A growing number of enterprises are shifting toward a multi-cloud environment with the rise of remote and hybrid work. In fact, 76% of organizations have already adapted to a multi-cloud infrastructure.
These dynamic networks offer companies many reported advantages, such as scalability, agility, and optimized performance. When it comes to a company’s digital transformation and transition to a multi-cloud environment, Software-Defined Wide-Area Networking (SD-WAN) often emerges as a top consideration.
What is SD-WAN?
Many companies with a multi-cloud network have replaced the conventional Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) transport protocols with SD-WAN.
SD-WAN refers to a software-based method of managing wide-area telecommunication networks. With SD-WAN, you can combine transport services (including MPLS circuitry) through encrypted overlay tunnels to communicate and prioritize enterprise data across internal applications.
There is a good reason for SD-WAN’s widespread appeal. While the MPLS has proven reliable for decades in handling predetermined communication pathways, it lacks the flexibility and agility for managing modern multi-cloud environments with vast and dispersed endpoints.
Unpacking the SD-WAN architecture
SD-WAN networks run on an abstract infrastructure divided into a control and forwarding plane. The control plane functions from a centralized location as a remotely controlled network, eliminating the need for on-premise technicians. At a granular level, SD-WAN features three components that comprise its virtualized infrastructure, removing the reliance on specific hardware.
SD-WAN Edge
The SD-WAN Edge refers to the user endpoint within the network. These may include multi-cloud systems, on-premise data centers, and SaaS platforms.
SD-WAN Controller
An SD-WAN Controller offers a transparent view of connected networks and facilitates decision-making policies for orchestrators. Essentially, an SD-WAN controller provides centralized management of enterprise data flow and authenticates devices linked to your network.
SD-WAN Orchestrator
Your designated SD-WAN Orchestrator manages and systematizes policies and traffic among authorized controllers. The component streamlines intuitive workflows across your enterprise networks (e.g., branch offices). Essentially, orchestrators are the definitive bridge between your controller and edge routers. You can upgrade orchestrator functions by providing enhanced analytics and performance SLAs that expedite troubleshooting processes and network fixes.
Top SD-WAN providers
The modern market features an assortment (and an ever-growing number) of SD-WAN vendors, each providing unique features and functionalities. Therefore, you will benefit from researching the leading vendors to access the best solutions in network function virtualization (NFV) and software-defined networking (SDN) deployments.
Fortinet Secure SD-WAN
With superior security standards, Fortinet offers services that drive high-performance network capabilities. The vendor’s SD-WAN structure helps your organization manage precious enterprise data without compromising speed or function. Also, Fortinet’s SD-WAN services have undergone rigorous testing, with Gartner validating the solution for its high performance, reliable security, and low total cost of ownership (TCO).
Using Fortinet’s SD-WAN technology guarantees several improvements to communication processes with built-in encryption protection and sandboxing features that prevent data loss. Fortinet provides frictionless integration to your branch infrastructure for smooth data management across LANs, optimizing hybrid SD-Branch layouts.
Versa Networks (OS)
Versa Networks’ SD-WAN solution features an integrated platform with premium security capabilities. The technology’s intuitive functions include multi-cloud connectivity, full multi-tenancy and micro-segmentation of businesses, and context-based network and security policies throughout registered networks.
Versa prioritizes optimal network security as one of its core missions. In 2021, Gartner recognized Versa Networks as a visionary in the Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Network Firewalls, emerging as the preferred choice from an in-depth comparison of the top 19 vendors in the communications industry. The SD-WAN offers access to Versa’s Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), enhancing user security through multi-factor authentication, data protection, and SSL decryption.
Aryaka
Aryaka is an innovative service provider that combines SD-WAN technology with a secure web gateway as a one-stop network solution. Specifically, Aryaka’s hybrid approach equips your organization with a zero-trust WAN that significantly reduces business and operational risks. As a result, Aryaka positions itself as a leader among SD-WAN vendors, promoting the fastest service of its kind within the industry.
Gartner has recognized the zero-trust vendor as the customer’s choice for three consecutive years through outstanding KPI standards, including 99.999% SLA performance and uptime and a 65 net promoter score rating five times the industry average. Your business can manage optimal security and communication performance from a single contact point through Aryaka’s SD-WAN layouts.
Understanding the pros of SD-WAN
SD-WANs give enterprise networks a general boost from conventional MPLS systems as they improve connectivity across separate applications and off-site locations.
Business traffic prioritization
SD-WAN helps your organization prioritize critical enterprise data by selecting the most cost-effective and efficient communication path. When you set up the technology’s load-balancing and traffic-steering capabilities, your SD-WAN network can recognize business applications and allocate bandwidth volume according to individual service requirements. Traffic steering lets your team manage multiple parallel connections in business traffic with a responsive system, providing rate-limitless sensitive applications with optimal bandwidth.
Affordability
An SD-WAN approach applies private and distributed data exchange and control measures, which function seamlessly across diverse project environments. The process optimizes network functionality and cost-effectiveness by securing data from the cloud and immediate networks.
Application performance optimization
SD-WAN’s structured infrastructure drives optimal application performance across enterprise networks. Specifically, the agile transport mode fulfills the latest enterprise compliance mandates and automates traffic steering based on business priorities. Additionally, SD-WAN provides a centralized control center for managing enterprise data across multi-cloud endpoints, connecting with authorized SaaS and IaaS collaborators and vendors without complication.
Diverse transport methods
With SD-WAN networks, users can access multiple transport channels, including direct broadband connection, 5G, and traditional MPLS circuits. The flexible arrangement improves data availability for undisrupted and optimized communications. You can expect optimal application performance across cloud systems, on-premise servers, and SaaS platforms like Microsoft 365 or Salesforce.
The cons of SD-WAN
While SD-WAN networks seem like a step in the right direction in multi-cloud environments, they pose some user considerations as a developing technology.
No on-site security function
SD-WAN networks lack an on-site security function, so you must separately install and manage a security policy to safeguard networks against online threats. An unprotected SD-WAN infrastructure might face considerable risks from data breaches such as the Colonial Pipeline Hack, which resulted in significant data loss and reputational damage.
No Quality of Service (QoS) under specific scenarios
Communication networks that rely on SD-WAN provisions lack a proper QoS. Essentially, these networks will not receive the full technical benefits of SD-WAN, including path control, traffic shaping, and forward error correction.
Vendor concerns
SD-WAN vendors may provide their services and equipment at a higher cost. Also, due to the variability of service standards, some vendors may need more capability to service software-based networking (SDN).
Revisiting MPLS
In the 1990s, MPLS replaced standard internet protocol (IP) routing and became the primary transport method for enterprise data. While the infrastructure offers scalability, optimized bandwidth utilization, and enhanced security – by serving as a virtual private network – it requires installing and maintaining physical links. This process has become increasingly complex, costly, and impractical in a progressively multi-cloud landscape.
MPLS infrastructure
MPLS is a protocol-independent solution with predetermined paths between routers in the MPLS network; each label comprises four components:
- The label value that determines the direction of the data packet
- The traffic class field
- The bottom of the stack flag
- The time-to-life (TTL) field
Functionalities of the MPLS
The MPLS moves network traffic through predetermined labels instead of conventional addresses, guiding the data through private WANs (wide-area networks).
MPLS functions as layer 2.5 in the OSI seven-layer hierarchy between data links that use LANs and networks that run on internet-wide addressing. This infrastructure attributes a forwarding equivalence class (FEC) to each data packet within a network, which routers can decipher by comparing them against descriptive tables.
The routers update the outermost layer of the data packet as it travels through the FEC pathway and to the next hop, which is examined and submitted to the next layer. Users of the MPLS method can customize the information for each packet, essentially driving top performance in unified networks.
Private MPLS networks can provide your organization with a consistent and reliable means of managing communications in cloud-based environments.
Pros of MPLS
Your MPLS transport modes remain segregated from the public internet, making the infrastructure invulnerable to prevalent web-based attacks such as distributed denial of service (DDoS). As such, the enhanced security of MPLS offers the optimal performance of real-time data transportation by avoiding potential interceptions and packet loss within the open internet.
Despite the general security of MLPS (with SD-WAN combinations), some decision-makers may seek added protection from automated cloud monitoring across public and private connections.
Cons of MPLS
Most of the downsides to MPLS relate to its physical limitations and high cost compared to SD-WAN alternatives. In its original design, the MPLS catered to organizations communicating through remote branches of enterprise data centers. MPLS would conventionally backhaul data from branch offices for comprehensive security processing and distribution through on-premise hubs. However, many companies now prefer cloud services over MPLS. Additionally, the backhauling process often increases latency and reduces application performance.
Comparing SD-WAN with MPLS
A significant highlight of SD-WAN, unlike MPLS, lies in its transport-agnostic overlay structure. Your organization can benefit from the arrangement by applying and modifying policies across your WAN from a centralized location. Alternatively, MPLS functions via predetermined routes through physically installed connections, but its fixed circuits make managing changes across multiple user environments costly and complex.
Although SD-WAN might replace MPLS as the more popular transport choice for some companies, the technologies could co-exist depending on your enterprise arrangements. For instance, some companies may adopt a hybrid network management approach. Specifically, decision-makers would restrict MPLS use to on-premise legacy applications while offloading cloud-based programs to SD-WAN.
Additionally, some organizational leaders have adopted internet-augmented MPLS with SD-WAN. The advanced process increases organizational flexibility by enhancing MPLS with internet broadband links. These links prioritize networking decisions according to specific requirements, such as application type and optimal bandwidth volume.
Hybrid approaches
Many organizations are adopting hybrid approaches that combine the strengths of SD-WAN and MPLS. This strategy allows businesses to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness by leveraging the unique benefits of each technology for specific use cases.
How hybrid SD-WAN/MPLS solutions work
A hybrid approach integrates MPLS circuits with SD-WAN’s flexible, software-defined overlay. MPLS handles latency-sensitive and mission-critical applications that require guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS), while SD-WAN manages less critical traffic using cost-effective broadband or other transport methods. By dynamically routing traffic based on application requirements, hybrid setups ensure that each data type is delivered efficiently and securely.
For example:
- MPLS role: Ensures low-latency, high-reliability communication for applications like VoIP, video conferencing, and financial transactions.
- SD-WAN role: Routes non-critical traffic, such as email, file backups, and SaaS applications, through broadband connections, reducing MPLS bandwidth requirements and costs.
Scenarios where hybrid approaches excel
- Real-time applications with high bandwidth demand
Businesses requiring uninterrupted service for real-time applications, such as hospitals using telemedicine or financial institutions running stock trading platforms, can dedicate MPLS to these tasks while leveraging SD-WAN for less critical operations. - Multi-branch organizations
Enterprises with numerous branch offices can use MPLS for their headquarters and key locations, ensuring consistent performance for sensitive operations while using SD-WAN to connect smaller branches with broadband. - Global operations with varying network needs
Hybrid solutions are ideal for multinational organizations with offices in regions where MPLS availability or affordability varies. In these cases, MPLS can be prioritized in key regions while SD-WAN manages connections in remote or less-developed areas. - Disaster recovery and business continuity
By combining MPLS and SD-WAN, businesses can create highly resilient networks with failover capabilities. If MPLS circuits experience outages, SD-WAN dynamically reroutes traffic to maintain uptime. - Cloud-first strategies
Hybrid approaches enable organizations transitioning to cloud-based operations to retain MPLS for legacy applications while offloading cloud workloads to SD-WAN. This ensures seamless performance across both on-premise and cloud environments.
Decision-making checklist: Choosing between SD-WAN and MPLS
Selecting the right networking solution for your organization requires carefully evaluating your unique needs, priorities, and constraints. Use the following checklist to guide your decision-making process and determine whether SD-WAN, MPLS or a hybrid approach is the best fit for your enterprise:
1. Assess your network requirements
Do you have latency-sensitive applications, such as VoIP, video conferencing, or financial transactions, demanding guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS)?
- If yes, MPLS or a hybrid approach may be necessary.
Are your users distributed across multiple remote locations or regions with varying connectivity needs?
- If yes, SD-WAN offers better scalability and flexibility.
2. Evaluate your budget
What is your budget for networking infrastructure, including installation, maintenance, and operational costs?
- MPLS typically requires higher initial and ongoing investments due to physical circuits and hardware.
- SD-WAN offers a cost-effective alternative by leveraging existing broadband or internet connections.
3. Consider Scalability
Is your organization rapidly expanding or adopting a multi-cloud strategy?
- SD-WAN provides seamless scalability for growing networks and dynamic environments.
- MPLS may need to be more adaptable due to its reliance on fixed circuits.
4. Analyze Security Needs
Do you require private, highly secure connections for sensitive data?
- MPLS offers inherent security through private circuits but may need cloud integration for modern environments.
- For comprehensive protection, SD-WAN requires additional security layers, such as Secure Access Service Edge (SASE).
5. Examine Application Performance
Are your applications cloud-native, such as SaaS platforms or IaaS solutions?
- SD-WAN is optimized for cloud connectivity, enabling direct and efficient access to cloud applications.
- MPLS is more suitable for legacy on-premise applications that rely on data center backhauling.
6. Assess Management and Operational Complexity
Do you need centralized, simplified network management?
- SD-WAN provides centralized control and automation for effortless network monitoring and troubleshooting.
- MPLS requires more hands-on management, often needing on-premise technical support.
7. Plan for Future-Proofing
Is your organization prioritizing digital transformation, including support for hybrid work and zero-trust security models?
- SD-WAN, combined with SASE, aligns with cloud-first and modern security trends.
- MPLS may need help to keep pace with the agility required for these transitions.
8. Evaluate Hybrid Options
Would a combination of SD-WAN and MPLS better meet your needs?
- Use MPLS for critical real-time applications and SD-WAN for cost-effective handling of general traffic.
Alternatives to MPLS and SD-WAN
While MPLS has been a reliable transport method for enterprise networks, advancements in networking technology offer alternative solutions better suited for modern, cloud-first environments. These alternatives provide flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency for organizations looking to evolve beyond traditional MPLS setups.
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
VPNs provide a secure, encrypted tunnel for data transmission over the public internet. While they lack the QoS guarantees of MPLS, VPNs are a cost-effective solution for connecting remote users and smaller branch offices to corporate networks. VPNs work well for businesses prioritizing affordability and basic security over high-performance requirements.
5G networks
The rise of 5G technology offers a compelling alternative for enterprise networks. With ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and widespread availability, 5G networks can support critical business applications that were previously reliant on MPLS. They are particularly effective for edge computing environments and mobile-first businesses.
Internet-based networking
Many organizations are turning to direct internet access (DIA) and broadband connections as replacements for MPLS. These options allow businesses to leverage high-speed, cost-effective public internet connections while pairing them with cloud-native security solutions like SASE to maintain performance and security.
Private LTE and CBRS
Private LTE and Citizen Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) networks are emerging as viable alternatives for enterprises requiring private, secure connectivity without the constraints of traditional MPLS. These technologies enable organizations to create their wireless networks, which are ideal for environments with unique coverage requirements, such as manufacturing facilities or campuses.
A summary of SD-WAN vs. MPLS
SD-WAN systems provide your organization with the trusted capabilities of managing multi-cloud environments with greater scalability and reliability. The modern data transport mode presents a more affordable and flexible solution that leverages MPLS, wireless, broadband, and virtual private networks (VPNs) to maintain high speed across remote environments.
On the other hand, MPLS boosts network efficiency through predetermined routes, and it is best suited for enterprise environments that continue to rely on data centers. In both instances, you can significantly improve observability by applying a trusted REST API that exposes all functionalities within your networks without tedious wrapper codes.
REST APIs with multiple integrations offer added convenience for managing data across multi-cloud platforms, preferably with automated webhooks that send real-time information between applications.
As the WAN continues to evolve, enterprise leaders must have the freedom and accessibility to navigate between private and public Internet infrastructures. Comparing SD-WAN vs. MPLS, you can successfully align your company’s specific requirements with the necessary product sets to achieve the best outcomes.
SD-WAN in the future of network communications
Through SD-WAN, your organization maintains optimized software functions regardless of location, elevating your overall user experience while reducing IT expenses. Combining SD-WAN networks with intelligent monitoring can help you streamline and optimize business continuity in work-from-home and hybrid settings.
Another major factor in SD-WAN adoption is its independence from tedious MPLS circuitry migrations. If your enterprise network currently runs on the public internet, you can choose to retain your service provider by moving or reconfiguring the virtualized elements of your WAN.
Next, SD-WAN capabilities support the core functions of Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) structures, a term Gartner coined in 2019. Advanced SASE setups provide your enterprise with a safe, reliable, unified cloud-based network.
SASE also helps your organization transport security and access between multiple user endpoints, such as branch offices and mobile applications. The structure operates through a combination of SD-WAN functionalities and cloud-based security solutions. Ultimately, SD-WAN proves integral in supporting your company through future-proofing communications for a cloud-first landscape.
Take your network management to the next level with LogicMonitor. Discover how our platform integrates seamlessly with SD-WAN to provide unparalleled visibility, performance monitoring, and scalability for your enterprise.
Using multiple cloud environments in overly complex networks with outdated architectures puts tremendous strain on infrastructures. One of the best solutions for combating overworked architectures is Catalyst SD-WAN, Cisco’s new and improved version of Viptela SD-WAN.
Unveiled in 2023, Catalyst SD-WAN (an updated and rebranded version of Viptela SD-WAN technology) is one of the first Software-Defined Wide Area Network solutions. It provides increased infrastructure speeds and several other key features, like centralized management and security integration. The many benefits of SD-WAN technology are discussed in detail below.
Is Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN the same as Viptela SD-WAN?
Founded in 2012, Cisco Viptela was one of the first vendors to provide SD-WAN solutions. The Viptela SD-WAN platform gained such popularity that Cisco acquired the brand along with Viptela SD-WAN in 2017 and integrated the Viptela technology into its product portfolio.
In 2023, Cisco introduced Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN, an updated version of Viptela SD-WAN that not only rebrands the Viptela technology package but also offers advanced capabilities, like improved network performance, better security, and increased cost efficiency. Available as a PDF download, the Cisco SD-WAN Design Guide provides a deeper look into the evolution of Cisco’s SD-WAN platform.
The need for Catalyst SD-WAN
As network infrastructures become more complex and challenging to manage, traditional Wide Area Network (WAN) architectures struggle with scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. Having an efficient, secure, and scalable network solution is no longer a luxury but a necessity, and Catalyst SD-WAN is one of the most effective solutions available. Using software-defined networking principles, Catalyst SD-WAN helps manage and control network traffic in a more agile and cost-effective manner.
How Catalyst SD-WAN works
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN is built on a flexible architecture that includes several key components—vEdge routers, vSmart controllers, vManage, and vBond orchestrators. These components create a secure, scalable, and efficient network environment.
Architecture overview
- vEdge routers: Can be physical or virtual and are deployed at a network’s edge to provide secure connectivity and create an overlay network. They support various transport methods like MPLS, broadband, and LTE, ensuring reliable data transfer.
- vSmart controllers: Manage the control plane, handling policy enforcement and route distribution across a network. They ensure that a network’s operational policies are applied consistently and securely.
- vManage: Allows administrators to configure, monitor, and manage an SD-WAN environment, providing a unified network view by integrating data center analytics, automation, and real-time monitoring. The LogicMonitor monitoring platform for Cisco SD-WAN solutions uses vManage API to monitor performance and availability metrics for various edge devices across networks.
- vBond orchestrators: Responsible for initial device authentication and establishing secure connections between vEdge routers, vSmart controllers, and vManage. It plays a critical role in maintaining on-premises and cloud network security and reliability.
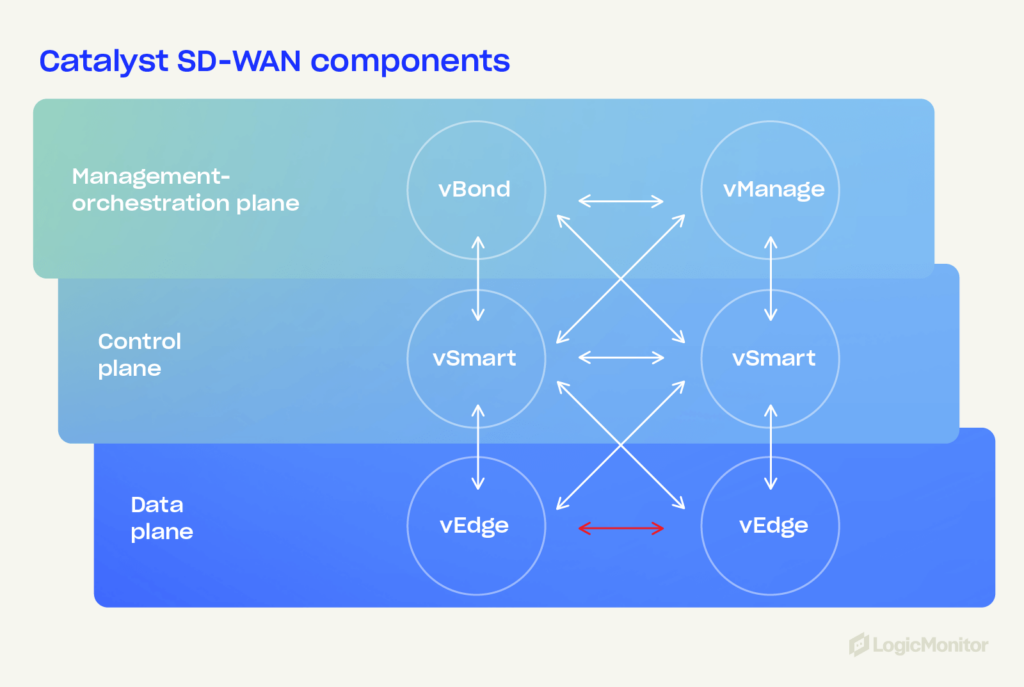
Data plane and control plane separation
Separating the data plane (data forwarding) from the control plane (network control) optimizes traffic flow and allows the application of security policies across networks.
Secure overlay network
An encrypted overlay network over existing transport mediums, such as MPLS, broadband, and LTE, ensures consistent and secure connectivity across all locations and provides a more reliable network foundation for business operations.
Policy enforcement mechanisms
Centralized policies that govern traffic flow, security rules, and application performance can be easily defined and updated based on business needs.
8 key features of Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN provides a powerful suite of features that streamline network management, bolster security, and optimize performance. From centralized control to comprehensive analytics, these eight key features are designed to address the complexities of modern network environments.
- Centralized management and policy enforcement: Centralized management through a single dashboard enables administrators to make real-time adjustments from anywhere and centralizes security policy enforcement across entire networks. It also provides uniform applications of security standards, reducing the risk of misconfigurations. LogicMonitor’s platform supports SD-WAN monitoring and offers a free downloadable solution brief to get started.
- Integrated security and threat protection: Provides end-to-end encryption and advanced threat protection, allowing for seamless management of both network and security policies through a single interface. Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN supports secure connectivity across multiple transport methods, including broadband, LTE, and MPLS.
- Zero-trust security model: Continuously verifies the identity of every device and user, reducing the risk of breaches. Complemented by secure device onboarding, the zero-trust security model of Catalyst SD-WAN automates the integration of new devices with Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) and automated certificate management.
- Advanced threat protection: Includes advanced threat protection mechanisms, such as intrusion prevention systems (IPS), anti-malware, and URL filtering, which detect and block sophisticated threats in real time before they impact networks. Integrating Cisco Talos Intelligence Group, one of the world’s largest commercial threat intelligence teams, ensures that Catalyst SD-WAN stays updated with the latest threat intelligence.
- Scalability and flexibility: Easily adapts to growing network demands and integrates seamlessly with other security solutions, particularly Cisco Umbrella for cloud-delivered security and Cisco Secure Network Analytics (formerly Stealthwatch) for network visibility and security analytics. Simple integration abilities extend security beyond the SD-WAN to provide comprehensive protection against threats throughout a network.
- Application-aware routing: Optimizes data traffic by tracking path characteristics and selecting the best routes for different applications. This ensures that critical applications receive the bandwidth and quality of service they need, reducing issues like jitter and packet loss.
- Network segmentation: Allows businesses to create multiple virtual networks over a single physical infrastructure. By isolating different types of traffic, critical applications remain unaffected by less important traffic.
- Comprehensive analytics and visibility: Offers real-time monitoring and reporting for more comprehensive visibility into network performance. With predictive analytics, administrators can proactively manage networks, identify potential issues, and prevent downtime.
Benefits of using Catalyst SD-WAN
Catalyst SD-WAN is an attractive solution for network management due to its potential for enhanced application performance. Reducing a network’s complexity reduces the risk of latency and connectivity issues and improves consumers’ user experience.
- Improved network performance: Optimizes network performance by reducing latency and increasing throughput for critical applications. By leveraging multiple transport services, the solution ensures businesses can maximize their available bandwidth.
- Enhanced security: Offers robust security protocols that protect data in transit and at rest. With integrated security features, businesses can simplify compliance with industry regulations and safeguard their networks against modern threats.
- Cost efficiency: Leveraging cost-effective transport options, such as broadband and Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN, reduces operational costs and lowers hardware and maintenance expenses through centralized management and automation.
- Simplified network management: Simplifies the deployment and management of complex networks, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to changing network demands. With minimal manual effort required, IT teams can focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine network maintenance.
- Greater agility and flexibility: Enables rapid provisioning of new sites and services through seamless integration with cloud services and third-party applications, allowing businesses to remain agile and responsive to market changes.
- Enhanced user experience: Delivers consistent and reliable application performance, leading to improved end-user satisfaction. By prioritizing critical applications, business continuity is maintained and the overall user experience is enhanced.
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN vs. traditional WAN solutions
Traditional WANs, rooted in hardware-centric models, struggle with scalability, flexibility, and the ability to adapt to modern network demands. Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN introduces a software-defined approach that addresses these challenges head-on. Upgrading network infrastructures requires understanding the distinct differences between SD-WAN and traditional WAN architecture.
Architecture comparison
Traditional WAN operations rely heavily on hardware, which isn’t always flexible and difficult to scale. In contrast, Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN uses a software-defined approach that separates network control from hardware, offering greater flexibility and scalability.
Performance and reliability
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN offers superior performance compared to traditional WANs, with enhanced redundancy and failover capabilities. The solution’s dynamic routing and real-time traffic management features—compared to fixed pathways for data transmission—ensure that critical applications remain accessible even in the event of network disruptions.
Security considerations
While traditional WANs often rely on perimeter-based security models that offer limited visibility into network traffic, Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN integrates security into every layer of the network. This approach addresses modern security threats more effectively, providing a comprehensive defense against potential vulnerabilities with features like encryption, advanced threat detection, malware sandboxing, and centralized security policy management.
Cost and ROI
Catalyst SD-WAN offers a lower total cost of ownership (TCO) compared to traditional WANs by reducing hardware dependencies and leveraging cost-effective transport options. Because of centralized management, an SD-WAN can also lead to faster deployment (and lower operational costs), allowing businesses to achieve a higher return on investment (ROI).
Scalability and flexibility
Traditional WANs can struggle to adapt to changing network scales and configurations because they often require on-site physical configuration changes and struggle to integrate with new technology. Catalyst SD-WAN, however, is designed for scalability, allowing businesses to integrate new technologies—both on-prem and cloud services—as needs evolve.
Real-world applications of Catalyst SD-WAN
Understanding the practical applications of Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN can help illustrate its benefits for various industries. Here are some real-life scenarios that showcase how organizations leverage SD-WAN to enhance their network performance, security, and scalability.
1. Retail chain with distributed branch locations
Challenge: A large retail chain with hundreds of branch locations across different regions faces the challenge of managing network connectivity and security consistently across all stores. This means employees may not be able to do their jobs or serve customers. The traditional WAN infrastructure is complex and costly to maintain, and it is limited in its ability to prioritize critical applications like point-of-sale systems and inventory management.
Solution: By implementing Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN, the retail chain can centralize network management across all branches to gain complete visibility into the IT infrastructure and make changes on both high and low levels. The solution provides secure connectivity, application-aware routing, and network segmentation, ensuring that critical applications receive priority while maintaining robust security standards. With Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP), new branch locations can be brought online quickly, reducing setup time and operational costs.
2. Global financial services firm
Challenge: A global financial services company needs to ensure secure, high-performance connectivity for its offices and remote workers worldwide. Lost connectivity means customers may not be able to access their funds, leading to panic and lost revenue for the firm. The traditional WAN setup struggles with latency and security concerns, particularly as the firm expands into new markets and increases its reliance on cloud services.
Solution: Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN offers a scalable solution that enhances the firm’s global connectivity through optimized routing and integrated security features, ensuring fast online services for customers (something especially important for trading services like high-frequency trading). The firm can securely connect its offices and remote workers, leveraging multiple transport methods (like MPLS, broadband, and LTE) while ensuring compliance with stringent financial industry regulations—protecting customer data and avoiding hefty legal fees. The centralized management provided by vManage allows the IT team to monitor and manage the network in real time, responding quickly to any issues or threats.
3. Healthcare provider with multiple facilities
Challenge: A healthcare organization with multiple hospitals, clinics, and remote care facilities needs reliable, secure connectivity to support critical applications like electronic health records (EHR), telemedicine, and real-time patient monitoring. Traditional WAN solutions struggle to deliver the necessary performance and security, particularly as the organization expands its services.
Solution: With Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN, the healthcare service provider can create a secure, high-performance network that supports critical applications across all facilities. The solution’s integrated security features, including end-to-end encryption and advanced threat protection, ensure that patient data is protected, while application-aware routing optimizes the performance of essential healthcare applications. The SD-WAN’s scalability also allows the organization to quickly integrate new facilities, services, and technology (like IoT devices) into the network as it grows.
4. Manufacturing company with a global supply chain
Challenge: A manufacturing company with a global supply chain needs efficient and secure communication between its production facilities, suppliers, and distribution centers. Traditional WAN solutions can’t keep up with the dynamic nature of modern manufacturing, where real-time data and agile responses are critical for maintaining inventory and delivery schedules.
Solution: Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN enables the manufacturing company to establish a secure and agile network that connects all elements of its global supply chain. Using application-aware routing and network segmentation, the company can prioritize and protect critical communications and data transfers, giving each location the information it needs to make decisions and serve customers. This setup improves operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and supports the company’s digital transformation initiatives, such as the adoption of IoT and smart manufacturing technologies.
5. Educational institution with multiple campuses
Challenge: A university with multiple campuses and remote learning centers must provide reliable, high-performance connectivity to support online learning platforms, campus security systems, and administrative applications. The traditional WAN infrastructure is not flexible enough to adapt to the growing demand for bandwidth from student activity, new educational resources, and security.
Solution: Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN provides the university with a flexible, scalable network solution that ensures consistent connectivity across all campuses and remote learning centers. The centralized management platform allows the IT team to deploy security policies uniformly, optimize bandwidth allocation for critical applications, and monitor network performance in real time. The SD-WAN’s ability to integrate with cloud-based learning platforms also supports the university’s digital education initiatives.
Conclusion
By addressing the limitations of traditional WAN architecture, Catalyst SD-WAN enhances application performance, reduces costs, and simplifies network management. Its flexible and secure architecture enables organizations across various industries to remain agile, protect their data, and efficiently manage their infrastructures, whether for cloud migration, distributed systems, or global operations.
LogicMonitor’s tools help businesses improve network visibility while obtaining the maximum amount of benefits from Catalyst SD-WAN.
In recent years, Software-Defined WAN Technology (SD-WAN) has changed the way networking professionals secure, manage, and optimize connectivity. As organizations continue to implement cloud applications, conventional backhaul traffic processes are now inefficient and can cause security concerns.
SD-WAN is a virtual architecture that enables organizations to use different combinations of transport services that can connect users to applications. Sending traffic from branch offices to data centers using SD-WAN provides consistent application performance, better security, and automates traffic based on application needs. It also delivers an exceptional user experience, increases productivity, and can reduce tech costs.
What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN implements software to safely and effectively manage the services between cloud resources, data centers, and offices. It does this by decoupling the data plane and the control plane. The deployment process often includes vCPE (virtual customer premise equipment) and existing switches and routers. These run software that control most management functions, such as networking, policy, and security.
Until recently, a Wide Area Network (WAN) was the best method for connecting users to applications on data center servers. This would typically include Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) circuits for secure connections. But today, MPLS is no longer adequate if you’re dealing with large amounts of data and working in the cloud. Backhauling from branch offices to corporate headquarters impairs performance. Gone are the days of connecting to corporate data centers to use business applications.
With SD-WAN, it’s now easier for you to deliver exceptional network experiences with less operational responsibility for IT staff.
What is the SD-WAN architecture?
Traditional WANs can limit growth and productivity due to their dependence on total hardwire network devices. SD-WAN depends on software to provide a virtual approach while implementing traditional technologies such as broadband connections.
The traditional architecture with conventional routers was not created for the cloud. Backhauling traffic was required from branch offices to data centers so detailed security inspection could occur. This method often hinders performance, causing a loss in productivity and a poor user experience.
SD-WAN, however, can fully support applications in on-site data centers. This includes SaaS services such as Microsoft 365 and Dropbox. The architecture can separate management and control functions, WAN transport services, and all applications. With centralized control, you can store and control all the data on the applications. The control plane can adapt traffic to fit application demands and provide a high-quality user experience.
How does SD-WAN work?
SD-WAN uses communication tunnels, network encryption, and firewall software to manage and safeguard computer networks across several locations. SD-WAN can distinguish and separate network hardware from central controls and streamline operations. A business that uses SD-WAN can create higher-performance WANS by using the internet instead of MPLS.
Traffic flows through a specific SD-WAN appliance, with each appliance centrally controlled and managed. This enables the consistent enforcement of policies. SD-WAN can determine each application traffic and has the ability to route each one to the correct destination. These machine learning-based capabilities enable the software to base destination routes on existing policies.
Because SD-WAN is built to work efficiently, these solutions generally offer greater bandwidth efficiency, increased application performance, and easy access to the cloud. Users enjoy all these benefits without sacrificing data privacy or security. This can also improve customer satisfaction and business productivity.
Furthermore, SD-WAN can identify different applications and provide specific security enforcement. This means that business needs are met, and the business is protected from threats. One of the reasons SD-WAN is so effective is because it can leverage new software technologies while implementing machine learning.
There are a few specific aspects of SD-WAN that enable it to work so well:
Ability to self-learn and adapt
SD-WAN normally guides traffic according to programmed templates and predefined rules. It has the ability to continuously self-monitor and learn. This is done by adapting to various changes in the network. These changes could include transport outages, network congestion, or brownouts. This adaptation occurs automatically and in real time. This limits the amount of manual technical intervention that is needed.
Ability to simultaneously use multiple forms of WAN transport
If a particular path is congested or fails, the system can implement solutions to redirect traffic to another link. SD-WAN can manage each transport service seamlessly and intelligently. The primary purpose of SASE is to provide the best experience possible for cloud applications. The ultimate goal is to be high quality for the user. The advanced capabilities provided by SD-WAN are necessary to enable optimum SASE and find solutions for these purposes in the event of technical problems.
How does SD-WAN and automation work?
SD-WAN already provides a certain amount of automation. To improve this process, each of the SD-WAN elements needs to communicate through APIs. Improving the communication will also enhance the changes the system can make to WAN edge devices. This affects the configuration of resources such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure. This way, automation works through the entire system, not just in individual components.
Real-time path selection is an example of automation. As communication within the systems improves, the ability to increase the speed and precision of automated decisions will also improve. Insights based on instantaneous data collection will continue to increase efficiency and precision. You will want to continually integrate and update SD-WAN solutions with various machine learning forms to improve manual tasks’ automation. This will enable you to simplify and scale your system to meet the specific needs of each business operation.
Several SD-WAN benefits result from improved automation. These include less human error, faster operations, and improving quality of service. In the long run, the more automation you have, the more likely you will reduce overall operating costs. Automation means reducing the need to hire more engineers and other IT professionals. A self-learning network will increasingly automate many tasks currently done by humans.
What are the benefits of SD-WAN?
SD-WAN is able to offer solutions to many of the challenges you will likely experience when using traditional WAN. The many benefits of SD-WAN include:
Greater agility
While MPLS is good at routing traffic when there are only a few static locations, it’s certainly not as effective when doing business on the cloud. Policy-based routing is the key to SD-WAN’s agility. Traffic is sent through a network focusing on the needs of each basic application. You can use several different transport structures in the WAN. SD-WAN provides predictable agility while supporting cloud migration. This agility includes the ability to use a variety of connections interchangeably, including MPLS, LTE, and broadband.
Increased efficiency
Sending traffic from remote offices to primary data hubs can cause delays. SD-WAN can effectively tie in cloud services. As the use of cloud applications and containers that need edge access increases, so does the need to implement SD-WAN technology. Cloud resources are easily connected with the data hubs in a fast and cost-effective manner. This enables private data centers to grow while organizations can still efficiently expand their use of public cloud services. There is also a reduction in latency issues, which means greater application performance.
Improved security
SD-WAN allows security specification for individual customers that is scalable. Organizations can set up secure zones to guide traffic based on their business policies. A company can protect critical assets with specific partitions while also using firewalls as part of the security process. You can create partitioned areas, basing them on particular roles or identities. You can also monitor network connections, enable deep packet inspection, add data encryptions, and log all security events.
Reduced costs
Backhauling is not only more time-consuming, it’s also costly. MPLS connections between offices and data centers cost more than wireless WAN links or internet broadband. It may take weeks or longer to supply new MPLS links, and MPLS bandwidth is potentially expensive. The same process takes only days when using SD-WAN. In many ways, particularly when it comes to expense, SD-WAN is superior to MPLS. It can also save money by lowering maintenance and equipment costs.
Increased simplification
SD-WAN simplifies turning up new links to remote offices while managing how each link is used more effectively. There is sometimes the need to use several stand-alone appliances with MPLS. You’re able to centralize operations and more easily scale a growing network when using SD-WAN.
Better app performance
Supporting cloud usage and SaaS apps is a necessary part of the digital progress. Applications generally need a lot of bandwidth. SD-WAN provides adequate support with high priority for critical applications. The network hardware separates from the control pane using an overlay network. Network connections then determine the best paths for every application in real time.
Remote access
Cloud access is the primary reason many organizations choose SD-WAN. No matter where your branch or office is, you can easily access all available cloud applications. You can also direct traffic through the data center for critical business applications.
What are the drawbacks of SD-WAN?
SD-WAN has some disadvantages, but the correct tools can overcome many of these drawbacks. Some disadvantages include:
Providing security
Because of how network security is set up, a breach could occur in several remote locations throughout the organization if a hacker breaches security and gains access to the central data branch. This type of connectivity could affect an entire company.
Training staff
Adapting to SD-WAN is not always easy if you’re running or working for a smaller business. Your current staff may not have adequate training to understand and implement this particular technology. In some cases, you may find it counterproductive to hire new IT personnel or train existing staff to build and maintain SD-WAN systems.
Supporting WAN routers
Your SD-WAN system may not support WAN routers. An ethernet connection is likely to interfere with the WAN architecture. You’ll have to come up with a method to eliminate this potential problem. Time-division multiplexing is one option.
How do you select the best SD-WAN?
You’ll want to consider several factors when selecting any SD-WAN model:
- The SD-WAN you select should have the ability to collect real-time statistics.
- The model should connect with all endpoints from any software and application.
- Your selection must be able to encrypt all traffic over the network.
- You should choose a model that provides policy-driven solutions.
- You’ll want an SD-WAN with advanced security that meets your organization’s needs.
- You’ll want to select an SD-WAN that can efficiently utilize bandwidth.
- Your selection should have mobility features, including access control and automatic ideal route selection.
- Your selection should be able to connect with several stations with various internet data services.
What SD-WAN choices are available?
The following are a few of the best-rated SD-WAN solutions:
- Cisco Meraki SD-Wan – This model provides visibility and connects to any application.
- Oracle SD-WAN – Besides routing and firewall, Oracle provides cost-efficient internet connections and high bandwidth.
- CenturyLink SD-WAN – This will help you create a more agile and wide network. It also gives users data reports and analytics.
- Fortinet FortiGate SD-WAN – This solution offers next-generation firewall and advanced routing.
- Wanify SD-WAN – This model delivers VeloCloud SD-WAN through a partnership with VeloCloud. You’ll have end-to-end process management and Wanify’s customer support.
- Aruba Edge Connect – Ratings state that this software is one of the easier types to use. It focuses on reducing costs while simplifying the process.
- Masergy SD-WAN – Masergy has built-in Fortinet security. It also uses AI for its IT operations.
If your organization is using the cloud and subscribing to SaaS, connecting back to a central data center to access applications is no longer efficient or cost-effective. SD-WAN provides a software-centric process that will give your organization optimal access to cloud applications from all remote locations. Your team can create a network that relates to the company’s business policies and promotes the long-term goals of the organization.
Want to invest in a virtual private network or SD-WAN tunnel but don’t know which one to use? It’s important to realize these technologies have many differences and serve unique purposes in your business environment. This guide will teach you more and help you make the right purchasing decision for your business.
Virtual private networks explained
A virtual private network (VPN) creates a secure connection between a device — say your computer — and a network via the internet. It can also connect two separate networks. The great thing about a VPN is that it encrypts your data, meaning servers that intercept it don’t know your identity or location.
VPNs provide protection when you are on the internet. For example, you can avoid third parties, including your internet service provider (ISP), from knowing which websites you visit. VPNs transfer your data to a website through a network of servers maintained by your VPN provider. So your ISP will only see that your data has come from a VPN server — not your device.
There are several use cases for VPNs. The first is remote access, where people working away from the office can access their company’s private network. For example, a remote worker in a coffee shop can use a VPN to connect to a private network instead of a local Wi-Fi hotspot, improving security and confidentiality.
Another use case for VPNs is site-to-site connectivity, which facilitates a connection between two or more networks, such as a corporation network and a branch office network. Again, this protects sensitive data shared over the internet.
SD-WAN tunnels explained
An SD-WAN tunnel or overlay tunnel is a communication pathway that exists between data centers, cloud computing services, or other endpoints. It is part of the software-defined wide-area networking (SD-WAN) architecture, which connects businesses in separate locations via broadband internet, 4G LTE, or another wide-area network (WAN).
SD-WAN tunnels enable two endpoints to communicate with one another. WAN interfaces are located at both ends of a tunnel and exchange information with the underlay network layer in SD-WAN architecture to allow this communication.
SD-WAN tunnels make connectivity more efficient and agile. They use algorithms to guide IP packets between WAN paths, increasing the reliability and performance of network connections in SD-WAN architecture. They can also aggregate two or more WAN resources simultaneously.
What are the differences between VPN and SD-WAN tunnels?
While VPNs and SD-WAN tunnels might make up part of your networking architecture, that’s the end of their similarities. Here are some differences between these technologies.
Configuration and management
A VPN is a network, while an SD-WAN tunnel is a component of SD-WAN architecture, so it’s difficult to compare the two. Manually configuring and managing both requires a steep learning curve; however, VPN and SD-WAN vendors allow you to use these technologies without any networking experience. Vendors take care of configuration and management so you don’t have to.
Handling traffic
VPNs scramble network traffic with high-level encryption, protecting your identity on the internet. SD-WAN tunnels only allow two endpoints to communicate with one another so aren’t responsible for handling traffic. However, SD-WAN architecture as a whole uses a central control pane to route traffic to different destinations based on user policies and algorithms. For example, SD-WAN can determine the best route for application traffic from historical performance data, reducing the likelihood of network outages that can impact your business.
Costs
Again, it’s easier to compare the costs of VPNs with those of SD-WAN architecture as SD-WAN tunnels are just one component of this technology. Generally speaking, VPNs are more cost-effective than SD-WAN because they have a more straightforward design. However, both can provide a significant return on investment if they fulfill your business use case over time. For example, a VPN keeps data safe when remote employees connect to their company’s private network, which can be priceless.
Scalability
You can’t scale an SD-WAN tunnel, but you can certainly expand SD-WAN architecture to meet your business needs. For instance, this technology can accommodate new devices as your company grows. The only way you can increase the scope of a VPN is by adding new users to the network, so SD-WAN is inherently more scalable.
Metrics
Many VPN providers allow you to view metrics about performance, reliability, and other functions. For instance, you can learn the quality of your VPN connection and how many people use it at a particular time. SD-WAN vendors might also provide metrics, allowing you to track
latency, packet loss, and other variables at regular intervals. You might also be able to learn about the performance of SD-WAN tunnels specifically. However, vendors don’t usually make insights about individual components of SD-WAN available and instead provide insights about this technology as a whole.
VPN benefits
The advantages of a virtual private network include enhanced security, remote access, and compatibility with existing infrastructure in your business.
Increased security
VPNs encrypt your data so you can enjoy the internet anonymously. They do this using public and private keys, ensuring only you can access your browsing history. There are several use cases for investing in a VPN for security. For example, you might want to use this technology to prevent hackers from seeing your passwords and usernames for online banks, email services, and social media accounts.
Remote access
Remote workers often use VPNs when away from the office. A VPN will allow them to connect to their company’s private network wherever they are in the world. If you have remote workers in your organization, you can use a VPN to keep all your employees on the same network.
Compatibility with infrastructure
Another great thing about VPNs is that they provide anonymity and remote access via different infrastructure types. This includes hardware such as computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and even video game consoles. That means you don’t need to purchase new equipment to get value from a VPN.
SD-WAN tunnel benefits
The advantages of SD-WAN tunnels include dynamic path selection, improved application performance, and centralized management.
Dynamic path selection
As mentioned, SD-WAN tunnels don’t specifically handle traffic. However, SD-WAN architecture can improve the flow of traffic with dynamic path selection, which determines the best traffic route for applications based on algorithms and user policies. SD-WAN can also keep your network functioning with automatic failover, which suggests traffic takes a different path when a failure occurs.
Improved application performance
Again, SD-WAN tunnels won’t enhance application performance directly. However, by choosing the right traffic path for an application, SD-WAN architecture can certainly improve the performance of an app. For example, an app can continue to function even in periods of high traffic and network congestion. SD-WAN can also prioritize traffic for your most important apps, which will receive networking resources before less important apps.
Centralized management
SD-WAN vendors provide a central control pane that allows you to monitor different components of SD-WAN architecture, including tunnels. You can also define user policies for SD-WAN from this console rather than using several tools, reducing the complexities of network management.
Should you choose a VPN or SD-WAN tunnel for your business?
VPN and SD-WAN tunnels serve different purposes. The former creates a secure connection between a device and the internet, while the latter is a communication pathway in SD-WAN architecture that provides connectivity solutions. This article goes into great detail about the differences between these technologies.
There are other factors to consider when choosing between VPN and SD-WAN tunnels. Ultimately, the technology you choose depends on your use case, company size, networking requirements, and the future growth of your organization. It’s also important to note that SD-WAN architecture, which includes SD-WAN tunnels, can be more expensive than a VPN, so you should evaluate your budget as you make a purchasing decision. That said, both technologies can provide a return on your investment if they provide your company with value.
Also, think about the scenarios where you might use a VPN or SD-WAN tunnel. A virtual private network is best suited for remote work set-ups or protecting your identity on the internet. An SD-WAN tunnel, however, helps you if you want two endpoints in your SD-WAN architecture to communicate with one another.
Integrating SD-WAN into your organization allows you to leverage transport services for seamless connection to applications. Various technologies facilitate this process by routing traffic between different sites. However, Juniper Network’s Contrail SD-WAN offers enhanced routing, intelligent traffic steering, zero-touch provisioning, and other features that build on the capabilities of traditional SD-WAN architecture. Learn more about Contrail SD-WAN below.
What is Juniper Contrail SD-WAN?
Traditional SD-WAN architecture routes traffic via a controller, multiple sites, several overlay tunnels, and different connections between sites comprising the underlay network. Juniper Contrail SD-WAN reference architecture has a controller that serves as an orchestration layer, making it different from conventional setups. It allows you to manage devices directly at sites.
The Contrail SD-WAN architecture, based on the Hybrid WAN model, utilizes a hub-and-spoke topology that locates customer premises equipment (CPE) devices at branch sites. Juniper explains how this process works on its website:
“On the local side of the site, the CPE devices connect to LAN segments and participate in dynamic routing protocols with other LAN devices. On the WAN side, the CPE devices connect across two or more links to a provider hub device.”
Due to its hub-and-spoke topology, Contrail SD-WAN directs traffic from one site to another through a provider hub. Internet traffic also travels through this hub. Juniper’s Contrail Service Orchestration (CSO) software
utilizes SLA policies and other guidelines to direct the flow of traffic across different available paths. It also implements the SD-WAN controller and orchestrator functions.
Understanding SDN
It’s impossible to talk about SD-WAN without mentioning software-defined networking (SDN). SDN is a networking approach that uses APIs or software-based controllers to exchange information with hardware infrastructure. It also directs traffic on networks.
One important distinction about SDN is that it differs from traditional networking approaches. Instead of relying on routers, switches, and other hardware devices to manage traffic, SDN creates a virtual network through software and controls traditional hardware using that software.
The Importance of SDN
SDN provides more flexibility than traditional networking. It eliminates the need for manual programming of hardware devices and allows you to control traffic flows over networks through a software-based controller. This can save time and resources in your organization.
SDN also generates a single source of truth about your networks, helping you identify security threats that might jeopardize your business. For example, you can create separate “zones” for hardware that require different security requirements.
SDN and SD-WAN
While SDN and SD-WAN are closely related, they serve different functions. SDN facilitates internal functions within a Local Area Network (LAN) or the core network of your software provider. On the other hand, SD-WAN provides software-defined application routing to a Wide Area Network (WAN) and centralizes your different data centers, branch offices, and other locations.
Contrail SD-WAN brings SDN-like abilities to your business. It offers automation, agility, and fast automated recovery from any failed WAN links you might encounter. It also helps control WAN costs. Juniper explains on its website:
“You can add connectivity options such as broadband or cellular Internet connections to your existing IP/MPLS VPN services, allowing you to prioritize critical traffic across the connections, as well as move traffic proactively to a backup link if the primary link’s quality degrades enough to put a service–level agreement (SLA) at risk.”
Key Features of Contrail SD-WAN
Contrail SD-WAN features include zero-touch provisioning, routing, and connectivity. Here is a more detailed explanation of these features:
Zero-touch provisioning
Contrail SD-WAN allows you to plug and play spoke devices through autoinstallation or zero-touch provisioning (ZTP). Juniper’s CSO software implements ZTP using an internet-located redirect server. However, for “true ZTP,” the company recommends using a redirect server. CSO 4.1 and later releases reduce the required bandwidth for zero-touch provisioning to 2 Mbps.
Routing
Contrail SD-WAN uses intelligent traffic steering to determine the best path for routing traffic between sites. It takes into account factors such as latency, bandwidth, and other considerations for traffic routing, and can quickly adjust its processes when conditions change. Because of this, Contrail SD-WAN can be more effective for routing traffic than traditional SD-WAN architecture.
Connectivity
Contrail SD-WAN’s intelligent traffic steering makes it easier to connect to applications. The technology also connects locations, such as data centers and branch offices, by deploying VPNs on top of your WAN architecture. This process, known as site-to-site connectivity, isn’t unique to Contrail SD-WAN. However, it can improve your workflows and make it simple to leverage transport services.
Benefits of Using Contrail SD-WAN
Benefits of Juniper Contrail SD-WAN include:
- Enhanced security: Contrail SD-WAN provides access to a comprehensive security suite, including next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) and unified threat management (UTM)
- Compliance with open standards: Contrail SD-WAN supports third-party CPEs and enterprise infrastructure through open protocols and APIs
- Full routing support: The architecture supports BGP, IS-IS, MPLS, OSPF, and other routing protocols
- Scalability: Contrail SD-WAN scales horizontally, allowing your architecture to expand as your business grows
Takeaway
Juniper’s Contrail SD-WAN offers more functionality and features than traditional SD-WAN architecture, helping you connect to business applications. Features such as enhanced routing, intelligent traffic steering, and zero-touch provisioning allow you to route traffic between different sites and improve network management in your organization.
Contrail and LogicMonitor
While LogicMonitor doesn’t currently have a native integration for Juniper Contrail SD-WAN, we are constantly updating our integrations offerings. If you are interested in learning more about creating a custom HTTP integration, check out our blog post: https://logicmonitor.com/blog/the-flexibility-to-meet-you-where-you-work-creating-custom-http-alert-integrations. For more information about our Juniper Mist integration, visit: https://logicmonitor.com/integrations/juniper-mist
Over the past five years, enterprise networking has undergone a significant transformation driven by advancements in technology, the rise of cloud and SaaS applications, the decentralization of the workforce, and the need for agility, scalability, and cost mitigation. These factors have led organizations to shift from on-premise network management systems (NMS) to cloud-managed networking platforms and to adopt technologies like Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN). These network transformation initiatives have garnered substantial investments from Chief Information Officers (CIOs) seeking to modernize their infrastructure and drive digital transformation. This blog post explores these key networking trends, and their implications for hybrid IT infrastructure monitoring, and highlights the investments made by CIOs in these initiatives.
The Impact of Cloud Adoption, SaaS Applications, and Workforce Decentralization:
The rapid adoption of cloud and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications has revolutionized how businesses operate, access critical resources, and deliver services. Organizations are increasingly leveraging cloud services to enhance collaboration, improve productivity, and reduce infrastructure costs. Additionally, the decentralization of the workforce, with employees working remotely or across multiple locations, has created the need for secure, scalable, and reliable network connectivity. These trends have significantly impacted enterprise networking, necessitating agile and scalable solutions that can seamlessly connect distributed users and resources.
Transition to Cloud-Managed Networking Platforms:
To meet the challenges posed by cloud adoption and workforce decentralization, organizations are transitioning from traditional on-premise NMS to cloud-managed networking platforms. These platforms support the latest enterprise wired and wireless technologies, like 6 GHz WiFi 6e, offer centralized network management, real-time visibility, and simplified operations across geographically dispersed locations. By moving network management to the cloud, organizations can leverage the benefits of scalability, flexibility, and ease of deployment. CIOs have recognized the value of these platforms and have made substantial investments to modernize their network infrastructure and optimize their operations.
Embracing SD-WAN for Enhanced Network Connectivity:
In response to the need for scalable and cost-effective network connectivity, organizations have increasingly embraced SD-WAN. SD-WAN offers significant cost savings opportunities compared to Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), and leverages software-defined networking principles to optimize wide-area network connectivity by dynamically steering traffic and prioritizing applications across multiple links and providers. SD-WAN also allows organizations to establish secure, high-performance connections between various locations, including branch offices, remote sites, and cloud environments. CIOs have allocated significant investments to implement SD-WAN solutions, recognizing their potential to enhance network performance, reduce costs, and improve overall business efficiency.
Investments in Network Transformation Initiatives:
CIOs have made substantial investments in network transformation initiatives, driven by the strategic importance of modernizing their infrastructure and enabling digital transformation 1. These investments include:
1. Cloud-Managed Networking Platforms:
CIOs have allocated significant budgets to deploy and manage cloud-managed networking platforms. These investments cover licensing fees, hardware infrastructure, and ongoing operational expenses. The cost of these platforms varies based on the scale and complexity of the network, the number of locations, and the level of functionality and support required.
2. SD-WAN Implementations:
Recognizing the benefits of SD-WAN in improving network performance and reducing costs, CIOs have invested in deploying SD-WAN solutions. These investments encompass hardware and software costs, licensing fees, professional services for deployment and integration, and ongoing management and maintenance.
3. Network Monitoring Platforms:
To ensure comprehensive visibility and proactive support in hybrid IT environments, CIOs have invested in SaaS-based hybrid-infrastructure monitoring platforms. These platforms enable IT teams to monitor network availability, health, and performance, detect anomalies, and proactively address issues before they impact users. The investments are typical OpEx rather than CapEx, and don’t carry the monitoring infrastructure and upkeep costs of on-premise IT Infrastructure Monitoring tools.
Conclusion:
CIOs have recognized the significance of network transformation initiatives in enabling digital transformation and keeping up with the evolving demands of the modern business landscape. The investments made in cloud-managed networking platforms, SD-WAN implementations, and advanced network monitoring and management tools demonstrate their commitment to building agile, scalable, and cost-effective networking infrastructures.
By embracing cloud-managed networking platforms, organizations can centralize network management, achieve real-time visibility, and simplify operations across distributed locations. These investments empower IT teams to streamline network provisioning, configuration, and troubleshooting, ultimately reducing complexity and improving operational efficiency.
Furthermore, the adoption of SD-WAN allows organizations to enhance network connectivity, dynamically steer traffic, and prioritize critical applications. CIOs have recognized the potential of SD-WAN to optimize network performance, reduce costs, and improve overall business efficiency.
However, investments in SaaS-based hybrid-infrastructure monitoring platforms like LogicMonitor are essential to ensure comprehensive visibility and proactive support of these transforming environments. LogicMonitor enables IT teams to monitor availability, health, and performance, detect anomalies, and address issues before they impact business operations. The investments made in a monitoring platform highlight the commitment to maintaining a robust and reliable hybrid infrastructure. For more information about how LogicMonitor helps you monitor the health and performance of your entire network infrastructure in a single unified platform, visit logicmonitor.com/network-monitoring.
In conclusion, the evolving enterprise networking trends of cloud adoption, SaaS applications, workforce decentralization, and the need for agility, scalability, and cost mitigation have driven CIOs to invest significantly in network transformation initiatives. By leveraging cloud-managed networking platforms, implementing SD-WAN, and adopting a SaaS-based monitoring platform, organizations can mitigate risk by providing assurance that the transforming hybrid infrastructure is resilient and high-performing to support their digital transformation goals. As hybrid infrastructures continue to evolve, it is crucial for organizations to stay abreast of these trends and invest in the right technologies and strategies to ensure their networks remain agile, secure, and efficient in the face of changing business requirements.
References:
1. Worldwide SD-WAN Infrastructure Forecast, 2022–2026. https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=US48793922
SD-WAN and SASE both build on traditional network models, such as those used to connect a company’s offices. While the two models share some features and advantages, they have different structures and approaches. In the simplest terms, an SD-WAN inspects and routes data more efficiently, while a SASE combines networking and security functions into a single service. Here’s what you need to know.
What is SD-WAN (software-defined wide area network)?
A wide area network connects devices in multiple locations, usually meaning some data goes over the Internet rather than solely through dedicated cabling. The network usually routes data between any two points through a specific device to allow analysis, filtering, and security checks. This process, called backhauling, can slow performance.
An SD-WAN breaks the link between the security/control process and the network’s physical hardware. Inspecting the data in the cloud allows more efficient routing.
Key characteristics of an SD-WAN include:
- A central control interface accessible from anywhere (with the right authorization)
- The SD-WAN can work with multiple connection types, such as fixed line connections, LAN cabling, and cellular connections.
- Dynamic path selection means the network can prioritize specific data types in different ways — for example, to reduce latency or maximize security.
- SD-WANs can comprise a combination of cloud services, locally hosted software, and on-site physical hardware.
What is SASE (secure access service edge)?
At first glance, SASE may appear similar to SD-WAN, but it is a different concept and architecture. It rethinks the design of a network to eliminate the need for a central inspection and filtering point. In other words, there’s no backhauling.
A SASE setup treats every user device as being at the network’s edge (hence the “service edge”). SASE works by viewing these as endpoints rather than as devices. The data inspection occurs at these “Points of Presence,” meaning the data can be routed here as efficiently as possible.
SASE can also carry out parallel traffic inspection, meaning multiple filters or checks are carried out simultaneously and then combine the results to determine the next steps. That contrasts with SD-WAN, which chains together individual inspection elements in series, requiring more time.
In effect, SASE combines networking and security into a single service.
Key characteristics of SASE include:
- Networking features include WAN optimization, caching, content distribution networks, and bandwidth aggregation.
- Security features include firewall as a service and zero trust network access (which controls access based on the user, device, and application, not location and IP address.)
- SASE is entirely cloud-based.
- SASE is usually offered as a single service rather than separate components.
What’s the relationship between SASE and SD-WAN?
Exactly how to describe the relationship between SASE and SD-WAN depends on your perspective. For example, some people see it as an evolution, with SASE being SD-WAN plus “security as a service.” Others consider it a complete rethinking, with SD-WAN being just one component in the overall SASE package.
Perhaps the easiest way to think of it is like this:
- SD-WANs use the same structural concept as traditional WANs but with a different physical technology;
- SASE uses a different structural concept from traditional WANs and SD-WANs.
Consider this analogy: in place of data inspection on a computer network, imagine if the US Postal Service (USPS) had to inspect every parcel. They would have to check the address, check the size and weight, or check for illegal or dangerous contents.
A traditional WAN model would mean every package, no matter its origin or destination, had to go to the USPS headquarters in Washington, DC, for inspection. This would greatly slow down deliveries, even if the sender and recipient were close to one another.
Switching from WAN to SD-WAN would mean the USPS could now inspect the packages at any post office or even in trucks that could go anywhere. This would speed up deliveries by allowing more efficient routing while inspecting every package.
In both cases, the analogy works by likening individual devices to cities across the US. This analogy doesn’t translate to the SASE model. Instead, imagine the network as the US and every device as a border city in Canada or Mexico. The network inspects data like the local immigration and customs checkpoints on either side of the border. People and vehicles are inspected at the point they enter or leave the country in the same way that SASE inspects data at the very edge of the network.
What are the key differences in practice?
- Security is an inherent feature of SASE. With SD-WAN, you will need to add security measures.
- SASE offers more customization options but is also more complex.
- Businesses may handle SD-WAN components in-house, outsource some components, or have an external supplier handle everything. For now, at least, SASE is most commonly offered as a complete single service by external suppliers.
What are the typical use cases for SD-WAN and SASE?
While every business is different, some use cases are more suited to one technology over the other. For example:
- Businesses with established IT departments and relatively straightforward networking needs (such as connecting multiple offices) may find an SD-WAN an adequate improvement on traditional WANs.
- Larger businesses with more complex needs (such as requiring precise, granular user access controls) may find SASE a more flexible and scalable option.
- Businesses that use hybrid and remote working may find the access controls of SASE more useful. The costs may also work out lower than using an SD-WAN that requires additional security components to suit remote working.
- Growing businesses may prefer a hybrid approach. This could involve using or maintaining an SD-WAN for straightforward connections between sites but incorporating this into SASE to add new users and locations.
What’s the next step?
If you’re still uncertain whether SD-WAN or SASE is best for your needs, or if you want more advice on making the transition, we’ll be happy to help. Contact us today.
SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Networking) centralizes and automates the configuration of network devices and how they route traffic. This is increasingly important as not all network traffic is created equal; there are specific business-critical applications that are relied on more heavily than others. In addition to intelligent routing benefits, SD-WAN also allows IT managers to deploy internet-connectivity quickly, reliability, and securely.
As one of the most requested integration requests from our global enterprise and MSP customers, LogicMonitor has always focused on building the most extensive monitoring coverage within the Cisco portfolio. With our continued expansion of Cisco SD-WAN, we have cemented our partnership even further.
LogicMonitor customers will now have greater visibility in their networks, an immediate view of how their network is affecting service delivery, and drastically reduced alert noise with LogicMonitor’s advanced intelligence capability.
Map Topology of vManage Environments
vManage is the console to manage and configure Viptela devices. LogicMonitor collects metrics from vManage and the configured devices.

View Health and Performance Across Viptela
Viptela is typically chosen by larger companies with more complex hybrid network architecture because of the more granular networking approach. Aside from the data collected from the API, LogicMonitor collects additional metrics via SNMP. All of the Viptela components are monitored out of the box: vSmart controller, vEdge routers, vBond Orchestrator, and vManage.

View Health and Performance Across Meraki Access Points
Meraki is favored in small to medium businesses since it is easier to set up and requires fewer people to manage. The list of supported Meraki device types are access points (MR), cloud-managed access points, security appliances (MX), switches (MS), and teleworker gateways (Z). The data is collected via SNMP.

If you have any questions regarding these new monitoring integrations, please reach out or contact your CSM for more information. Or you can try LogicMonitor for free.
SD-WAN (software-defined wide area network) has grown over the last four years: from a concept spoken about only in forums and dimly lit DevOps departments to software that is littered across every IT company’s flyer as their new cutting edge product. In 2017, NetworkWorld estimated that SD-WAN held less than 5% of the WAN market share but with the 59% annual growth in revenue for SD-WAN vendors, predictions for 2020 look to a $1.2 billion market.
What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN is the next step of software-defined networking (SDN), which is used primarily in local area networks (LANs), to enable connections over WAN. SD-WAN effectively allows the simplification of the management and operation of a WAN by splitting the networking hardware from its control mechanism. This allows the consolidation of a complex infrastructure of WAN path controllers, WAN optimizers, and firewalls into either a single box or software that runs on any commercial infrastructure.
Why is SD-WAN Important?
From a business perspective, this consolidation of infrastructure required for effective WAN architecture has allowed for massive savings in the form of both capital and operational expenditure. When Gartner looked into these promises of savings they found that on average, the introduction of SD-WAN into an enterprise environment would lead to 64.8% savings over the course of three years. This drastic drop in budget requirement helps enterprise-sized companies reallocate resources (both fiscal and technical) to projects focused more on the generation of revenue. This ‘price drop’ also allows mid-market and SMB companies who had previously lacked the resources to build an effective WAN architecture to be able to take advantage of this technology.
With the flexibility of SD-WAN, businesses will have more options with vendors and provide extra resiliency to their networks. On top of that, the convenience of a centralized management system and full visibility across branch networks can help network teams troubleshoot issues quicker than before.
How does LogicMonitor fit in with SD-WAN?
At LogicMonitor, there is a central drive to provide an infrastructure monitoring solution that proactively grows with each new technology in the market. With our SaaS-based tool, we provide a growing library of 2,000+ integrations both in hardware and software across any hybrid environment. This includes public (i.e. AWS, GCP, and Azure) and private cloud as well as on-premises infrastructure. Our focus to be leaders in the infrastructure monitoring space has resulted in the production coverage of microservices, container monitoring and orchestration tools such as Kubernetes. But in relation to SD-WAN, LogicMonitor commands extensive monitoring of the leaders in the market of SD-WAN as established in 2018 by Gartner, including Meraki, Silver Peak, Viptela, and Riverbed to name a few. We can provide metrics to help you track the health and performance of your SD-WAN environment as you make this critical transition in your organization.
Overall, SD-WAN is one of many technological strides being made within the infrastructure space to enable efficiency, automation, scalability, and consolidation. At LogicMonitor, we not only emulate these values but also look forward to the variety of technologies on the cusp of entering this ever-changing field.



