A growing number of enterprises are shifting toward a multi-cloud environment with the rise of remote and hybrid work. In fact, 76% of organizations have already adapted to a multi-cloud infrastructure.
These dynamic networks offer companies many reported advantages, such as scalability, agility, and optimized performance. When it comes to a company’s digital transformation and transition to a multi-cloud environment, Software-Defined Wide-Area Networking (SD-WAN) often emerges as a top consideration.
What is SD-WAN?
Many companies with a multi-cloud network have replaced the conventional Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) transport protocols with SD-WAN.
SD-WAN refers to a software-based method of managing wide-area telecommunication networks. With SD-WAN, you can combine transport services (including MPLS circuitry) through encrypted overlay tunnels to communicate and prioritize enterprise data across internal applications.
There is a good reason for SD-WAN’s widespread appeal. While the MPLS has proven reliable for decades in handling predetermined communication pathways, it lacks the flexibility and agility for managing modern multi-cloud environments with vast and dispersed endpoints.
Unpacking the SD-WAN architecture
SD-WAN networks run on an abstract infrastructure divided into a control and forwarding plane. The control plane functions from a centralized location as a remotely controlled network, eliminating the need for on-premise technicians. At a granular level, SD-WAN features three components that comprise its virtualized infrastructure, removing the reliance on specific hardware.
SD-WAN Edge
The SD-WAN Edge refers to the user endpoint within the network. These may include multi-cloud systems, on-premise data centers, and SaaS platforms.
SD-WAN Controller
An SD-WAN Controller offers a transparent view of connected networks and facilitates decision-making policies for orchestrators. Essentially, an SD-WAN controller provides centralized management of enterprise data flow and authenticates devices linked to your network.
SD-WAN Orchestrator
Your designated SD-WAN Orchestrator manages and systematizes policies and traffic among authorized controllers. The component streamlines intuitive workflows across your enterprise networks (e.g., branch offices). Essentially, orchestrators are the definitive bridge between your controller and edge routers. You can upgrade orchestrator functions by providing enhanced analytics and performance SLAs that expedite troubleshooting processes and network fixes.
Top SD-WAN providers
The modern market features an assortment (and an ever-growing number) of SD-WAN vendors, each providing unique features and functionalities. Therefore, you will benefit from researching the leading vendors to access the best solutions in network function virtualization (NFV) and software-defined networking (SDN) deployments.
Fortinet Secure SD-WAN
With superior security standards, Fortinet offers services that drive high-performance network capabilities. The vendor’s SD-WAN structure helps your organization manage precious enterprise data without compromising speed or function. Also, Fortinet’s SD-WAN services have undergone rigorous testing, with Gartner validating the solution for its high performance, reliable security, and low total cost of ownership (TCO).
Using Fortinet’s SD-WAN technology guarantees several improvements to communication processes with built-in encryption protection and sandboxing features that prevent data loss. Fortinet provides frictionless integration to your branch infrastructure for smooth data management across LANs, optimizing hybrid SD-Branch layouts.
Versa Networks (OS)
Versa Networks’ SD-WAN solution features an integrated platform with premium security capabilities. The technology’s intuitive functions include multi-cloud connectivity, full multi-tenancy and micro-segmentation of businesses, and context-based network and security policies throughout registered networks.
Versa prioritizes optimal network security as one of its core missions. In 2021, Gartner recognized Versa Networks as a visionary in the Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Network Firewalls, emerging as the preferred choice from an in-depth comparison of the top 19 vendors in the communications industry. The SD-WAN offers access to Versa’s Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), enhancing user security through multi-factor authentication, data protection, and SSL decryption.
Aryaka
Aryaka is an innovative service provider that combines SD-WAN technology with a secure web gateway as a one-stop network solution. Specifically, Aryaka’s hybrid approach equips your organization with a zero-trust WAN that significantly reduces business and operational risks. As a result, Aryaka positions itself as a leader among SD-WAN vendors, promoting the fastest service of its kind within the industry.
Gartner has recognized the zero-trust vendor as the customer’s choice for three consecutive years through outstanding KPI standards, including 99.999% SLA performance and uptime and a 65 net promoter score rating five times the industry average. Your business can manage optimal security and communication performance from a single contact point through Aryaka’s SD-WAN layouts.
Understanding the pros of SD-WAN
SD-WANs give enterprise networks a general boost from conventional MPLS systems as they improve connectivity across separate applications and off-site locations.
Business traffic prioritization
SD-WAN helps your organization prioritize critical enterprise data by selecting the most cost-effective and efficient communication path. When you set up the technology’s load-balancing and traffic-steering capabilities, your SD-WAN network can recognize business applications and allocate bandwidth volume according to individual service requirements. Traffic steering lets your team manage multiple parallel connections in business traffic with a responsive system, providing rate-limitless sensitive applications with optimal bandwidth.
Affordability
An SD-WAN approach applies private and distributed data exchange and control measures, which function seamlessly across diverse project environments. The process optimizes network functionality and cost-effectiveness by securing data from the cloud and immediate networks.
Application performance optimization
SD-WAN’s structured infrastructure drives optimal application performance across enterprise networks. Specifically, the agile transport mode fulfills the latest enterprise compliance mandates and automates traffic steering based on business priorities. Additionally, SD-WAN provides a centralized control center for managing enterprise data across multi-cloud endpoints, connecting with authorized SaaS and IaaS collaborators and vendors without complication.
Diverse transport methods
With SD-WAN networks, users can access multiple transport channels, including direct broadband connection, 5G, and traditional MPLS circuits. The flexible arrangement improves data availability for undisrupted and optimized communications. You can expect optimal application performance across cloud systems, on-premise servers, and SaaS platforms like Microsoft 365 or Salesforce.
The cons of SD-WAN
While SD-WAN networks seem like a step in the right direction in multi-cloud environments, they pose some user considerations as a developing technology.
No on-site security function
SD-WAN networks lack an on-site security function, so you must separately install and manage a security policy to safeguard networks against online threats. An unprotected SD-WAN infrastructure might face considerable risks from data breaches such as the Colonial Pipeline Hack, which resulted in significant data loss and reputational damage.
No Quality of Service (QoS) under specific scenarios
Communication networks that rely on SD-WAN provisions lack a proper QoS. Essentially, these networks will not receive the full technical benefits of SD-WAN, including path control, traffic shaping, and forward error correction.
Vendor concerns
SD-WAN vendors may provide their services and equipment at a higher cost. Also, due to the variability of service standards, some vendors may need more capability to service software-based networking (SDN).
Revisiting MPLS
In the 1990s, MPLS replaced standard internet protocol (IP) routing and became the primary transport method for enterprise data. While the infrastructure offers scalability, optimized bandwidth utilization, and enhanced security – by serving as a virtual private network – it requires installing and maintaining physical links. This process has become increasingly complex, costly, and impractical in a progressively multi-cloud landscape.
MPLS infrastructure
MPLS is a protocol-independent solution with predetermined paths between routers in the MPLS network; each label comprises four components:
- The label value that determines the direction of the data packet
- The traffic class field
- The bottom of the stack flag
- The time-to-life (TTL) field
Functionalities of the MPLS
The MPLS moves network traffic through predetermined labels instead of conventional addresses, guiding the data through private WANs (wide-area networks).
MPLS functions as layer 2.5 in the OSI seven-layer hierarchy between data links that use LANs and networks that run on internet-wide addressing. This infrastructure attributes a forwarding equivalence class (FEC) to each data packet within a network, which routers can decipher by comparing them against descriptive tables.
The routers update the outermost layer of the data packet as it travels through the FEC pathway and to the next hop, which is examined and submitted to the next layer. Users of the MPLS method can customize the information for each packet, essentially driving top performance in unified networks.
Private MPLS networks can provide your organization with a consistent and reliable means of managing communications in cloud-based environments.
Pros of MPLS
Your MPLS transport modes remain segregated from the public internet, making the infrastructure invulnerable to prevalent web-based attacks such as distributed denial of service (DDoS). As such, the enhanced security of MPLS offers the optimal performance of real-time data transportation by avoiding potential interceptions and packet loss within the open internet.
Despite the general security of MLPS (with SD-WAN combinations), some decision-makers may seek added protection from automated cloud monitoring across public and private connections.
Cons of MPLS
Most of the downsides to MPLS relate to its physical limitations and high cost compared to SD-WAN alternatives. In its original design, the MPLS catered to organizations communicating through remote branches of enterprise data centers. MPLS would conventionally backhaul data from branch offices for comprehensive security processing and distribution through on-premise hubs. However, many companies now prefer cloud services over MPLS. Additionally, the backhauling process often increases latency and reduces application performance.
Comparing SD-WAN with MPLS
A significant highlight of SD-WAN, unlike MPLS, lies in its transport-agnostic overlay structure. Your organization can benefit from the arrangement by applying and modifying policies across your WAN from a centralized location. Alternatively, MPLS functions via predetermined routes through physically installed connections, but its fixed circuits make managing changes across multiple user environments costly and complex.
Although SD-WAN might replace MPLS as the more popular transport choice for some companies, the technologies could co-exist depending on your enterprise arrangements. For instance, some companies may adopt a hybrid network management approach. Specifically, decision-makers would restrict MPLS use to on-premise legacy applications while offloading cloud-based programs to SD-WAN.
Additionally, some organizational leaders have adopted internet-augmented MPLS with SD-WAN. The advanced process increases organizational flexibility by enhancing MPLS with internet broadband links. These links prioritize networking decisions according to specific requirements, such as application type and optimal bandwidth volume.
Hybrid approaches
Many organizations are adopting hybrid approaches that combine the strengths of SD-WAN and MPLS. This strategy allows businesses to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness by leveraging the unique benefits of each technology for specific use cases.
How hybrid SD-WAN/MPLS solutions work
A hybrid approach integrates MPLS circuits with SD-WAN’s flexible, software-defined overlay. MPLS handles latency-sensitive and mission-critical applications that require guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS), while SD-WAN manages less critical traffic using cost-effective broadband or other transport methods. By dynamically routing traffic based on application requirements, hybrid setups ensure that each data type is delivered efficiently and securely.
For example:
- MPLS role: Ensures low-latency, high-reliability communication for applications like VoIP, video conferencing, and financial transactions.
- SD-WAN role: Routes non-critical traffic, such as email, file backups, and SaaS applications, through broadband connections, reducing MPLS bandwidth requirements and costs.
Scenarios where hybrid approaches excel
- Real-time applications with high bandwidth demand
Businesses requiring uninterrupted service for real-time applications, such as hospitals using telemedicine or financial institutions running stock trading platforms, can dedicate MPLS to these tasks while leveraging SD-WAN for less critical operations. - Multi-branch organizations
Enterprises with numerous branch offices can use MPLS for their headquarters and key locations, ensuring consistent performance for sensitive operations while using SD-WAN to connect smaller branches with broadband. - Global operations with varying network needs
Hybrid solutions are ideal for multinational organizations with offices in regions where MPLS availability or affordability varies. In these cases, MPLS can be prioritized in key regions while SD-WAN manages connections in remote or less-developed areas. - Disaster recovery and business continuity
By combining MPLS and SD-WAN, businesses can create highly resilient networks with failover capabilities. If MPLS circuits experience outages, SD-WAN dynamically reroutes traffic to maintain uptime. - Cloud-first strategies
Hybrid approaches enable organizations transitioning to cloud-based operations to retain MPLS for legacy applications while offloading cloud workloads to SD-WAN. This ensures seamless performance across both on-premise and cloud environments.
Decision-making checklist: Choosing between SD-WAN and MPLS
Selecting the right networking solution for your organization requires carefully evaluating your unique needs, priorities, and constraints. Use the following checklist to guide your decision-making process and determine whether SD-WAN, MPLS or a hybrid approach is the best fit for your enterprise:
1. Assess your network requirements
Do you have latency-sensitive applications, such as VoIP, video conferencing, or financial transactions, demanding guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS)?
- If yes, MPLS or a hybrid approach may be necessary.
Are your users distributed across multiple remote locations or regions with varying connectivity needs?
- If yes, SD-WAN offers better scalability and flexibility.
2. Evaluate your budget
What is your budget for networking infrastructure, including installation, maintenance, and operational costs?
- MPLS typically requires higher initial and ongoing investments due to physical circuits and hardware.
- SD-WAN offers a cost-effective alternative by leveraging existing broadband or internet connections.
3. Consider Scalability
Is your organization rapidly expanding or adopting a multi-cloud strategy?
- SD-WAN provides seamless scalability for growing networks and dynamic environments.
- MPLS may need to be more adaptable due to its reliance on fixed circuits.
4. Analyze Security Needs
Do you require private, highly secure connections for sensitive data?
- MPLS offers inherent security through private circuits but may need cloud integration for modern environments.
- For comprehensive protection, SD-WAN requires additional security layers, such as Secure Access Service Edge (SASE).
5. Examine Application Performance
Are your applications cloud-native, such as SaaS platforms or IaaS solutions?
- SD-WAN is optimized for cloud connectivity, enabling direct and efficient access to cloud applications.
- MPLS is more suitable for legacy on-premise applications that rely on data center backhauling.
6. Assess Management and Operational Complexity
Do you need centralized, simplified network management?
- SD-WAN provides centralized control and automation for effortless network monitoring and troubleshooting.
- MPLS requires more hands-on management, often needing on-premise technical support.
7. Plan for Future-Proofing
Is your organization prioritizing digital transformation, including support for hybrid work and zero-trust security models?
- SD-WAN, combined with SASE, aligns with cloud-first and modern security trends.
- MPLS may need help to keep pace with the agility required for these transitions.
8. Evaluate Hybrid Options
Would a combination of SD-WAN and MPLS better meet your needs?
- Use MPLS for critical real-time applications and SD-WAN for cost-effective handling of general traffic.
Alternatives to MPLS and SD-WAN
While MPLS has been a reliable transport method for enterprise networks, advancements in networking technology offer alternative solutions better suited for modern, cloud-first environments. These alternatives provide flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency for organizations looking to evolve beyond traditional MPLS setups.
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
VPNs provide a secure, encrypted tunnel for data transmission over the public internet. While they lack the QoS guarantees of MPLS, VPNs are a cost-effective solution for connecting remote users and smaller branch offices to corporate networks. VPNs work well for businesses prioritizing affordability and basic security over high-performance requirements.
5G networks
The rise of 5G technology offers a compelling alternative for enterprise networks. With ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and widespread availability, 5G networks can support critical business applications that were previously reliant on MPLS. They are particularly effective for edge computing environments and mobile-first businesses.
Internet-based networking
Many organizations are turning to direct internet access (DIA) and broadband connections as replacements for MPLS. These options allow businesses to leverage high-speed, cost-effective public internet connections while pairing them with cloud-native security solutions like SASE to maintain performance and security.
Private LTE and CBRS
Private LTE and Citizen Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) networks are emerging as viable alternatives for enterprises requiring private, secure connectivity without the constraints of traditional MPLS. These technologies enable organizations to create their wireless networks, which are ideal for environments with unique coverage requirements, such as manufacturing facilities or campuses.
A summary of SD-WAN vs. MPLS
SD-WAN systems provide your organization with the trusted capabilities of managing multi-cloud environments with greater scalability and reliability. The modern data transport mode presents a more affordable and flexible solution that leverages MPLS, wireless, broadband, and virtual private networks (VPNs) to maintain high speed across remote environments.
On the other hand, MPLS boosts network efficiency through predetermined routes, and it is best suited for enterprise environments that continue to rely on data centers. In both instances, you can significantly improve observability by applying a trusted REST API that exposes all functionalities within your networks without tedious wrapper codes.
REST APIs with multiple integrations offer added convenience for managing data across multi-cloud platforms, preferably with automated webhooks that send real-time information between applications.
As the WAN continues to evolve, enterprise leaders must have the freedom and accessibility to navigate between private and public Internet infrastructures. Comparing SD-WAN vs. MPLS, you can successfully align your company’s specific requirements with the necessary product sets to achieve the best outcomes.
SD-WAN in the future of network communications
Through SD-WAN, your organization maintains optimized software functions regardless of location, elevating your overall user experience while reducing IT expenses. Combining SD-WAN networks with intelligent monitoring can help you streamline and optimize business continuity in work-from-home and hybrid settings.
Another major factor in SD-WAN adoption is its independence from tedious MPLS circuitry migrations. If your enterprise network currently runs on the public internet, you can choose to retain your service provider by moving or reconfiguring the virtualized elements of your WAN.
Next, SD-WAN capabilities support the core functions of Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) structures, a term Gartner coined in 2019. Advanced SASE setups provide your enterprise with a safe, reliable, unified cloud-based network.
SASE also helps your organization transport security and access between multiple user endpoints, such as branch offices and mobile applications. The structure operates through a combination of SD-WAN functionalities and cloud-based security solutions. Ultimately, SD-WAN proves integral in supporting your company through future-proofing communications for a cloud-first landscape.
Take your network management to the next level with LogicMonitor. Discover how our platform integrates seamlessly with SD-WAN to provide unparalleled visibility, performance monitoring, and scalability for your enterprise.
IT automation uses software and technology to handle repetitive IT tasks automatically, reducing the need for manual work and accelerating processes like infrastructure management and application deployment. This transformation is essential for IT teams needing to scale efficiently, as seen in the case of Sogeti, a Managed Service Provider (MSP) that provides tech and engineering resources worldwide.
Sogeti had a crucial IT challenge to solve. The MSP operates in more than 100 locations globally and uses six different monitoring tools to monitor its customers’ environments. It was a classic example of tool sprawl and needing to scale where multiple teams of engineers relied on too many disparate tools to manage their customers’ environments. It soon became too arduous for the service provider to collect, integrate, and analyze the data from those tools.
Sogeti had teams of technicians managing different technologies, and they all existed in silos. But what if there was a way to combine those resources?
IT automation provided a solution.
After working with LogicMonitor, Sogeti replaced the bulk of its repeatable internal processes with automated systems and sequences. The result? Now, they could continue to scale their business with a view of those processes from a single pane of glass.
Conundrum cracked.
That’s just one example of how IT automation tools completely revolutionizes how an IT services company like an MSP or DevOps vendor can better execute its day-to-day responsibilities.
By automating repeatable, manual processes, IT enterprises streamline even the most complicated workflows, tasks, and batch processes. No human intervention is required. All it takes is the right tech to do it so IT teams can focus on more strategic, high-priority efforts.
But what exactly is IT automation? How does it work? What are the different types? Why should IT companies even care?
IT automation, explained
IT automation is the creation of repeated software processes to reduce or eliminate manual or human-initiated IT tasks. It allows IT companies with MSPs, DevOps teams, and ITOps teams to automate jobs, save time, and free up resources.
IT automation takes many forms but almost always involves software that triggers a repeated sequence of events to solve common business problems—for example, automating a file transfer. It moves from one system to another without human intervention or autogenerates network performance reports.
Almost all medium and large-sized IT-focused organizations use some automation to facilitate system and software processes, and smaller companies benefit from this tech, too. The most successful ones invest heavily in the latest tools and tech to automate an incredible range of tasks and processes to scale their business.
The production, agricultural, and manufacturing sectors were the first industries to adopt IT automation. However, this technology has since extended to niches such as healthcare, finance, retail, marketing, services, and more. Now, IT-orientated companies like MSPs and enterprise vendors can incorporate automation into their workflows and grow their businesses exponentially.
How does IT automation work?
The software does all the hard work. Clever programs automate tasks that humans lack the time or resources to complete themselves.
Developers code these programs to execute a sequence of instructions that trigger specific events from specific operating systems at specific times. For example, programming software so customer data from a customer relationship management system (CRM) generates a report every morning at 9 a.m. Users of those programs can then customize instructions based on their business requirements.
With so many benefits of IT automation, it’s no wonder that two-thirds of CFOs plan to accelerate the automation of repetitive tasks within their companies.
Why do businesses use IT automation?
IT-focused businesses use automation for various reasons:
- It makes life easier for tech teams. For example, engineers and technicians at MSP companies no longer have to execute tasks like network performance analysis, data security management, or reporting manually. The software takes care of everything for them so they can better focus their efforts on other tasks.
- It makes life easier for non-tech teams. Employees across all departments within an IT-focused organization benefit from automation because they can carry out responsibilities on software and systems with less manual work. For example, administrative employees in a DevOps consulting firm can generate payroll reports without manually entering information into a computer by hand.
- It helps CIOs and executives scale their businesses because other employees, such as engineers and MSP professionals, can complete jobs with minimum effort. Automation frees up tech resources and removes as much manual IT work as possible, allowing IT-centered organizations to improve their margins and grow.
- It helps CIOs and executives fulfill client-orientated objectives by improving service delivery. Automation can also advance productivity across an organization, which results in better service level agreement (SLA) outcomes. Again, the right automation software reduces as much manual work for tech teams so businesses can grow and carry out responsibilities more efficiently.
- It allows MSPs and other IT companies, especially smaller ones, to survive in ever-competitive environments. By automating IT processes, these enterprises can stay competitive with more tech resources and reduced manual labor.
- It allows for improved profitability in IT companies. For example, MSPs can onboard more clients without hiring new engineers. That’s because automated systems delegate tasks and resources seamlessly.
- It reduces costs for IT companies by saving time and improving operational efficiencies. For example, by freeing up human resources, enterprises can focus on generating more sales and revenue. As a result, CIOs and executives have more money to spend on labor and can add highly skilled IT professionals to their tech teams.
Key benefits of IT automation
IT automation delivers many advantages that extend beyond simple task delegation. Let’s look at a few benefits your organization will see.
Enhanced organizational efficiency
With the complexity of modern IT infrastructure, modern environments may handle thousands of requests daily—everything from password resets to system failures. Automation can help reduce the time it takes to handle many of those requests. For example, look at an IT telecommunications company with a lot of infrastructure. They can automate their network configuration process, cutting the deployment time from a few weeks to less than a day.
Reduce errors
Human error in IT environments can be costly. Errors can lead to unexpected system downtime, security breaches, and data entry errors—all of which you can avoid by standardizing consistency and standards through automation. Automation helps your team eliminate routine data entry and other tasks and greatly reduces the chance of human error. For example, your team may decide to create backup scripts for more complicated setups to ensure you always have reliable backups.
Faster service delivery
Automation helps speed up responses to common IT requests. If your IT team is stuck needing to perform every task manually, it increases incident response time and the length of time your customer waits on the other end of the line for a fix. Automation speeds up common tasks—setting up VPN access, account resets, report creation, and security scans—allowing your team to focus on finding the root cause of problems, deploying resources, and bringing systems back online.
Streamlined resource allocation
Your organization’s IT needs may fluctuate depending on how many users you have and their activities. A strict guide for resource usage may result in some users being unable to work efficiently because of slow systems. Automation can help by automating resource allocation. For cloud services, you can scale your servers based on demand, and for network traffic, you can dynamically adjust traffic routes based on usage.
Enhanced compliance and security
Automated systems can help your team maintain detailed audit trails and enforce consistent security policies. They can also help with continuous monitoring, allowing your team to get alerts immediately when your solution detects suspicious activity. Additionally, your IT systems can automatically generate compliance reports, such as SOC 2, for review, helping your team find potential problems and comply with audit requests.
Different IT automation types
IT companies benefit from various types of IT automation.
Artificial intelligence
A branch of computer science concerned with developing machines that automate repeatable processes across industries. In an IT-specific context, artificial intelligence (AI) automates repetitive jobs for engineers and IT staff, reduces the human error associated with manual labor, and allows companies to carry out tasks 24 hours a day.
Machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a type of AI that uses algorithms and statistics to find real-time trends in data. This intelligence proves valuable for MSPs, DevOps, and ITOps companies. Employees can stay agile and discover context-specific patterns over a wide range of IT environments while significantly reducing the need for case-by-case investigations.
Robot process automation
Robot Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that instructs ‘robots’ (machines) to emulate various human actions. Although less common in IT environments than in AI and ML, RPA still provides value for MSPs and other professionals. For example, enterprises can use RPA to manage servers, data centers, and other physical infrastructure.
Infrastructure automation
IT infrastructure automation involves using tools and scripts to manage computing resource provisioning with manual intervention. This includes tasks like server provisioning, bandwidth management, and storage allocation. This allows for dynamic resource usage, with the most resources going to the users and applications with the most need.
How can businesses use IT automation?
A proper automation strategy is critical for IT companies. CIOs and executives should decide how to achieve automation within their organizations and then choose the right tools and technologies that facilitate these objectives.
Doing so will benefit your business in many ways.
- Improve your company’s operation by removing redundant tasks and freeing up time to work on more mission-critical jobs
- Enhance customer satisfaction by more quickly responding and resolving problems
- Improve employee satisfaction by making sure business systems stay online, helping meet their expectations and improving their ability to do their jobs
Here are some examples of how IT companies use automation:
Templating/blueprints
Companies can automate templates and blueprints, promoting the successful rollout of services such as network security and data center administration.
Workflow/technology integration
Automation allows companies to integrate technology with workflows. As a result, CIOs and executives complete day-to-day tasks more effectively with the latest hardware and software. For example, automating server management to improve service level management workflows proves useful if clients expect a particular amount of uptime from an MSP.
AI/ML integration
AI and ML might be hard for some companies to grasp at first. However, teams can learn these technologies over time and eventually combine them for even more effective automation within their organizations.
Auto-discovery
Automated applications like the LogicMonitor Collector, which runs on Linux or Windows servers within an organization’s infrastructure, use monitoring protocols to track processes without manual configuration. Users discover network changes and network asset changes automatically.
Auto-scaling
IT companies can monitor components like device clusters or a VM in a public cloud and scale resources up or down as necessary.
Automated remediation/problem resolution
Hardware and software can provide companies like MSPs with all kinds of problems (downtime, system errors, security vulnerabilities, alert storms, etc.). Automation, however, identifies and resolves infrastructure and system issues with little or no human effort.
Performance monitoring and reporting
Automation can automatically generate regular performance reports, SLA reports, compliance reports, and capacity planning forecasts. It can also generate automated alerting systems in case of problems and report trends to help your business with capacity planning.
Best practices for automation success
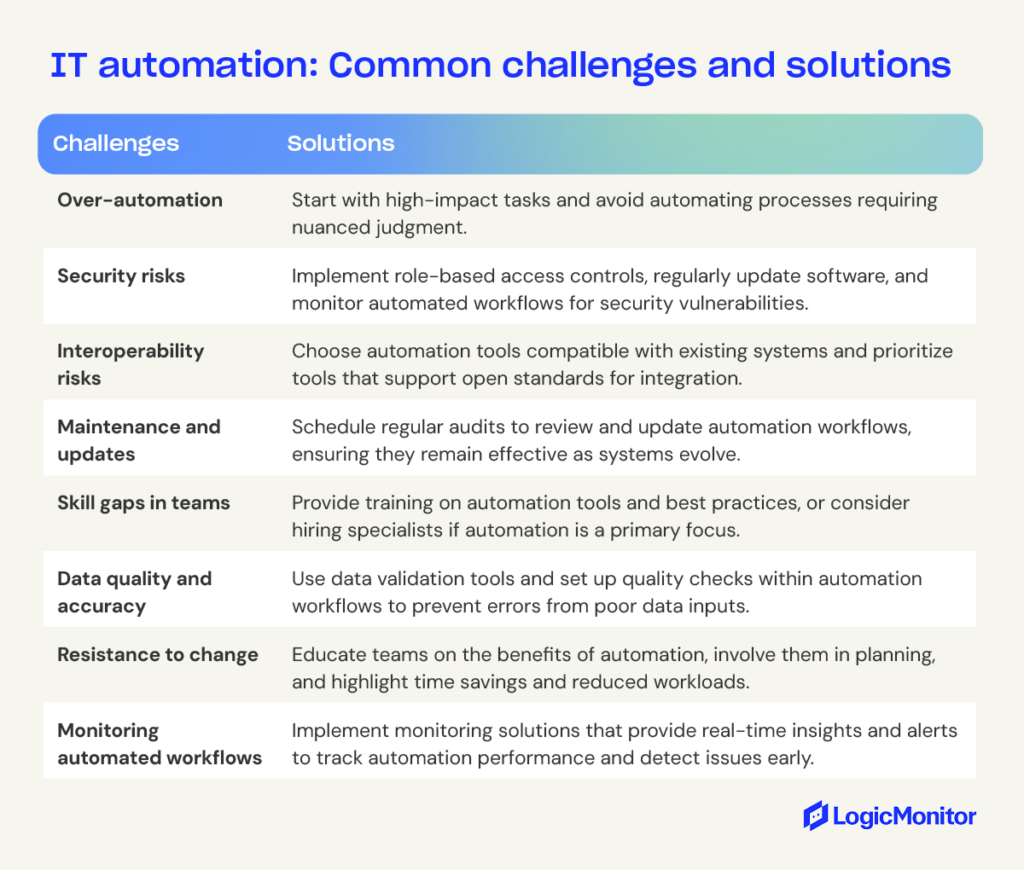
Successfully automating IT in business requires careful planning and thoughtful execution. Follow these best practices to avoid the common mistakes and maximize efficiency:
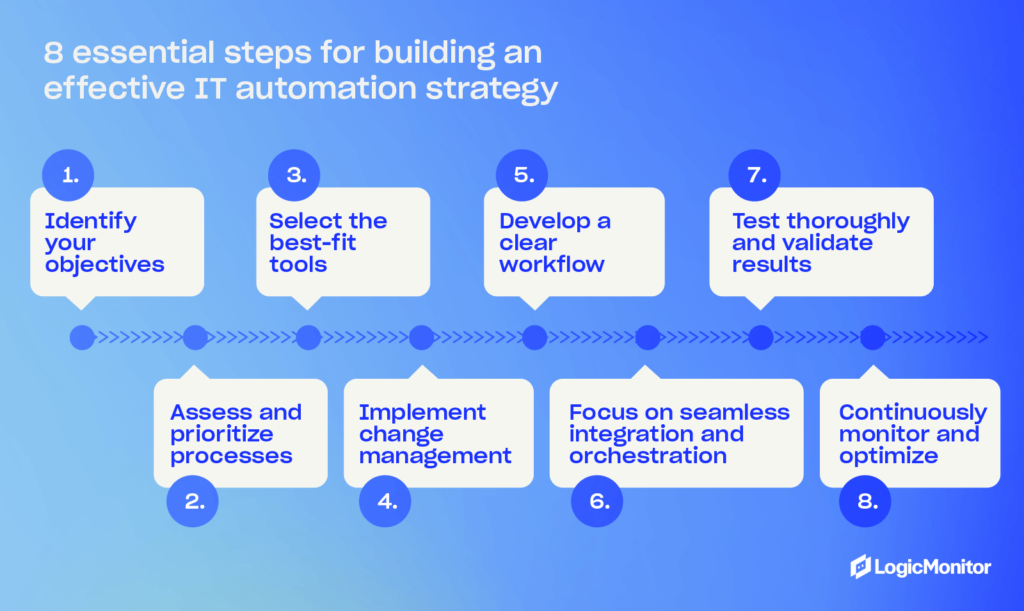
- Align automation and business goals: Don’t just start automating everything possible without a plan. Begin by identifying what you want to achieve with automation. Look for areas to reduce operational costs, improve service, and enhance customer satisfaction, and start with the areas that have the most impact and help you reach your goals. Consider asking stakeholders and employees about their biggest friction points and the ability to automate them.
- Start small: Investing in IT automation is an ongoing task, and you may not do things right the first time. Start small with quick wins. Learn what works for your business and pilot your initial automation tasks to test how they work. Eventually, begin scaling as you gain insights from smaller projects to inform larger, more impactful ones.
- Focus on security: Although your team may not be working with data manually as much, security is still a must with IT automation. Integrate secure protocols at every layer of your systems and processes. Look at your regulatory requirements to determine your needs, and regularly audit your systems to identify potential weaknesses.
- Document everything: If things go wrong, you need detailed records about your automation process. Create documents that detail every system, automation tools and scripts that belong to those systems, and common troubleshooting tips for quickly dealing with problems. Make documentation available to team members so all your team members can look up how things work and manage their designated automation systems.
- Monitor performance: Establish metrics that indicate the success of your automation efforts. Look for improvements in uptime, response time, and other performance data. Regularly look for areas that don’t meet your performance metrics and investigate areas of improvement.
IT Automation Pros and Cons
Here are some pros and cons of automation for those working in IT:
Pros
- Enhanced productivity (improved workflows, higher production rates, better use of technologies and human resources, freeing up IT resources, etc.).
- Better customer/client outcomes (improved SLAs, faster and more consistent services, higher-quality outputs, enhanced business relationships, etc.).
- Reduced total cost of ownership (auto-discovery tools prevent expensive errors, freeing up labor resources, automatic discovery of cost-cutting technologies, etc.).
Cons
- Automation requires an initial cost investment and engineers’ time to set up. That’s why IT-focused companies should choose a cost-effective automation platform that generates an ongoing return on investment.
- Some team members may find it difficult to adopt automation technologies. The best course of action is to select a simplified automation tool.
- Automation may amplify security issues. Software and configuration vulnerabilities can quickly spread in your organization before being detected, which means security considerations and testing must be done before introducing automation.
Read more: The Leading Hybrid Observability Powered by AI Platform for MSPs
Will IT automation replace jobs?
There’s a misconception that IT automation will cause job losses. While this might prove true for some sectors, such as manufacturing, IT-focused companies have little to worry about. That’s because automation tools don’t work in silos. Skilled IT professionals need to customize automation tools based on organizational requirements and client demands. MSPs that use ML, for example, need to define and determine the algorithms that identify real-time trends in data. ML models might generate data trends automatically, but MSPs still need to select the data sets that feed those models.
Even if automation takes over the responsibilities of a specific team member within an IT organization, executives can upskill or reskill that employee instead of replacing them. According to LogicMonitor’s Future of the MSP Industry Research Report, 95% of MSP leaders agree that automation is the key to helping businesses achieve strategic goals and innovation. By training employees who currently carry out manual tasks, executives can develop a stronger, higher-skilled workforce that still benefits from IT automation.
Future of IT automation
AI, machine learning, and cloud computing advancements are significantly altering how businesses manage their IT infrastructure. As these technologies continue to evolve, how you manage your business will change along with them.
Here’s what to expect in the future of IT automation:
Intelligent automation
Traditional automation tools use a rules-based approach: a certain event (e.g., time of day, hardware failure, log events) triggers an action through the automation systems.
Advanced AI operations tools are changing that with their ability to predict future events based on data. That leads to more intelligent automation that doesn’t require a rules-based system. These systems understand natural language, recognize patterns, and make decisions based on real-time data. They allow for more responsive IT systems that anticipate and fix problems.
Hybrid cloud automation
The growing adoption of cloud environments—which include private, public, and on-prem resources—requires your business to adopt new strategies to manage infrastructure and automate tasks. You need tools that seamlessly integrate with all environments to ensure performance and compliance where the data resides.
Hybrid environments also allow for more flexibility and scalability for IT infrastructure. Instead of being limited by physical constraints, your business can use the cloud to scale computing resources as much as needed. Automated provisioning and deployment means you can do this at scale with minimal IT resources.
Edge computing automation
As workforces and companies become more distributed, your business needs a way to provide resources to customers and employees in different regions. This may mean a web service for customers or a way for employees to access business services.
Edge devices can help supply resources. Automation will help your business manage edge devices, process data on the edge, and ensure you offer performant applications to customers and employees who need them.
Choosing the right IT automation platform
Successful data-driven IT teams require technology that scales as their business does, providing CIOs and executives with ongoing value. LogicMonitor is the world’s only cloud-based hybrid infrastructure monitoring platform that automates tasks for IT service companies like MSPs.
LogicMonitor features include:
- An all-in-one monitoring platform that revolutionizes digital transformation for MSPs and DevOps/ITOps teams worldwide.
- Complete 360-degree visibility of utilization, network performance, resource consumption, cloud instances, and much more.
- Full observability of technologies and resources such as servers, data centers, and cloud-based environments.
- The ability to identify problems with legacy tools before they happen.
- Real-time reports and forecasts that reduce internal costs, improve SLA outcomes, and power engineers and other IT professionals.
- No additional hardware maintenance or technical resources. LogicMonitor is ready out of the box.
Final Word
IT automation has revolutionized the IT sector, reducing the manual responsibilities that, for years, have plagued this industry. MSPs no longer need to enter network performance data into multiple systems, physically inspect servers, manage and provision networks manually, analyze performance reports, or perform other redundant tasks manually. Automation does a lot of the hard work so that these IT professionals can focus on far more critical tasks. By incorporating cloud-based infrastructure monitoring, AI, machine learning, and other new technologies, your IT executives improve productivity, enhance workflows, reduce IT resources, promote better client outcomes, and reduce costs over time.
NetApp, formerly Network Appliance Inc., is a computer technology company specializing in data storage and management software.
Known for its innovative approach to data solutions, NetApp provides comprehensive cloud data services to help businesses efficiently manage, secure, and access their data across diverse environments. Alongside data storage, NetApp offers advanced management solutions for applications, enabling organizations to streamline operations and enhance data-driven decision-making across hybrid and multi-cloud platforms.
What is NetApp?
NetApp is a computer technology company that provides on-premises storage, cloud services, and hybrid data services in the cloud. Its hardware includes storage systems for file, block, and object storage. It also integrates its services with public cloud providers. NetApp’s services offer solutions for data management, enterprise applications, cybersecurity, and supporting AI workloads. Some of its main products include different storage software and servers.
NetApp has developed various products and services, and according to Gartner, was ranked the number one storage company in 2019. The following includes detailed definitions of NetApp’s key terms and services.
Azure NetApp is a popular shared file-storage service used for migrating POSIX-compliant Linux and Windows applications, HPC infrastructure, databases, SAP HANA, and enterprise web applications.
Why choose NetApp?
NetApp provides organizations with advanced data storage and management solutions designed to support diverse IT environments, from on-premises to multi-cloud. For businesses looking to enhance their infrastructure, NetApp offers several key advantages:
- Cost efficiency: NetApp’s tools help optimize cloud expenses, enabling companies to manage data growth without excessive costs, while its efficient storage solutions reduce overall spending.
- Scalability: Built to grow with your business, NetApp’s services seamlessly scale across cloud, hybrid, and on-premises environments, making it easier to expand as data needs evolve.
- Enhanced security: NetApp prioritizes data protection with features designed to defend against cyber threats, ensuring high levels of security for critical information.
- Seamless cloud integration: With strong support for leading cloud providers like Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and AWS, NetApp simplifies hybrid cloud setups and provides smooth data migration across platforms.
Understanding the dos and don’ts of NetApp monitoring can help you maximize its benefits. By selecting NetApp, IT professionals and decision-makers can leverage streamlined data management, improved performance, and flexible integration options that fit their organization’s unique needs.
What are NetApp’s key services?
NetApp offers several important services and products to help customers meet their data storage and management goals.
Ansible
Ansible is a platform for automating networking, servers, and storage. This configuration management system enables arduous manual tasks to become repeatable and less susceptible to mistakes. The biggest selling points are that it’s easy to use, reliable, and provides strong security.
CVO
CVO (Cloud Volumes ONTAP) is a type of storage delivering data management for block and file workloads. This advanced storage allows you to make the most of your cloud expenses while improving application performance. It also helps with compliance and data protection.
Dynamic Disc Pool
Dynamic Disc Pool technology (DDP) addresses the problem of RAID rebuild times and the potential increase in disk failure and reduced performance this may cause. DDP delivers prime storage solutions while maintaining performance. The technology can rebuild up to four times more quickly while featuring exceptional data protection. DDP allows you to group similar disks in a pool topology with faster rebuilds than RAID 5 or 6.
For more on monitoring disk performance and latency in NetApp environments, explore how LogicMonitor visualizes these metrics to optimize storage efficiency.
FAS
FAS (Fabric Attached Storage) is a unified storage platform in the cloud. FAS is one of the company’s core products. NetApp currently has six models of storage to choose from, allowing users to select the best model that meets their organization’s storage needs. These products consist of storage controllers with shelves made of hard disk enclosures. In some entry-level products, the storage controller contains the actual drives.
Flexpod
Flexpod is a type of architecture for network, server, and storage components. The components of a Flexpod consist of three layers: computing, networking, and storage. Flexpod allows users to select specific components, making it ideal for almost any type of business. Whether you’re looking for rack components or optimizing for artificial intelligence, Flexpod can help you put together the architecture your organization needs.
FlexCache
FlexCache offers remote simplified file distribution. It can also improve WAN usage with lower bandwidth costs and latency. You can distribute through multiple sites. FlexCache provides a more significant storage system ROI, improves the ability to handle workload increases, and limits remote access latency. It’s also easier to scale out storage performance with read-heavy applications. ONTAP Select running on 9.5 versions or later, FAS, and AFF support FlexCache.
OnCommand (OCI)
An OnCommand Insight Server (OCI) provides access to storage information and receives updates involving environment changes from acquisition units. The updates pass through a secure channel and then go to storage in the database. OCI can simplify virtual environments and manage complex private cloud systems. OCI allows analysis and management across networks, servers, and storage in both virtual and physical environments. It specifically enables cross-domain management.
OnCommand has two different Acquisition units. These are the Local Acquisition Unit (LAU), which you can install along with the OnCommand Insight Server, and the Remote Acquisition Unit (RAU). This one is optional. You can install it on a single remote server or several servers.
ONTAP
This is the operating system for hybrid cloud enhancement that helps with staffing, data security, and promoting future growth. New features for ONTAP include greater protection from ransomware, simplification for configuring security profiles, and more flexibility for accessing storage.
StorageGRID
If your organization has large data sets to store, StorageGrid is a solution that can help you manage the data cost-efficiently. StorageGrid offers storage and management for large amounts of unstructured data. You can reduce costs and optimize workflows when you place content in the correct storage tier. Some of the reviews for NetApp StorageGRID state that three of its best features are its valuable backup features, easy deployment, and cost-effectiveness.
Snapshot
Snapshots are designed to help with data protection but can be used for other purposes. NetApp snapshots are for backup and restoring purposes. When you have a snapshot backup, you save a specific moment-in-time image of the Unified database files in case your data is lost or the system fails. The Snapshot backup is periodically written on an ONTAP cluster. This way, you’ll have an updated copy.
Solidfire
Solidfire is one of NetApp’s many acquisitions, as it took over the company in January 2016. Solidfire uses the Element operating system for its arrays. This NetApp product provides all-flash storage solutions. SolidFire is not as successful as other products at NetApp; ONTAP, in particular, overshadows SolidFire. Some industry professionals may question how long SolidFire will continue as a NetApp product. So far, SolidFire is still a private cloud hardware platform.
Trident
Trident is an open-source project that can meet your container application demands. It utilizes Kubernetes clusters as pods. This offers exceptional storage services and allows containerized apps to consume storage from different sources. Trident provides full support as an open-source project and uses industry-standard interfaces. These interfaces include the Container Storage Interface.
NetApp’s integration with public cloud platforms
NetApp’s solutions are designed to support organizations working across hybrid and multi-cloud environments, offering seamless compatibility with major cloud providers like GCP and AWS. NetApp’s tools, including CVO and StorageGRID, enable efficient data management, transfer, and protection, ensuring that businesses can maintain control of their data infrastructure across platforms.
- CVO: CVO offers data management across cloud environments by combining NetApp’s ONTAP capabilities with public cloud infrastructure. This solution allows organizations to optimize cloud storage costs and manage data protection, compliance, and performance. For example, a company using CVO with GCP can streamline its data backup processes, reducing both costs and latency by storing frequently accessed data close to applications.
- StorageGRID: Designed for storing large amounts of unstructured data, StorageGRID enables multi-cloud data management with the flexibility to tier data across cloud and on-premises environments. By supporting object storage and efficient data retrieval, StorageGRID allows businesses to manage compliance and access requirements for big data applications. A healthcare organization, for example, could use StorageGRID to store and retrieve extensive medical records across both private and public cloud environments, ensuring secure and compliant access to data when needed.
With NetApp’s hybrid and multi-cloud capabilities, businesses can reduce the complexity of managing data across cloud platforms, optimize storage expenses, and maintain compliance, all while ensuring data accessibility and security across environments.
What are NetApp’s key terms?
To understand how NetApp works, it’s necessary to know some of its terminology and product selections. The following are some basic terms and products with brief definitions.
Aggregate
An aggregate is a collection of physical disks you can organize and configure to support various performance and security needs. According to NetApp, if your environment contains certain configurations, you’ll need to create aggregates manually. A few of these configurations include flash pool aggregates and MetroCluster configurations.
Cluster MTU
This feature enables you to configure MTU size by using an ONTAP Select multi-node cluster. An MTU is the maximum transmission unit size that specifies the jumbo frame size on 10 Gigabit interfaces as well as 1 Gigabit Ethernet. Using the ifconfig command, you can select the particular MTU size for transmission between a client and storage.
FlexVol Volume
FlexVol volumes are a type of volume that generally connects to each of its containing aggregates. Several FlexVol volumes can receive their storage sources from a single aggregate. Since these volumes are separate from the aggregates, you can dynamically change the size of each FlexVol volume without a disruption in the environment.
Initiator
An initiator is a port for connecting with a LUN. You can select an iSCSI hardware or software adapter or an FC. The ONTAP System Manager enables you to manage initiator groups. If you want to control which LIFs each initiator has access to, you can do this with portsets.
IOPS
IOPS measures how many Input/Output operations per second occur. You would generally use IOPS to measure your storage performance in units of bytes for read or write operations. You’ll sometimes need different IOP limits in various operations that are in the same application.
License Manager
This software component is part of the Deploy administration utility. This is an API you can use to update an IP address when the IP address changes. To generate a file, you need to use the License Lock ID (LLID) and the capacity pool license serial number.
LUN
LUNs are block-based storage objects that you can format in various ways. They work through the FC or iSCSI protocol. ONTAP System Manager is able to help you create LUNS if there is available free space. There are many ways you can use LUNs; for example, you might develop a LUN for a QTree, volume, or aggregate that you already have.
Multiple Cluster Systems
If you need an at-scale system for a growing organization, you’ll want to consider NetApp systems that have multiple clusters. A cluster consists of grouped nodes to create scalable clusters. This is done primarily to use the nodes more effectively and distribute the workload throughout the cluster. An advantage of having clusters is to provide continuous service for users even if an individual node goes offline.
ONTAP Select Cluster
You can create clusters with one, two, four, six, or even eight nodes. A cluster with only one node doesn’t produce any HA capability. Clusters with more than one node, however, will have at least one HA pair.
ONTAP Select Deploy
You can use this administration utility to deploy ONTAP Select clusters. The web user interface provides access to the Deploy utility. The REST API and CLI management shell also provide access.
Qtrees
Qtrees are file systems that are often subdirectories of a primary directory. You might want to use qtrees if you’re managing or configuring quotas. You can create them within volumes when you need smaller segments of each volume. Developing as many as 4,995 qtrees in each internal volume is possible. Internal volumes and qtrees have many similarities. Primary differences include that qtrees can’t support space guarantees or space reservations. Individual qtrees also can’t enable or disable snapshot copies. Clients will see the qtree as a directory when they access that particular volume.
Snapshot Copy
Snapshot copy is a read-only image that captures a moment-in-time of storage system volume. The technology behind ONTAP Snapshot enables the image to take up a minimum of storage space. Instead of copying data blocks, ONTAP creates Snapshot copies by referencing metadata. You can recover LUNS, contents of a volume, or individual files with a Snapshot copy.
SnapMirror
This replication software runs as a part of the Data ONTAP system. SnapMirror can replicate data from a qtree or a source volume. It’s essential to establish a connection between the source and the destination before copying data with SnapMirror. After creating a snapshot copy and copying it to the destination, the result is a read-only qtree or volume containing the same information as the source when it was last updated.
You will want to use SnapMirror in asynchronous, synchronous, or semi-synchronous mode. If at the qtree level, SnapMirror runs only in asynchronous mode. Before setting up a SnapMirror operation, you need a separate license and must enable the correct license on the destination and source systems.
Storage Pools
Storage pools are data containers with the ability to hide physical storage. Storage pools increase overall storage efficiency. The benefit is that you may need to buy fewer disks. The drawback is disk failure can have a ripple effect when several are members of the same storage pool.
System Manager
If you’re just beginning to use NetApp and need a basic, browser-based interface, you may want to consider the OnCommand System Manager. System Manager includes detailed tables, graphs, and charts for tracking past and current performance.
Discover the power of NetApp with LogicMonitor
NetApp provides valuable data and storage services to help your organization access and manage data throughout multi-cloud environments more efficiently. With various products and services, NetApp enables you to put together the data management and storage solutions that meet your organization’s needs.
As a trusted NetApp technology partner, LogicMonitor brings automated, insightful monitoring to your NetApp environment. Transition seamlessly from manual tracking to advanced automated monitoring and gain access to essential metrics like CPU usage, disk activity, and latency analysis—all without configuration work.
With LogicMonitor’s platform, your team can focus on strategic goals, while LogicMonitor ensures efficient and precise monitoring across your NetApp systems, including ONTAP.
HAProxy (High Availability Proxy) is free, open-source software that acts as a load balancer and proxy for managing TCP and HTTP traffic, ensuring reliable performance and high availability. Known for its speed and efficiency, HAProxy provides high availability by distributing incoming web traffic across multiple servers, preventing overloads at startup, and improving overall reliability.
The tool’s popularity has grown among developers and network engineers due to the volume of features available, which help reduce downtime and manage web traffic. This article discusses those features, as well as uses, load-balancing techniques, and key features of 2.7.0, the latest version of HAProxy.
HAProxy includes reverse proxy and load-balancing capabilities for HTTP-based applications and TCP-based applications. Load balancing involves routing traffic to servers based on pre-configured rules, such as looking for high-performance servers with the least amount of traffic or telling proxies to send connections to multiple servers.
Why use HAProxy?
HAProxy also provides SSL termination, health checks, and detailed logging capabilities, along with its load-balancing features. This open-source software is ideal for websites and web applications that experience high volumes of traffic or traffic that spikes on occasion.
As such, many large organizations prefer HAProxy for its efficiency, scalability, and strong supportive community. It simplifies the management experience and reduces downtime by persistently load-balancing heavy traffic, which increases availability for applications and network layers, improving the user experience.
Top reasons to use HAProxy
- Scalability: Handles increased traffic without compromising performance
- Reliability: Trusted by organizations like JPMorgan Chase & Co. and Boeing, the largest aerospace company in the world (HG Insights)
How does HAProxy work?
HAProxy can be installed free using a system’s package manager or as a Docker container.
- Frontend and backend setup: Configure HAProxy by defining the front end (receiving traffic) and backend (managing servers). You can set rules to direct traffic to specific servers based on IP addresses, ports, or HTTP load-balancing algorithms.
- Traffic management: Intelligently routes traffic based on configurations, ensuring optimal server usage and reliability.
HAProxy One offers a range of tools and platforms that enhance the benefits of HAProxy’s free proxy and load-balancing software.
Load balancing techniques
Load balancing in a web application environment depends on the type of load balancing used.
- Web server load balancing (layer 4): The simplest load balancing solution for multiple web servers is layer 4, or transport layer, load balancing. This setup uses a load balancer, a predefined range of IP addresses, and a port to determine where to route traffic, allowing multiple servers to respond to user requests efficiently.
- Application server load balancing (layer 7): Layer 7 load balancing routes requests to different backend servers, depending on requests, and requires more complex rules to connect user requests to the correct backend servers. For example, you might house blog articles on one server while you host an e-shop page on another. So, a request for a blog article will be routed through a different server than a request for an e-shop product, even though the requests are generated from the same website.
- Reverse proxy: Reverse proxies sit between applications and backends to ensure user requests reach appropriate servers. They also provide security, reliability improvements, and traffic management.
Key features of HAProxy
Due to its extensive features, HAProxy is preferred over alternative proxies like NGINX and LoadMaster.
- HTTP/2 protocol support: Enhances web performance
- SSL/TLS termination: Improves security by managing encryption and decryption
- Detailed logs: Offers comprehensive logs for monitoring and observability
- RDP cookie support: Supports secure, reliable sessions
- CLI for management: Provides in-depth server management capabilities
Implementing HAProxy: A step-by-step guide
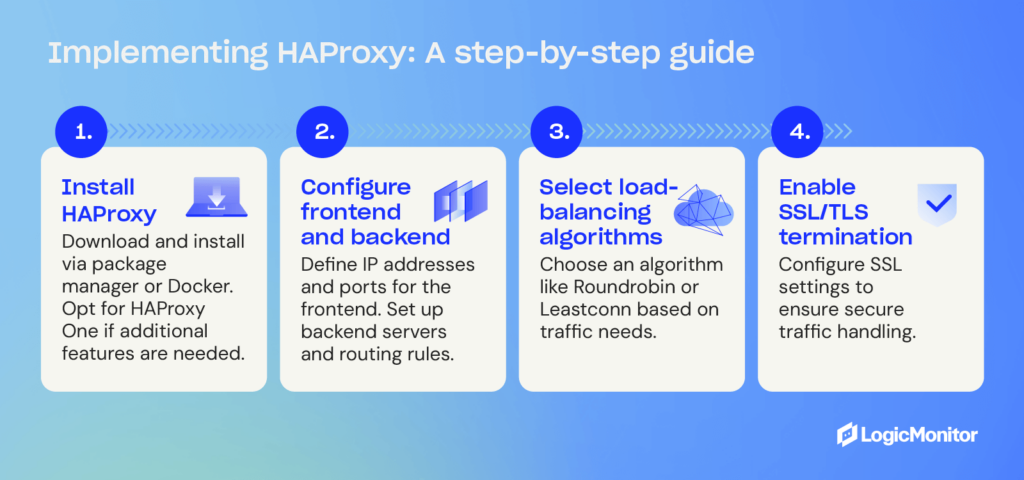
Step 1: Install HAProxy
- Download and install via package manager or Docker.
- Opt for the HAProxy One version if additional features are needed.
Step 2: Configure the frontend and backend
- Define the IP addresses and ports for the frontend.
- Set up the backend servers and the rules for routing traffic.
Step 3: Select load-balancing algorithms
- Based on traffic needs, choose an algorithm like Roundrobin or Leastconn. Roundrobin is the default load-balancing algorithm that selects servers in a specific order, and Leastconn is an alternative algorithm that searches for servers with the fewest connections.
Step 4: Enable SSL/TLS termination
- Configure SSL settings to ensure secure traffic handling.
HAProxy vs. other solutions
When evaluating load balancers and proxy solutions, it is important to choose one that best fits the specific infrastructure needs. HAProxy, NGINX, and LoadMaster are among the top contenders, each offering distinct features that cater to different operational demands.
HAProxy vs. NGINX
Both HAProxy and NGINX are popular choices for managing web traffic, but they excel in different areas.
- Performance: HAProxy is optimized for low-latency environments, making it ideal for applications that require real-time responsiveness and high availability. In contrast, NGINX is better suited for caching and delivering static content, offering a simpler solution for web applications that prioritize speed over complexity.
- Logging: One of HAProxy’s major advantages is its detailed logging capabilities. For environments that require deep traffic analysis and precise monitoring, HAProxy provides comprehensive logs that track each request and connection. NGINX, while effective, offers more basic logging, which may not be sufficient for enterprises needing extensive traffic visibility.
- Configuration complexity: HAProxy offers more advanced configuration options, allowing users to customize traffic routing based on a wide range of conditions. This flexibility comes with increased complexity, making it a better fit for organizations with dedicated DevOps teams or advanced networking needs. On the other hand, NGINX provides a simpler, more beginner-friendly configuration process, making it an appealing choice for smaller projects or businesses with less demanding requirements.
HAProxy vs. LoadMaster
The distinction between HAProxy and LoadMaster is open-source flexibility and proprietary convenience.
- Flexibility: As an open-source solution, HAProxy allows full customization, enabling businesses to tailor the tool to their specific needs without paying for additional features or upgrades. This makes HAProxy particularly attractive to organizations that want to maintain control over their infrastructure. In contrast, LoadMaster, a proprietary tool, provides pre-configured solutions that are easier to deploy but may lack the flexibility needed for more complex environments.
- Cost-Effectiveness: HAProxy’s open-source nature means it can be implemented at no cost, regardless of the scale of operations. For businesses that need to manage large volumes of traffic without the burden of licensing fees, HAProxy presents a cost-effective solution. LoadMaster, however, is a paid option that includes professional support and additional features. While this may benefit enterprises that prioritize customer support and streamlined implementation, it can become costly, especially as traffic demands grow.
Real-world use cases
The power of HAProxy is demonstrated by organizations like GitHub, which rely on it to manage millions of concurrent connections efficiently. In these large-scale environments, HAProxy’s ability to handle complex configurations and provide real-time performance metrics far surpasses the capabilities of NGINX and LoadMaster without significant customization.
Which to choose?
Ultimately, HAProxy stands out as the optimal choice for organizations looking for maximum flexibility, scalability, and a robust feature set to manage high volumes of traffic. For environments with static content or simpler traffic needs, NGINX may be a more suitable option. LoadMaster offers a more simplified, pre-configured solution but may be costly, particularly for enterprises looking to scale.
Community support and resources
HAProxy’s community support and resources are vast, offering many user options, from official documentation to active community forums. With a HAProxy One subscription, users can benefit from expanded paid support options.
HAProxy supports users of current and latest versions and assists in critical fixes on any version. Documentation, including configuration tutorials and detailed manuals, is available on the HAProxy website, and the HAProxy blog offers helpful articles that you can filter according to specific inquiries. Current HAProxy One subscribers can contact support through the HAProxy Portal, providing convenient access to assistance.
Conclusion
HAProxy is a powerful, scalable solution for managing heavy or unpredictable web traffic. As a free, open-source tool, it provides smaller organizations the same reliability and performance enjoyed by large enterprises like JPMorgan Chase & Co. and Boeing. Implementing HAProxy is a strategic move for any business looking to enhance its web infrastructure’s reliability and performance.
VMware NSX is a comprehensive virtual networking and security platform that transforms how organizations manage and secure digital infrastructure by providing advanced network virtualization and security services. VMware NSX offers scalability and flexibility that meet the demands of growing businesses.
Plus, it helps bolster software-defined data center capabilities. This detailed overview covers core components, features, benefits, and real-world applications of VMware NSX, the comprehensive virtual networking and security platform built from VMware’s vCloud Networking and Security and Nicira’s Network Virtualization Platform.
What is network virtualization?
Network virtualization creates a layer between physical hardware and applications and services that rely on it. This layer allows third-party vendors like VMware to deliver networking hardware and software virtually, which means physical infrastructures are not needed to control network traffic. Decoupling software-defined networking operations from hardware offers numerous benefits, including eliminating the need for on-premises hardware and reducing costs associated with maintaining routers, switches, and physical equipment.
How VMware NSX works
VMware NSX achieves complete network virtualization by utilizing network automation and encapsulation. This process involves wrapping network traffic within protocols that traditional physical networking hardware supports, such as Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE). It then divides physical networks into separate and independent virtual networks, eliminating the need for expensive in-house equipment while allowing the use of physical networking hardware through gateways that connect to VMware NSX’s virtual network. At the heart of VMware NSX is the NSX networking data center, which virtualizes various networking elements such as firewalls, VPNs, and load balancing.
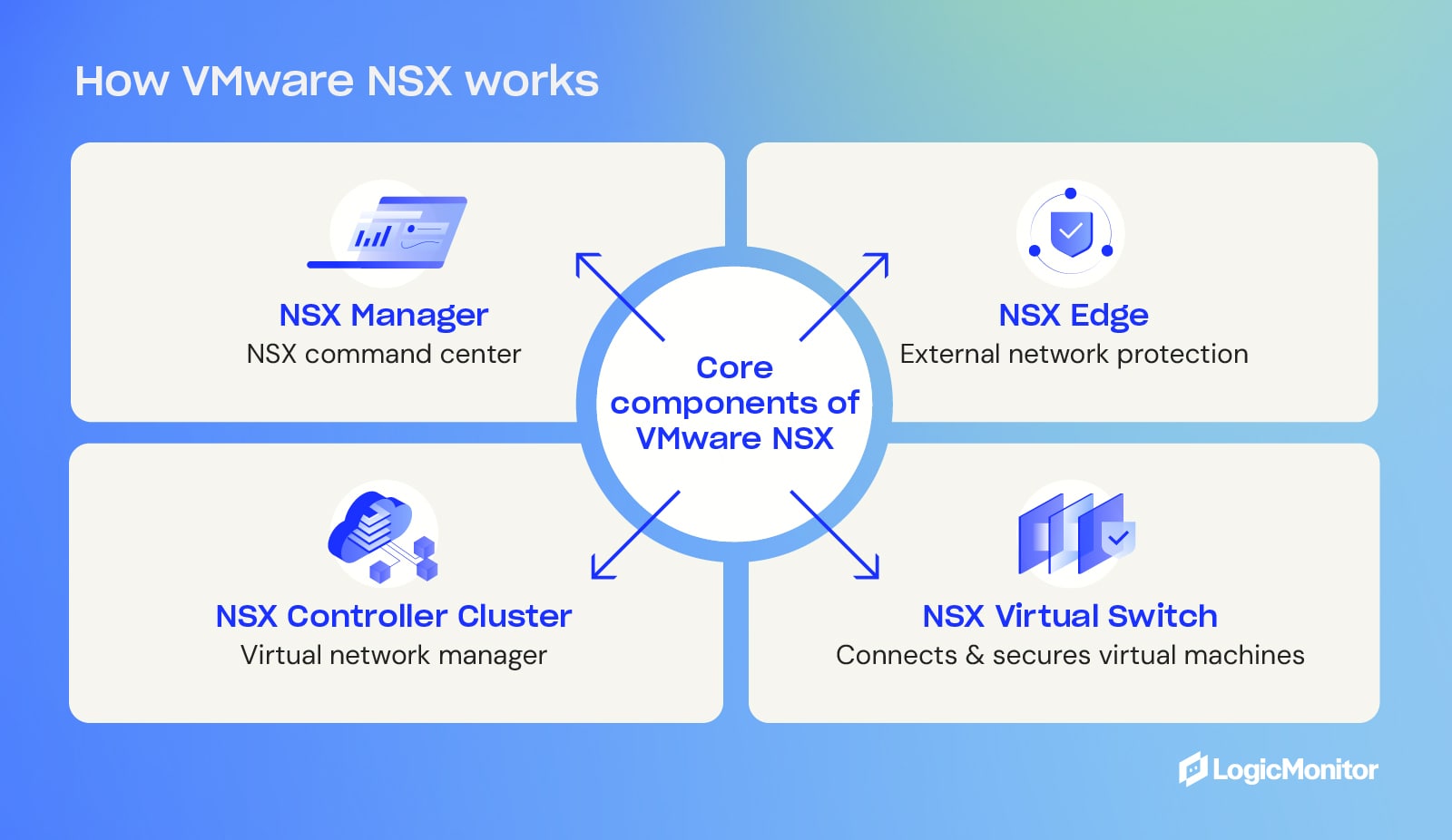
Core components of VMware NSX
VMware NSX includes several key components that facilitate network virtualization:
- NSX Manager: This is the command center for the NSX platform, providing centralized control and monitoring using a web-based user interface and virtualization management.
- NSX Controller Cluster: Helps manage and control virtual networks by mediating the interaction between monitoring, communication, and traffic control.
- NSX Virtual Switch: Connects and manages virtual machines within a server, ensuring communication and security.
- NSX Edge: This service serves as firewall management and gateway-access security, combining an edge services gateway, and distributed logical router with the ability to assign IP addresses and use network address translation (NAT) to hide addresses from external networks.
Features of VMware NSX
VMware NSX offers an array of features that enhance networking capabilities:
- Logical switching and distributed routing: Provides logical switching capabilities with L2 logical networks that isolate workloads across multiple virtual networks and distributed routing through a distributed logical router (DLR) that connects interfaces with hosts when VM connectivity is required; virtual distributed switches utilize VXLAN technology to transit ESXi hosts in a cluster over an L3 fabric.
- Load balancing: Distributes incoming network traffic across different backend servers to help manage heavy traffic loads and ensure smooth network performance.
- VPN and distributed firewall: Provides L2 and L3 VPN solutions to create tunnels between pairs of NSX Edge devices in isolated data centers and securely connect to remote data center networks.
- Network function virtualization: Replaces network hardware with virtual machines, allowing virtual networks to operate on standard servers via hypervisors, providing a more cost-effective approach compared to investing in hardware devices.
Benefits of integrating VMware NSX
VMware NSX seamlessly integrates with numerous third-party companies, expanding its functionality and compatibility. A few notable integration partners include Arista Networks, Dell EMC Open Networking, and Juniper Networks. Integrating VMware NSX into a tech stack offers several benefits, including the following:
Enhanced network security
VMware NSX provides robust network security features, such as IDS/IPS, NTA/NDR, and sandboxing, to protect against ransomware and other malicious threats. The platform ensures consistent networking by synchronizing configuration and operational state across all sites. In addition, NSX offers micro-segmentation, allowing the division of data centers into different segments for enhanced security policies and control during data center virtualization.
Scalability and flexibility
VMware NSX allows the scaling of network designs to accommodate increasing workloads in businesses. The platform’s virtual private cloud (VPC) enables scalable NSX security and networking services while also providing flexibility to implement isolation as needed.
Streamlined data center design
With VMware NSX, data centers are no longer limited by physical equipment. They can be customized and optimized in a cloud network based on specific business requirements. Additionally, NSX offers various use cases for multi-cloud environments, including data center extension and multi-data center pooling.
Improved speed and agility
VMware NSX automates the deployment of network resources, reducing the time required to set up networking infrastructure in a virtual environment. The platform allows virtual network deployment across public clouds and private clouds, data centers, physical servers, and container platforms, enhancing the agility of network resources.
In addition to these essential components VMware NSX provides, it offers a wide array of features that simplify networking and enhance overall performance.
Real-world applications of VMware NSX
Various industries use VMware NSX to enhance network infrastructure:
- Media and Entertainment: NSX ensures high performance and security for media streaming and content delivery. Its robust features allow it to manage traffic even as viewership spikes, making it an ideal solution for large-scale streaming operations.
- Financial Services: VMware NSX provides a secure and scalable network infrastructure for financial transactions and data management. Services across the financial sector utilize NSX technology to create infrastructures that maintain compliance while quickly adapting to ever-changing markets. Financial institutions like Deutsche Bank rely on its performance for rapid scaling and easy integration.
- Healthcare: VMware NSX enables the secure and efficient handling of sensitive patient data and medical applications. Prominent electronic medical record (EMR) companies like Epic rely on its performance and security.
Is VMware NSX worth investing in?
As a trusted leader in virtualization solutions, VMware offers a highly effective product with VMware NSX. The platform provides features like load balancing, logical switching, distributed routing, and network function virtualization. By integrating VMware NSX into tech stacks, organizations can enhance network security, scalability, and streamline data center design.
Get detailed information on how to maximize VMware NSX investments at VMware Integration.
Transform your IT infrastructure today
Check out LogicMonitor’s detailed guides and resources to learn more about network virtualization and the benefits of VMware NSX. Get insights from the 2023 G2 Network Monitoring Grid Report.
Building upon momentum from the first half of the year, LogicMonitor maintains several Leader rankings across G2 Fall 2023 Reports, including Grid Reports, across multiple categories. Released on September 12, 2023, G2’s Fall 2023 Reports award badges and recognition based on responses of real users featured in the G2 review form.
Excelling in categories like Cloud Infrastructure Monitoring, Network Monitoring, Log Analysis & Monitoring, and Enterprise Monitoring, LogicMonitor has proven to be a trusted partner to customers through core capabilities like ease of use, automation, and enhanced visibility into hybrid environments.
Thanks to almost 500 real customer reviews with an overall 4.5 star rating, LogicMonitor was able to both maintain and gain new Leader badges across multiple categories in the most recent reports.
Take a look inside the G2 Fall 2023 Enterprise Monitoring Report highlights below to see where LogicMonitor stood out among the rest:
Enterprise Monitoring
For G2’s Fall 2023 reports, LogicMonitor maintained a Leader status on both the Momentum Grid® and Grid® reports. To be included in the Leader quadrant, vendors are ranked by customer satisfaction and market presence. Real user reviews ranked LogicMonitor favorably across multiple capabilities when it comes to monitoring activity and performance of multiple IT systems, including real-time analytics, intelligent alerting to prevent potential outages and failures, and enhanced reporting capabilities.
LogicMonitor stands out from the rest by providing single pane visibility into complex enterprise environments, including networks, cloud, containers, servers, and more. Enterprise users also have access to LogicMonitor’s AIOps capabilities to prevent system outages and optimize overall service delivery.

Learn more about how LogicMonitor stacks up against competitors, like DataDog, when it comes to observability, time to value, scalability, and billing here.
LogicMonitor received higher than average Satisfaction scores and user adoption versus other vendors mentioned in G2’s Fall 2023 Enterprise Monitoring Report, with 98% of users providing a rating of 4 or 5 stars, 94% of users believing LogicMonitor is headed in the right direction, and 91% of users saying they’d be likely to recommend LogicMonitor.


Enterprises have continued to say yes to LogicMonitor to go beyond traditional uptime monitoring and reduce risk, increase efficiency and drive growth. By partnering with LogicMonitor, customers have been able to diminish noisy alerts with dynamic thresholds, illuminate patterns with rich visualizations and topology, and reduce mean time to resolution (MTTR) with root cause analysis.
Learn more about ways to reduce MTTR with LogicMonitor in our on-demand webinar, where the LogicMonitor team discusses common IT challenges that impact time to resolution and how the right monitoring platform can solve these challenges.
Hear more directly from our customers:
| “It helped me to monitor servers, networks, storage and applications in my infrastructure. As a result, I was able to find and fix problems before they caused service interruptions. The support has been fantastic, and the goal of producing a lot of results has succeeded. It’s fantastic and has served its strategic purpose admirably.” – Vira K. Computer Software |
| “We were able to get monitoring up and running quickly because of LogicMonitor’s easy configuration and deployment. Adoption can be accelerated and operational efficiency improved thanks to the easy-to-use, well-organized interface that simplifies browsing and configuration of individualized alerts, reports and dashboards.” – Jacob A. Software Engineer |
| “The amount of monitoring capabilities and the web portal functionality/uptime is exceptional. We have been using LM on a global scale utilizing VM collectors and have not had one portal outage. The scale of our environment is ~2500 devices that we monitor and the portal performance and load times are exceptional.” – Logan G. Enterprise |
| “LogicMonitor provides rich data visualization options, including charts, graphs, and customizable dashboards. These visualizations help you understand complex data at a glance, identify trends, and gain actionable insights. LogicMonitor also offers reporting features that allow you to generate and schedule reports for various stakeholders, helping you track key performance metrics and demonstrate compliance.” – Evangelos C. IT Operations |
Explore all of G2’s Fall 2023 reports by logging into my.G2.com – and learn more about LogicMonitor’s platform for hybrid observability, LM Envision, here.
LogicMonitor would like to extend a huge thank you to their innovative and incredible customers for your time and honest feedback that helps the team work better to serve you.
Learn more about what real users have to say (or leave your own review) on G2’s LogicMonitor review page!
G2’s Spring 2023 Reports were announced March 30, 2023, with LogicMonitor grabbing several number-one spots and Leader rankings. This recognition is based on the responses of real users featured in the G2 review form.
“Rankings on G2 reports are based on data provided to us by real software buyers,” said Sara Rossio, Chief Product Officer at G2. “Potential buyers know they can trust these insights when researching and selecting software because they’re rooted in vetted, verified, and authentic reviews.”
Our customers have shared their honest feedback about features, capabilities, and implementation, with consistent praise of LogicMonitor’s ease of use, automation, and single pane of glass visibility into hybrid environments. Thanks to our customer reviews, LogicMonitor was able to both maintain and gain new Leader badges.
Take a look inside the G2 Spring 2023 report highlights below to see how LogicMonitor stacked up:
Overall Cloud Infrastructure Monitoring Leader: Relationship Index
The Relationship Index is based on ratings by business professionals, and products are required to receive 10 or more reviews and five responses for each of the relationship-related questions to qualify.
This quarter, LogicMonitor was ranked #1 in the Relationship Index for Cloud Infrastructure Monitoring, where elements such as the ease of doing business, quality of support, and how likely a customer is to recommend LogicMonitor come into play.
| “The main area that I would like to recommend would be the discovery and implementation. The system was well designed around our needs and requirements and the help received from the team to get the system fully live was outstanding.” – Verified User, Telecommunications |
Overall Cloud Infrastructure Monitoring Leader: Momentum Grid
A product’s Momentum score is calculated by a proprietary algorithm that factors in social, web, employee, and review data that G2 has deemed influential in a company’s momentum, in addition to a minimum of 10 reviews and a year of G2 data to be included in this report.
LogicMonitor maintained the #1 Leader spot for the Overall Momentum Grid Report for Cloud Infrastructure Monitoring, with above average Satisfaction Ratings. These ratings include:
- 91% of reviewers are likely to recommend LogicMonitor
- 92% of reviewers agree that the product is going in the right direction
- 92% agree that it meets their requirements
Check out more about LogicMonitor’s Cloud monitoring solutions here.
| “The intuitive consistent UI makes the app simple to use. Monitoring for on-premise and cloud infrastructure can be deployed in minutes. Having tried a big number of infrastructure monitoring products, LogicMonitor was a breath of fresh air – simple and quick.” – Dave S. IT Manager |
Overall Leader for Enterprise Monitoring: Grid Report
Products are ranked by customer satisfaction (based on user reviews) and market presence (based on market share, seller size, and social impact) and placed into four categories on the Grid.
LogicMonitor maintained a Market Leader position at #2 in the Overall Grid Report for Enterprise Monitoring, in addition to remaining in the #1 Leader spot for the Overall Relationship Index Report for Enterprise Monitoring. New to G2’s Spring 2023 Results Index for Enterprise Monitoring, LogicMonitor gained momentum and moved up to #2 in this category.
| “LogicMonitor has allowed us to monitor our Enterprise in a way not possible before.” – Adam M. Systems Architect |
Overall Leader for Network Monitoring: Best Relationship and Usability
LogicMonitor performed well in the Mid-Market Grid Report for Network Monitoring, similar to the Grid Report for Enterprise Monitoring, and remained in the #1 Leader position. LogicMonitor also maintained Best Relationship and Best Usability Badges, combined with #1 Leader spots for both Mid-Market Relationship Index and Enterprise Usability Index for Network Monitoring.
| “If you need a solution that can monitor your infrastructure from anywhere, has 24/7 online support, is highly compatible with most (if not, all) hardware, is cost-effective and easy to deploy and manage….then LOGICMONITOR is the ONE.” – David S. Infrastructure Specialist |
Learn more about LogicMonitor’s Infrastructure monitoring capabilities, including the LM Envision platform, here.
LogicMonitor would like to extend a huge thank you to their innovative and incredible customers for your time and honest feedback that helps the team work better to serve you.
Learn more about what real users have to say (or leave your own review) on G2’s LogicMonitor review page!
Data hygiene is a critical but often overlooked concept for businesses of all sizes. Think of any activity that involves the use and storage of data, like customer relationship management (CRM), marketing automation, customer service, or analytics; then add in trends like increasing regulations and customer expectations around privacy. Data hygiene needs to be on the top of your list when you’re managing customer relationships across multiple channels.
Here we’ll cover what data hygiene is, why it’s important, and how the principles behind data hygiene impact customer trustworthiness, leadership development strategies in your company culture, as well as safeguarding proprietary rights to your business’ unique digital assets.
What is data hygiene?
Data hygiene is the practice of keeping a database clean and accurate by taking steps to ensure its integrity. It involves regular cleaning, validating, and updating data to make sure that it is accurate, up-to-date, complete, consistent, and reliable. This helps organizations avoid costly errors such as incorrect information on customer records or inaccurate segmentation of target audiences.
Data hygiene is a critical part of any data management strategy and should be conducted regularly as your data accumulates in databases over time. To do this, organizations must ensure that their database systems contain the most up-to-date information. This includes removing incorrect or outdated records, performing deduplication processes to eliminate duplicate records, implementing address standardization to ensure consistent formats across different sources, and validating data against established quality rules.
Organizations can also use data profiling techniques to uncover potential issues with their data before attempting any type of cleanup. Data profiling provides an initial analysis of existing datasets so that organizations can understand the structure and content of their datasets before taking more specific steps toward improving their quality.
Data hygiene is also important for organizations when it comes to complying with data privacy regulations and laws, especially those related to consumer data protection. It’s essential to keep customer records accurate and up-to-date so organizations can ensure that the data shared with third parties is secure, valid, and compliant with the relevant legislation. Furthermore, it helps organizations protect themselves from malicious activities like identity theft or fraud.
Finally, data hygiene helps organizations leverage their customer data more effectively by enabling them to better divide customers into meaningful segments for marketing campaigns and other insights-driven initiatives. By having a well-regulated database that contains clean and reliable information about customers and prospects, marketers can gain a deeper understanding of their target audiences and create highly personalized campaigns that are more likely to resonate with customers.
Why is data hygiene important?
Data hygiene is an integral part of data management, and it is becoming increasingly important as organizations collect, store, and use more data than ever before. The main goal of data hygiene is to ensure that all relevant datasets are accurate and consistent across all systems. Without proper data hygiene processes in place, organizations run the risk of making decisions based on inaccurate or outdated information, which can be costly and damaging to the business. A good data hygiene plan should enable organizations to identify, analyze, and resolve any issues with their data quickly and effectively.
Data hygiene is essential for businesses looking to gain a competitive edge in today’s market. Poorly maintained databases can lead to inaccurate customer segmentation, incorrect reporting, faulty marketing campaigns, and ultimately lost customers or revenue. On the other hand, having clean data helps businesses obtain valuable insights into customer behaviors which they can use to deliver better products and services as well as more effective marketing strategies. Clean data also makes it easier for businesses to comply with privacy regulations such as the GDPR or CCPA by ensuring all personal information is stored securely and used appropriately.
Benefits of data hygiene
The benefits of engaging in proper data hygiene can be seen across many business functions.
- When it comes to customer relationships, maintaining clean data is essential for providing accurate responses when customers contact organizations with questions or requests. By having access to up-to-date information, including contact details and purchase history, companies are able to respond quickly and accurately – a key component in providing top-notch customer service. Good customer engagement also depends on data accuracy, and when customer data is incorrect or out-of-date, it can lead to frustrated customers who may turn away from your business for a competitor.
- When marketing campaigns are based on inaccurate or incomplete data, the results can be costly. Messages that are sent to an outdated list of contacts will not only fail to generate new leads, but they can damage brand reputation. Some companies have been known to send out inappropriate messages due to incorrect contact information – creating ill will with potential customers. On the flip side, having clean data helps ensure targeted emails reach the right people, who are more likely to become customers.
- In addition to helping businesses increase customer loyalty and satisfaction, clean databases also help them reduce costs associated with data management. When data is inaccurate or incomplete, organizations often spend more time and money to update it, resulting in lost productivity and higher overhead costs.
Data hygiene best practices
Data hygiene best practices are essential for any organization that collects and stores large amounts of data. It is paramount to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of the data in order to maximize its usefulness. Therefore, it is crucial to audit, automate and update your data at regular intervals.
Audit
Before making changes to your database or adding new records, it is important to conduct a thorough audit of all existing records. This allows you to identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies that may exist. It is also important to use appropriate methods when validating your database, such as cross-referencing with other sources or using automated tools which can flag inaccuracies quickly and accurately.
Automate
Automating certain tasks associated with data hygiene can help save you time and money while also ensuring accuracy. For example, automating processes such as data entry, data extraction, backup creation, and report generation can all help to streamline tasks and reduce the risk of human error.
Update
It is important to regularly update your database with new records or edits that have been made. As changes in the marketplace occur, so do the needs of customers; having an up-to-date database will ensure that your contact information remains accurate and relevant. Additionally, make sure to always back up your database before making any major changes or updates so that if anything goes wrong, you have a copy of what was previously there.
By utilizing these best practices for data hygiene, you can ensure the accuracy and efficiency of your data and maximize its value. Regularly auditing, automating, and updating your database will help to keep it accurate, compliant, and secure while also providing valuable insights into your customers’ needs.
Data hygiene vs. data quality
Data hygiene and data quality are both important components of any business’s successful data management strategy, but there is a distinct difference between them. Data hygiene is the process of ensuring that all data within an organization is clean and accurate by removing incorrect or incomplete records and fixing errors. Examples of such activities may include eliminating duplicates, correcting misspellings, completing missing fields, matching records across multiple databases, and formatting data consistently. Data quality, on the other hand, focuses more heavily on evaluating information to make sure it meets certain standards. This involves assessing things like completeness, accuracy, relevancy, and timeliness. It also entails testing for issues, such as errors in calculations or inconsistencies in formatting. The end goal here is to verify that the data is usable and valuable.
Data hygiene and quality efforts both ensure that an organization’s information is accurate, up-to-date, and meets certain standards. However, there are a few key differences between these two activities. Data hygiene is more focused on fixing errors in the data itself – or cleaning it up – while data quality involves evaluating the data to ensure it adheres to specific criteria and standards. Additionally, data hygiene attempts to ensure accuracy through manual processes such as eliminating duplicates or correcting misspellings. In contrast, data quality focuses more heavily on automated tests for integrity issues such as calculation errors or inconsistencies in formatting.
Given their distinct roles within a successful data management strategy, it is important for organizations to understand the difference between data hygiene and data quality. Companies should invest in both data hygiene and data quality solutions to ensure their data is up-to-date and reliable, leading to better decision-making, improved customer experiences, and increased operational efficiency.
Data hygiene vs. data integrity
Data hygiene vs. data integrity is another important distinction when it comes to managing data. Data integrity goes beyond data quality, which merely requires that data is reliable and accurate. Data integrity actually encompasses data quality. To ensure data integrity, it is important for organizations to have secure access control measures in place to prevent unauthorized access and manipulation of the data. This includes user authentication checks, encryption of sensitive information, regular backups of the database, and detailed audit trails to track user changes. Additionally, it is important to have a comprehensive set of rules and procedures that govern how user actions should be handled when dealing with the dataset. This ensures that any discrepancies or inconsistencies within the database can be quickly identified and addressed.
Ultimately, data hygiene and data integrity are two important aspects of data management that need to work together to ensure the accuracy and reliability of an organization’s data. While data hygiene focuses on improving the quality of data inputs, data integrity works to safeguard the integrity of those inputs and prevent unauthorized access or manipulation. By ensuring both processes are regularly implemented and maintained across an organization’s systems, businesses can trust their data to be reliable and accurate at all times.
Conclusion
Data hygiene is critical for businesses because it helps ensure that data is clean, accurate, and consistent. This can in turn help improve business efficiency and decision-making, as well as customer satisfaction. Implementing data audits, automation, and update processes are key to maintaining good data hygiene. It’s also important to understand the difference between data quality and integrity when managing your company’s data.
By following best practices for data hygiene, you can help your business run more smoothly and avoid potential issues down the road.
One of the improvements our new proprietary Time Series Database allows for is better visualization of long term data trends – a crucial component of proper enterprise monitoring.
When you’re viewing the trend of data for a long period of time (say a week or more) the system has to deal with how to present a lot of data. If you’re storing data every minute, then even a week’s worth of data is over 10,000 datapoints – way more points than can be shown even on a retina display. The situation becomes worse if you’re looking at a month or a year’s worth of data.
In the past, we condensed data in the same manner used by all Round Robin Database (RRD)-based systems out there. This is done by calculating the average of all values for a time period and using that as the display point. For example, if we want to show a graph of a week’s worth of data, and we have decided to show 500 pixels on this graph, then each pixel is going to represent just over 20 datapoints. So for each 20 minute period, we’d get all the datapoints, average them, and use that as the value to plot for that pixel. (RRD aggregation doesn’t quite work that way – it’s more like an average of averages – but this is close enough.)
This works well to condense a lot of data, but loses a lot of meaning and significance in the process.
For example, look at this one-day graph of one of our switch interfaces:
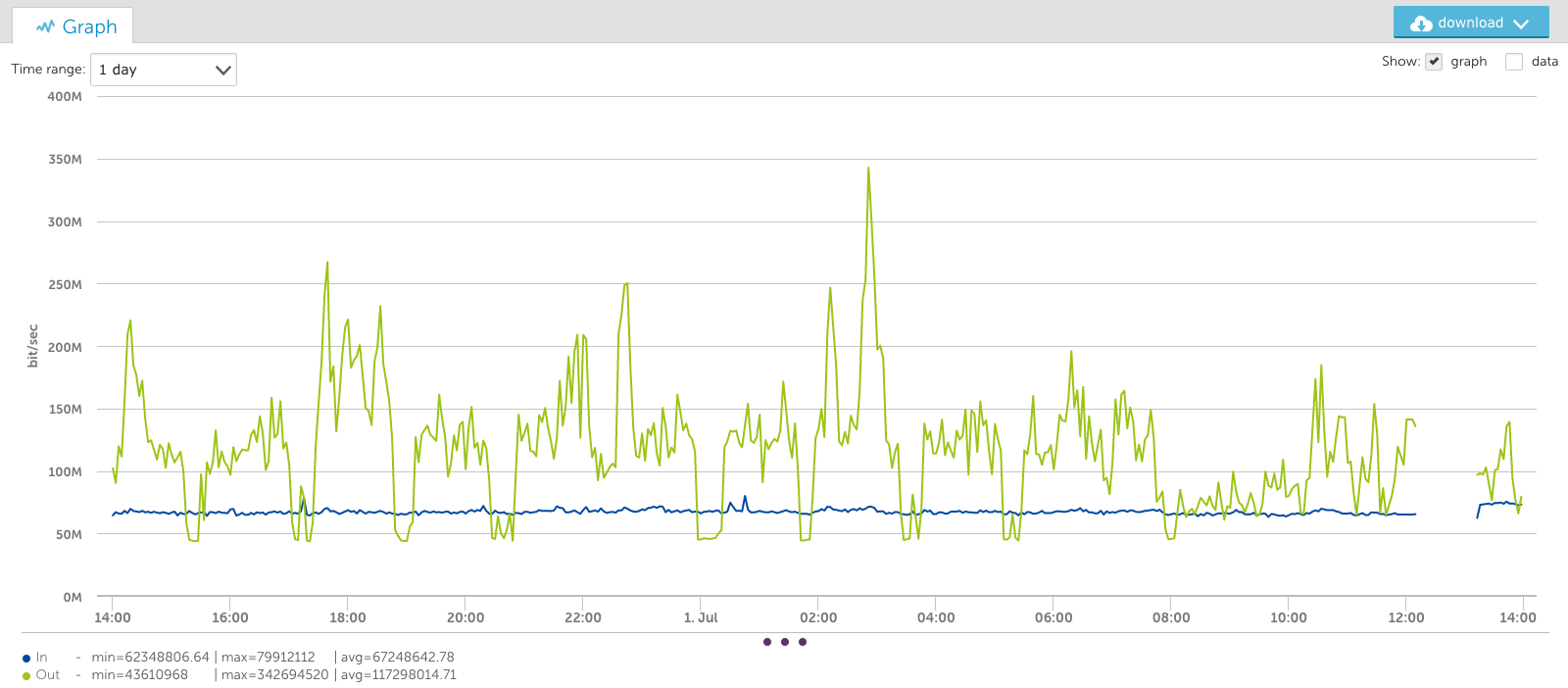
You’ll note the output data peaks at almost 350Mbps in the graph above, but in the view of this interface for the last week (below), the peak appears to be just 300Mbps. This is because it’s an average of the consolidated period:
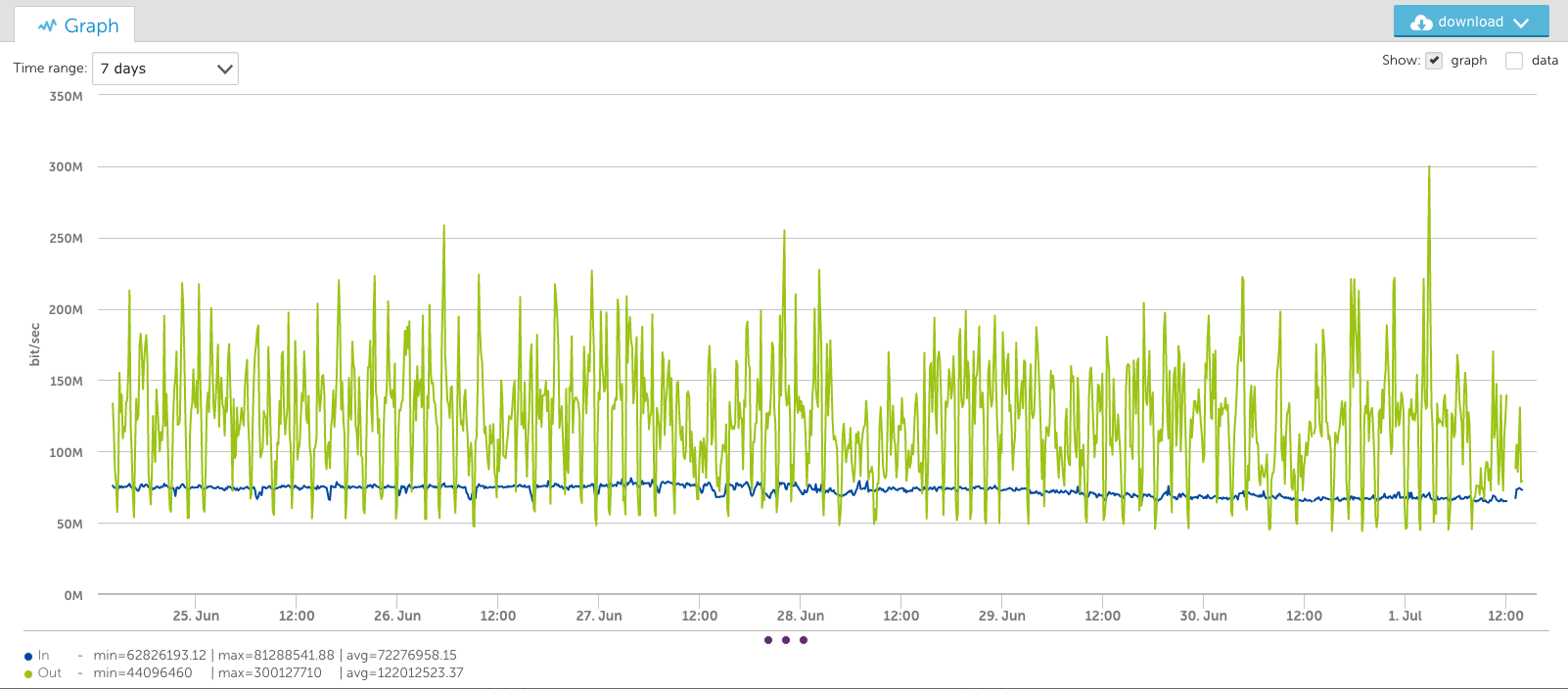
And in a 3 month view (below), the bandwidth seems to only peak at 140Mbps:
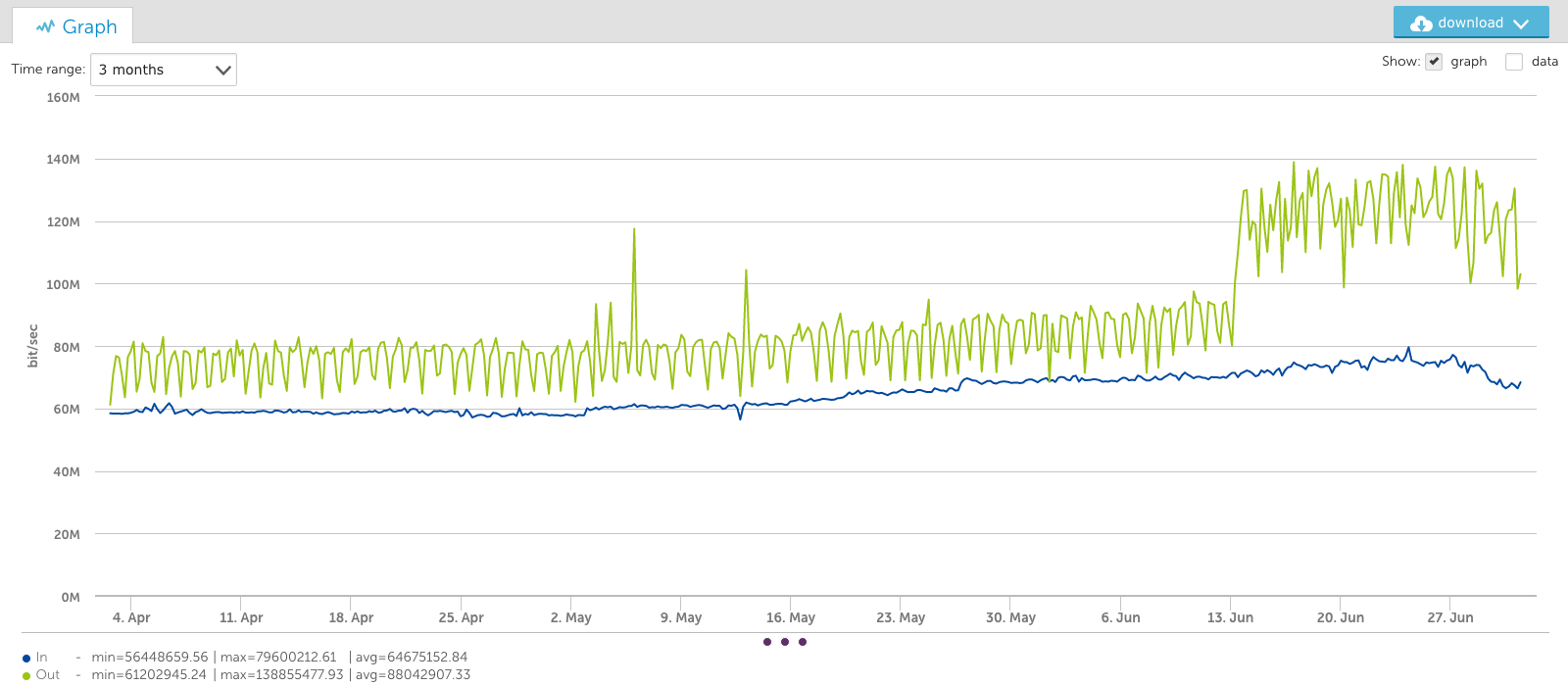
This averaging out of peaks could lead people to underestimate their long term capacity demands.
Introducing the VaST Algorithm
Our DataScience team could tackle this problem now that we have the all the raw data via TSDB – so they did. They implemented what we are calling the VaST algorithm: VisuAlly Significant Trending. The name VaST is appropriate, given it works by dealing with the vast amounts of data inherent to enterprise monitoring. Using complex math that is over my head, VaST can pick out the significant inflection points of the time series data and preserve them, regardless of the amount of data or the pixels by which the data has to be represented.
Looking at the same data as above, but using the VaST algorithm instead of the average algorithm, results in very different trending. The one day view is almost identical, as the data has not had to be consolidated a great deal:
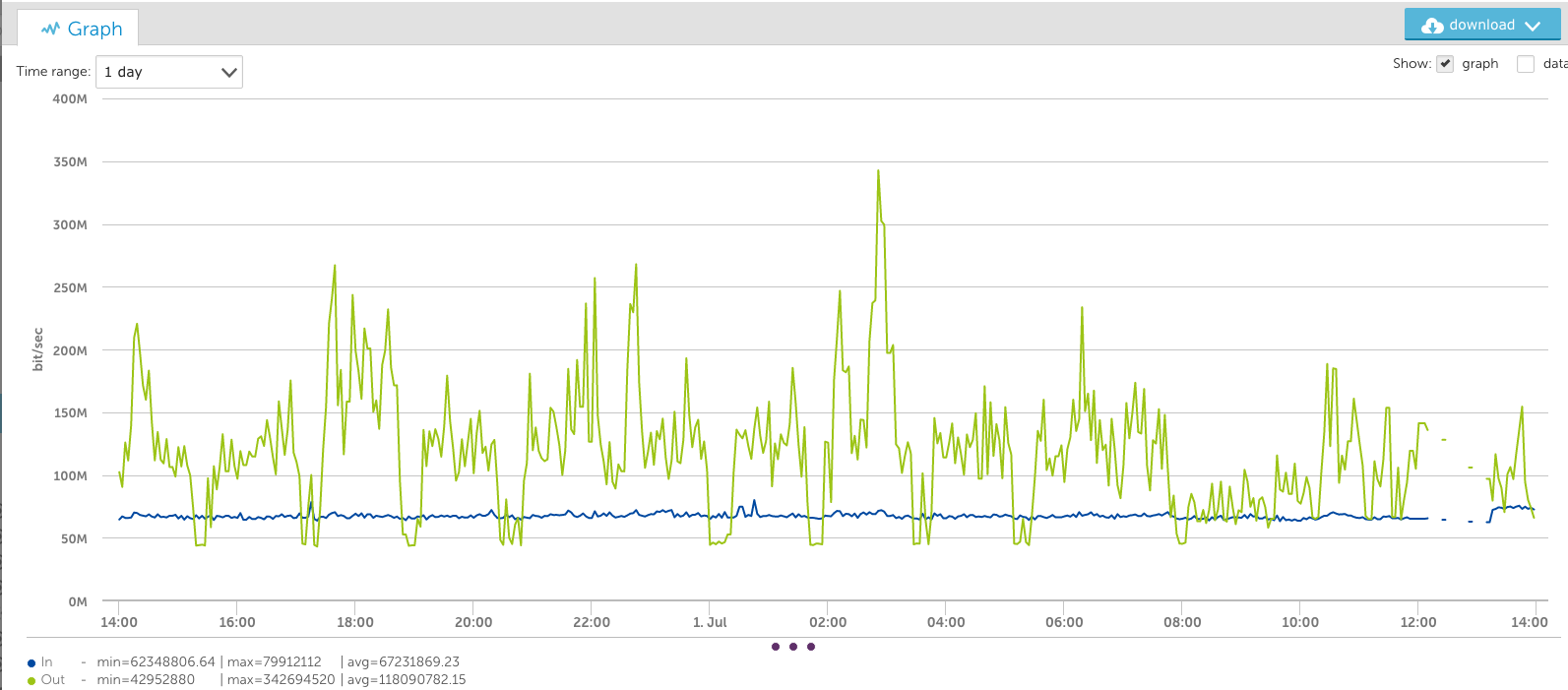
The one-week view shows a very different picture, however. Note that the peaks stay at the true value:
And the 3-month view below also maintains the peaks:
You’ll notice that for longer time periods (such as the 3-month views) different information is conveyed by the different aggregation methods.
VaST vs. Average: A Comparison
The average consolidation makes it easier to see broader trends over time and to observe the increased average over the last two weeks. The VaST consolidation makes it apparent that the required bandwidth went from 250Mbps to 350Mbps over the same time period – information not evident without zooming in on specific time ranges with the average consolidation.
So both methods of presenting data are useful – and necessary – for different use cases. LogicMonitor is rolling out options for VaST support in the current release, starting with Custom Graph Widgets on dashboards, with other graphs coming later.
Recommended Use
Our recommendations as to when you should use VaST for graphs, and when to use average, as a part of your enterprise monitoring are:
– If you are looking at short time ranges (less than a week) it doesn’t matter, as the output will be very similar.
– For longer time frames, if you are concerned about peak utilization, use VaST
– Otherwise, use average, to smooth out the peaks for easier trend analysis.
