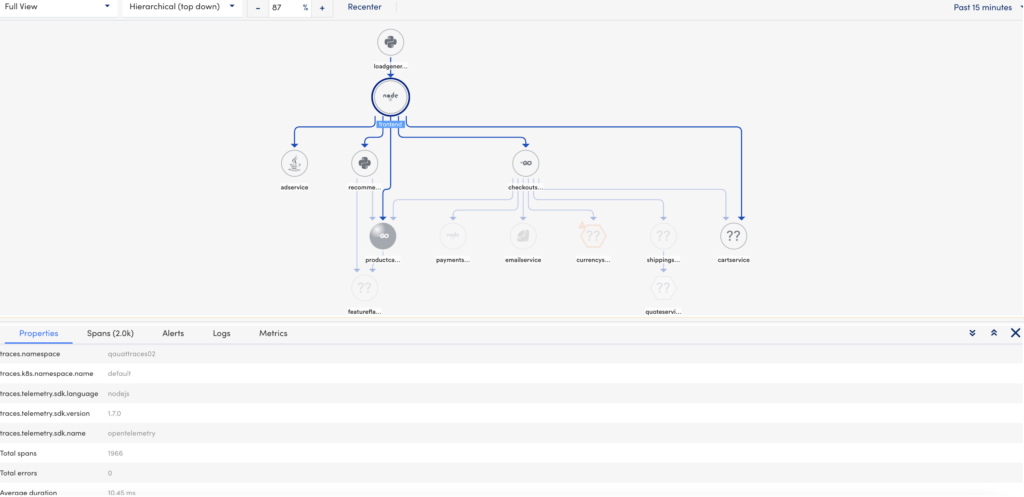
Selecting each service on the topology map displays information on which namespace it belongs to, a list of spans, associated alerts and logs. All this information displays in a tabular format below the topology map based on the selected service.
Note: There are some service nodes which appear in the topology map but when selected do not display data due to inadequate permissions.
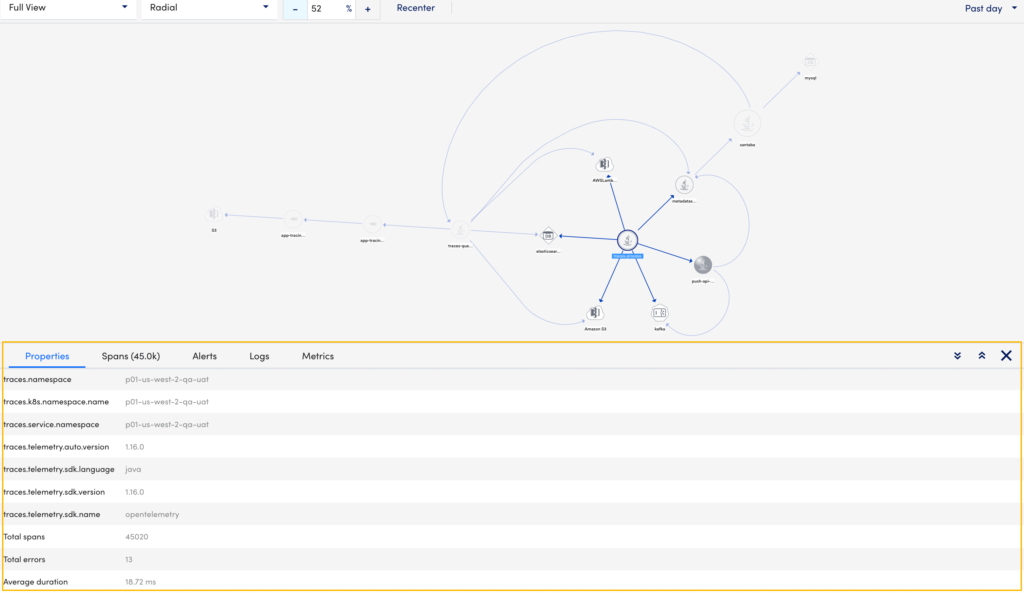
The application topology table displays the following details:
| Tab | Description |
| Properties | Displays the following information about the service:
|
| Spans | Displays all the spans information based on the time range selected in the sort data by time range option. This includes the service operation name, duration of the span, namespace or application name to which the service belongs, service name, and resource id. Note: You can select |
| Alerts | Displays all the alerts for the selected service. This includes information like severity, alert rules, instance, datapoint, escalation rule. For more information on alerts, see Managing Alerts from the Alerts page. Note:
|
| Logs | Displays all the relevant logs for the selected service. This includes the time, severity, and message for the selected service. |
| Metrics | Displays the metrics (Duration, OperationCount, ErrorOperationCount) of the operations associated to the service in a graph. The metrics displays for a time range (+/- 15 minutes) of the ingested span. You can zoom in on each graph. |
You can view the topology map for all your services for a given operation. This allows you to see how the different services are performing in your application and troubleshoot accordingly. If there are any alerts generated, the appropriate alert icon displays on the service itself. Clicking each service displays the overview, logs, alerts, and metrics information. For more information, see Application Topology Table.
Each external resource type is denoted with map icons that allow them to be recognized in the topology maps. For more information on these icons, see External Resource Types.
Note: There are some service nodes which appear in the topology map but when selected do not display data due to inadequate permissions.
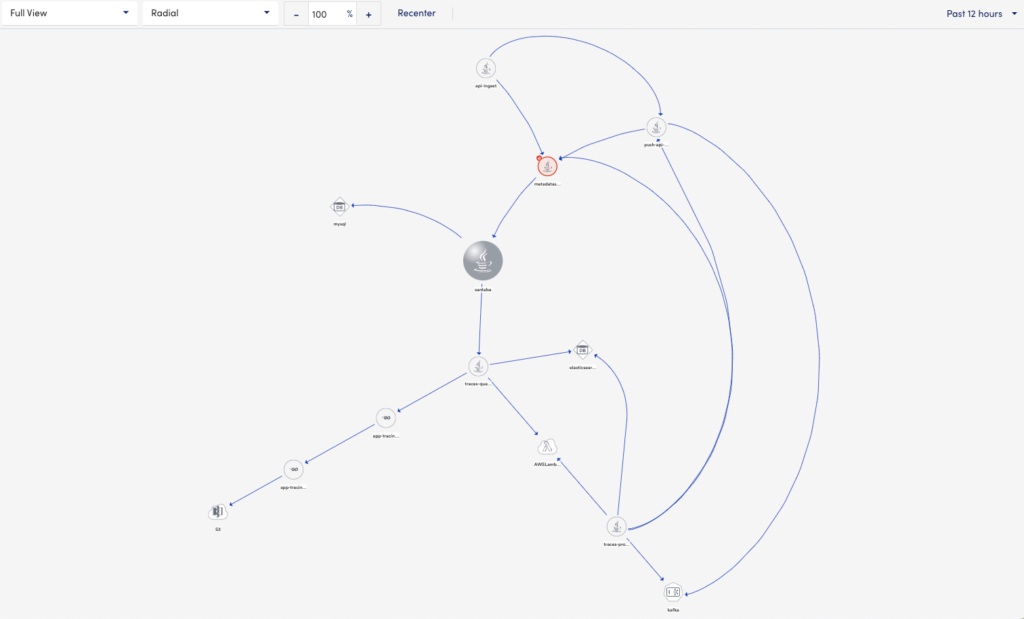
You can customize the map using the following options:
- View
- Layout
- Zoom
Note:
- You can recenter the entire topology map.
- You can sort the data using the time range drop-down. The default value is Past 15 minutes.
Using the View option
View option consists of the following:
- Full view (default)- Displays the entire view of the topology map for all the services.
- 1-Degree Away – Displays only the immediate or same-level services. This view does not display child services.
Using the Layout option
Layout option consists of the following:
- Radial (default)- Arranges all the services in a radial layout.
- Dynamic Layout – Arranges all the services in a dynamic layout. The services are listed in random order.
- Circular – Arranges all the services in a circular layout. For example, the traces-process service acts as a pivot node and all other services display around it.
- Hierarchical (top-down) – Arranges all the services in a hierarchy from top to bottom.
- Hierarchical (left to right) – Arranges all the services in a hierarchy from left to right.
Using the Zoom option
You can either type the zoom percentage to view the topology map or use the zoom controls.
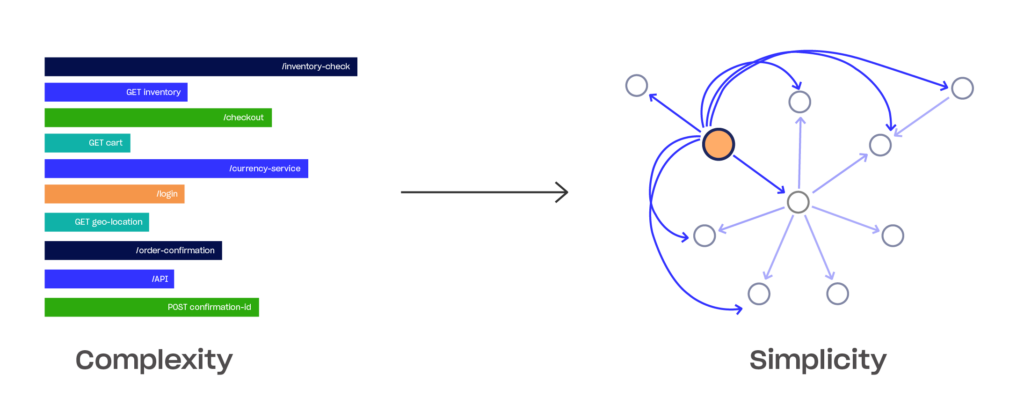
Application topology enables you to get a holistic insight into your application. You can visualize your complex application services and navigate based on topology relationships. In addition, troubleshoot alerts within your application on a topology map.
By default, the application topology page displays only a topology map of all your services within a given namespace (application) and how the services are linked to each other. If there are any alerts, they display on the service icons with the severity. In addition, you can individually click each service for more details.
Use Case for Application Topology
You can use application topology to investigate issues in an application that provides a checkout service. If you receive an abnormal error rate alert for the checkout operation in your application, you can use the topology map to investigate upstream services, such as cc-validation, and how the service impacts the downstream checkout service. You can locate the error within the operation that calls out to a third-party validation provider, allowing you to resolve the error.
Requirements for using Application Topology
To use application topology, you must have a LogicMonitor Enterprise license along with a LogicMonitor APM license. If you are using the LogicMonitor pre-configured OpenTelemetry Collector to send traces from your application into LogicMonitor, ensure the status of the collector is running. For more information, see to OpenTelemetry Collector for LogicMonitor Overview.
The following image illustrates how application topology simplifies your application’s complex operations:
Application Topology Page Components
Application topology is divided into the following two visual components:
- Topology Map—A topology map of all the services and their relations to each for a specific operation. For more information, see Application Topology Map.
Note:
- The topology maps for each service are stored for fifteen days.
- The initial mapping for application topology takes approximately fifteen minutes to populate.
- Topology Table—A table consisting of all the details for each of your services (properties, spans, alerts, and logs). For more information, see Application Topology Table.
Accessing the Application Topology Page
You can access the application topology page from the traces page. In the traces table, select ![]() against the service for a span or trace, you require to check. The topology map for that given namespace (application) displays.
against the service for a span or trace, you require to check. The topology map for that given namespace (application) displays.
If you did not use LogicMonitor to instrument your applications, you can modify the receiver value in the OpenTelemetry Collector configuration to forward traces to LogicMonitor. This enables the collector to receive traces in the format that the application was instrumented in, and then forward the traces to LogicMonitor in OpenTelemetry format via otlphttpexporter.
Forwarding Traces from Externally Instrumented Applications
Note: The following uses Jaeger as an example receiver value. Reference the applicable documentation from the libraries you used to instrument your applications.
In the OpenTelemetry Collector configuration, modify the receiver value to use the library you used to instrument your application, similar to the following:
receivers:
jaeger:
protocols:
grpc:
thrift_http:
exporters:
otlphttp:
endpoint:https://${LOGICMONITOR_ACCOUNT}.logicmonitor.com/rest/api/vi/traces
headers:
Authorization: Bearer ${LOGICMONITOR_BEARER_TOKEN}
service:
extensions: [nop]
traces:
receivers: [jaeger]
exporters: [otlphttp]Traces display in your LogicMonitor portal when the application emits the traces.
You can forward trace data from your applications directly to LogicMonitor without using an OpenTelemetry Collector. This allows you to quickly ingest traces from your applications without needing to install and manage a Collector. For example, if you want to gather trace data for Lambda functions in your environment, you can modify the variables during instrumentation that allows the function to emit trace data directly to your LogicMonitor portal.
Note: Using this method does not allow you to leverage the OpenTelemetry Collector’s Processors to modify and enhance data that is sent to the Collector. For more information, see Configurations for OpenTelemetry Collector Processors.
Requirements to Forward Trace Data without an OpenTelemetry Collector
To forward trace data without an OpenTelemetry Collector, you need the following:
- The endpoint of your LogicMonitor portal, similar to the following:
https://<PORTALNAME>.logicmonitor.com/rest/api/v1/traces - Valid API token
For more information, see API Tokens. - Manage permissions for the following:
- Data Ingestion
- Installed Modules
- Resources or HostGroups
Forwarding Trace Data without an OpenTelemetry Collector
Note: The following uses Java. For more information and examples of other languages, see LogicMonitor’s hosted demo application, HipsterShop.
Recommendation: Provide a valid service namespace while instrumenting your application. For example, -Dotel.resource.attributes=service.namespace=
During instrumentation, modify the variables in the application's configuration file to include the endpoint of your LogicMonitor portal, similar to the following:
java -javaagent:../opentelemetry-javaagent-all-1.9.0.jar \
-Dotel.exporter=otlp \
-Dotel.resource.attributes=service.name=pet-clinic \
-Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=https://<portalname>.logicmonitor.com/rest/api \
-Dotel.exporter.otlp.protocol=http/protobuf \
-Dotel.exporter.otlp.headers=Authorization="Bearer <token>" \
-jar spring-petclinic-2.5.0-SNAPSHOT.jarRecommendation: Use "OTLP" or "HTTP" as the protocol to send data directly to your LogicMonitor portal. These protocols use Protobuf payloads encoded either in binary format or in JSON format and use HTTP Post requests to send telemetry data from clients to servers.
When instrumenting an application in your Kubernetes infrastructure, you can leverage OpenTelemetry’s operator for Kubernetes. This allows you to automatically instrument your application by deploying the operator, defining an instrumentation resource, and then using an annotation to inject that instrumentation for your application containers.
Use OpenTelemetry Operator for Kubernetes from OpenTelemetry along with the following information to use OpenTelemetry’s operator.
Automatically Instrumenting an Application using the OpenTelemetry Operator
- Deploy OpenTelemetry’s Operator using Getting Started from OpenTelemetry.
- Define a custom instrumentation resource by providing sampling preferences, the LM OTEL Collector endpoint, and resource attributes to map traces to the correct monitored infrastructure in LogicMonitor to create a custom instrumentation resource similar to the following:
kind: Instrumentation
metadata:
name: my-instrumentation
spec:
env:
- name: OTEL_POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.podIP
exporter:
endpoint: http://mylmotelcollector.endpoint/
resource:
addK8sUIDAttributes: true
resourceAttributes:
{ "resource.type" : "kubernetes-pod", "ip" : "$(OTEL_POD_ID)" }
propagators:
- tracecontext
- baggage
- b3
sampler:
type: parentbased_traceidratio
argument: "0.25"- Apply the pod annotation to pods running applications for automatic instrumentation. This injects the auto instrumentation agent as an init container that downloads the JAR and makes it accessible to the application at startup. For example, you can patch your application deployment using the following:
kubectl patch deployment my-deployment -p '{"spec": {"template":{"metadata":{"annotations":{"instrumentation.opentelemetry.io/inject-java":"my-instrumentation"}}}} }'