Multiple Operation Updates get Generated for Annotations and Labels
Cause
If an annotation or label updates on a Kubernetes resource frequently (every 1 minute), then multiple operation updates occur despite no considerable changes.
Resolution
Add annotations.ignore and labels.ignore fields with variables (displayed in the following table) under argus.monitoring section to ignore unnecessary updates of annotations or labels using Helm. For more information on syntax, see the Govaluate expressions manual.
| Value | Variable Name | Value Datatype | Comments |
| type | Resource Type | String | The operators “==”, “!=”, “in” work on the type variable. Note: The “in” operator on the type variable doesn’t work when the array has only one element. |
| name | Resource Name | String | Not applicable |
| namespace or ns | Resource Namespace | String | Displays empty for resources that are not namespace scoped. |
| key | Annotations or Label Name | String | Name of the annotations or label based on which section it is used in. |
| value | Annotations or Label Name | String | Name of the annotations or label based on which section it is used in. |
The following is an example of the annotation.ignore and label.ignore fields added in the configuration file:
argus:
monitoring:
annotations:
ignore:
- 'key == "t1" && type == "pod"'
- 'key in ("virtual-kubelet.io/last-applied-node-status", "control-plane.alpha.kubernetes.io/leader")'
- 'key =~ "control-plane."'
- '"control-plane.alpha.kubernetes.io/leader" =~ "lead"'
- 'value =~ "renewTime"'
- 'key =~ "control-plane." && type == "endpoint"'
- 'key == "control-plane.alpha.kubernetes.io/leader" && type == "endpoint" && ns == "kube-system"'argus:
monitoring:
labels:
ignore:
- 'value =~ "renewTime" && type == "endpoint" && ns == "logicmonitor"'
- 'key == "l1" && type == "endpoint" && ns == "logicmonitor"'Important: This applies to LM Container services using LM Container Helm Chart 1.0.0 or later.
Requirements for Upgrading LM Container Charts
- You already have an LM Container Chart installed on your system. For more information, see Installing LM Container Chart using CLI.
- Ensure you have the necessary permissions on the Kubernetes cluster. For more information, see Kubernetes Monitoring Considerations and Required Permissions.
Note: You can migrate old configurations to LM Container Charts. For more information, see Migrating Existing Kubernetes Clusters Using LM Container Helm Chart.
Methods of LM Container Charts Upgrade
You can upgrade LM Container Charts as follows:
- Upgrading LM Container Charts using the Upgrade Wizard (recommended)
- Upgrading LM Containers Charts using Command-Line Interface (CLI)
Upgrading LM Container Charts using Upgrade Wizard
Recommendation: LogicMonitor recommends upgrading the LM Containers using the upgrade wizard.
- In LogicMonitor, navigate to Resource Tree> select Kubernetes Cluster group.
- Select (Manage)
 > Upgrade.
> Upgrade.
Note: You need to run theaddCategory_LMContainerConfigPropertySource, if you use LM Container Charts 6.1.0 version or lower.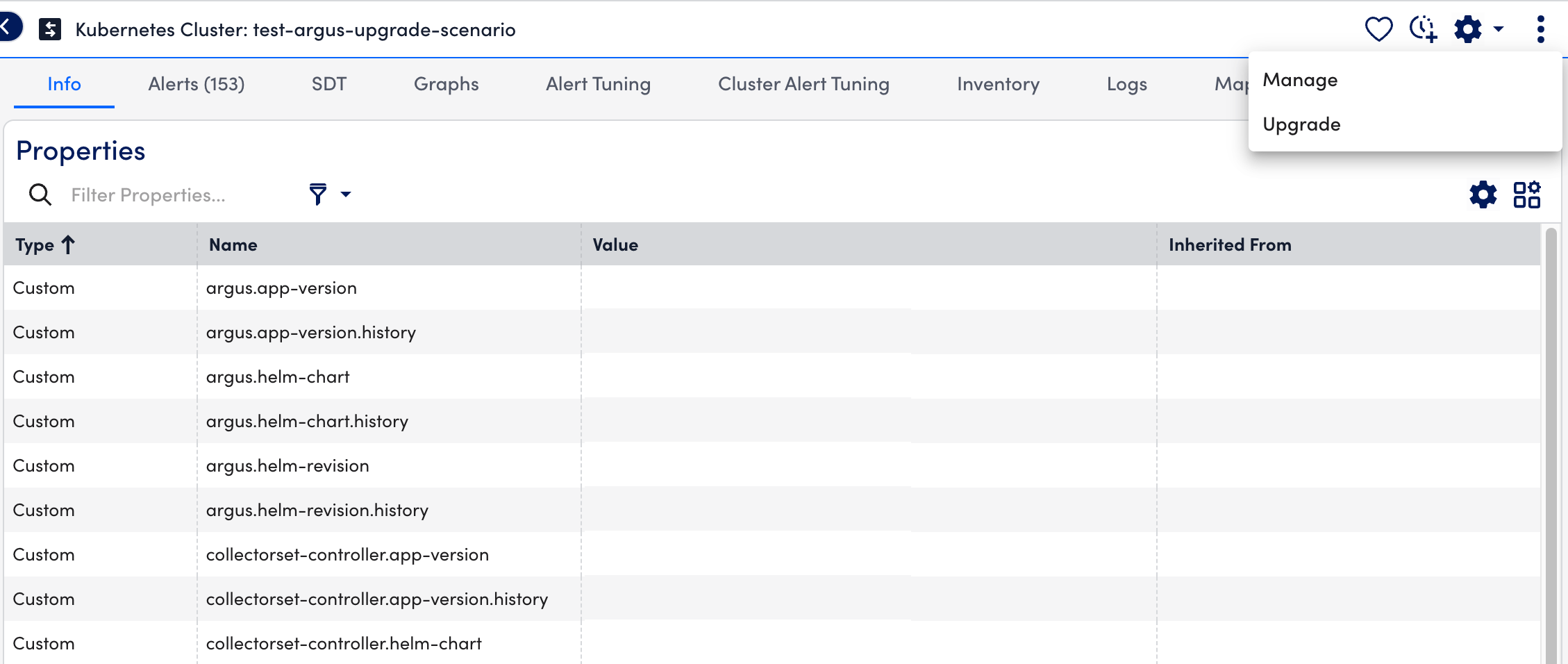
- At the Configuration step of the wizard, select the required version from the LM Container Helm Chart Version dropdown menu.
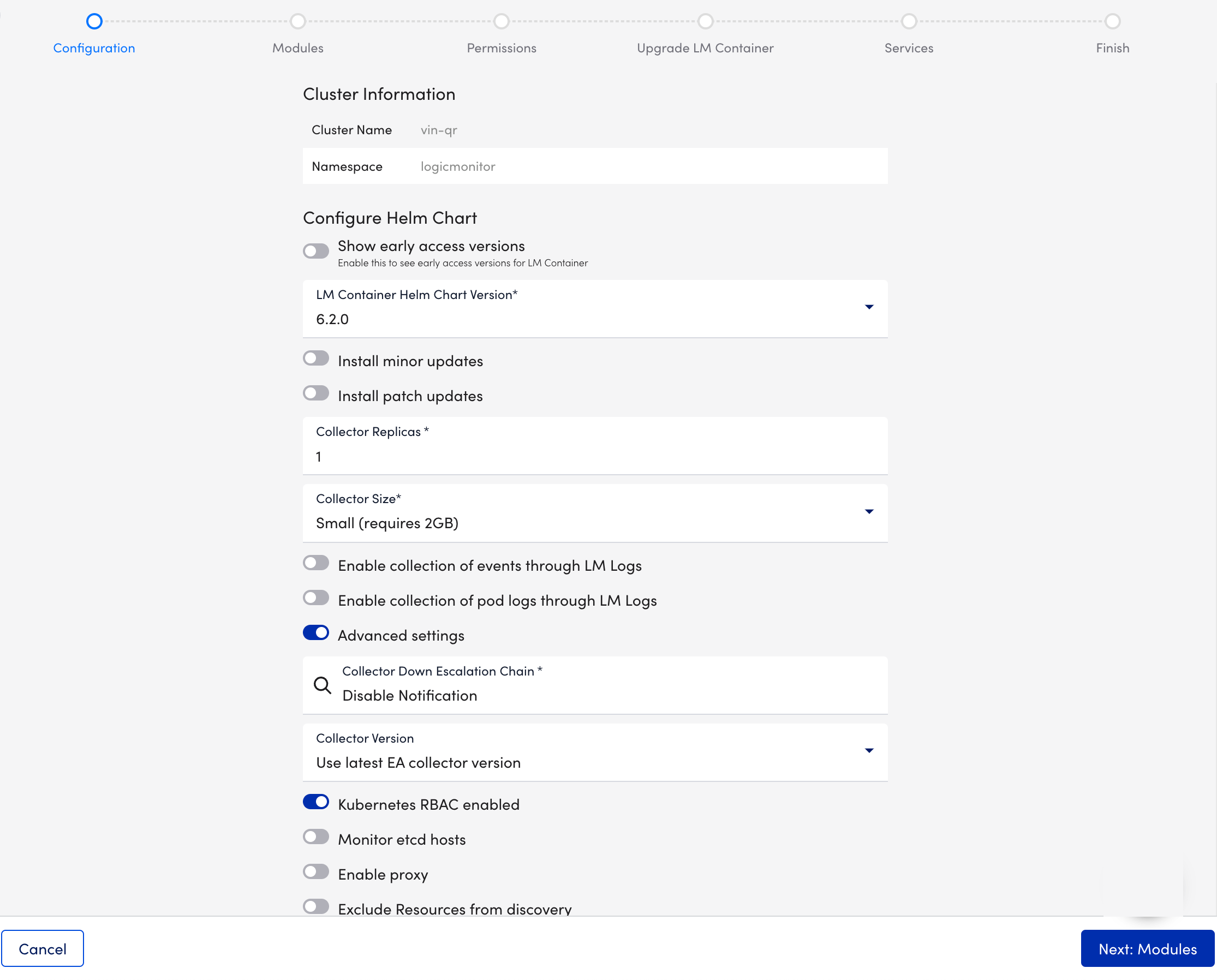
- Select Next:Modules.
- At the Modules step of the wizard, upgrade the required modules from the Exchange page.
This step only shows the list of the modules and their current status (For example, which modules are awaiting installation or degradation).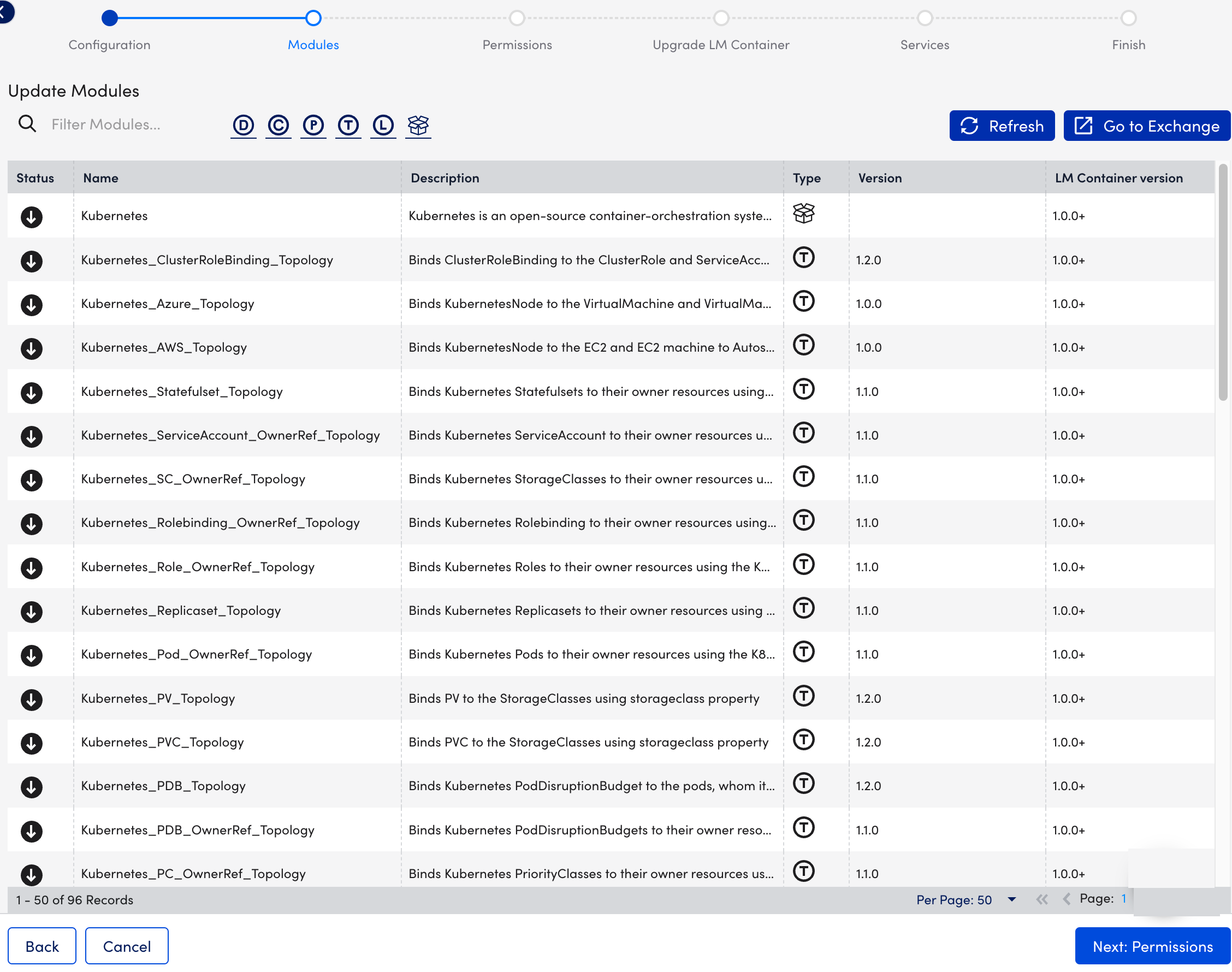
- Select Next: Permissions.
- At the Permissions step of the wizard, the options display the user details used during initial installation.
You can change them if required.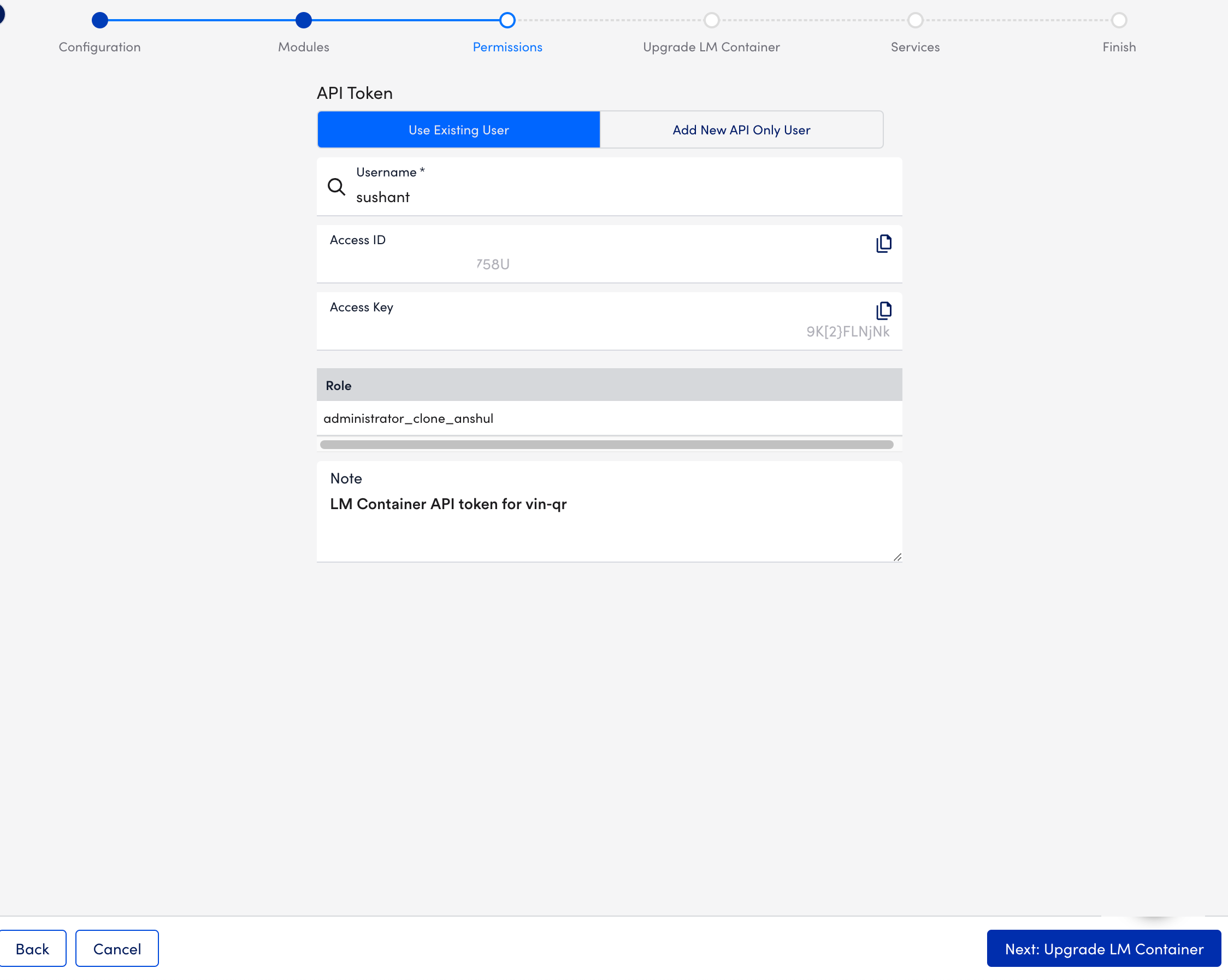
- Select Next: Update LM Container.
- At the Update LM Container step of the wizard, do the following:
- Copy or Download the generated LM Container Configuration file.
- Run the Helm commands displayed in the Run the Installation Command section to install LM Container from the shell where the helm is installed and the Kubernetes cluster is made accessible.
- Once you run the commands successfully, ensure all pods in the LogicMonitor namespace(or where the LM Container has installed them) are up and running with healthy status. (For example, x/y – x are running healthy from expected y to run.)
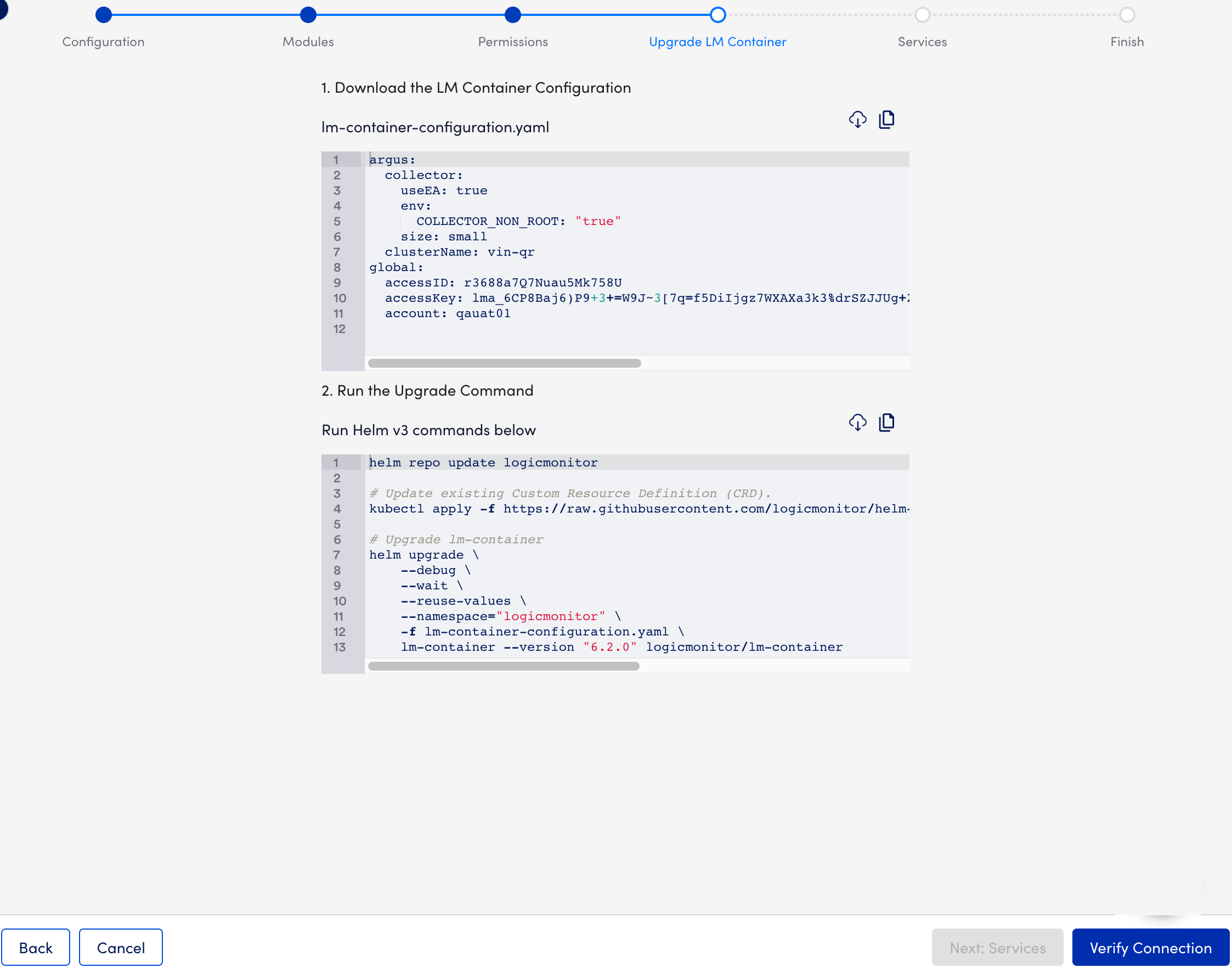
- Return to the Install LM Container page, and select Verify Connection.
- Select Next: Services.
- At the Services step of the wizard, add Kubernetes label key-value pairs.
For more information, see Adding a Service.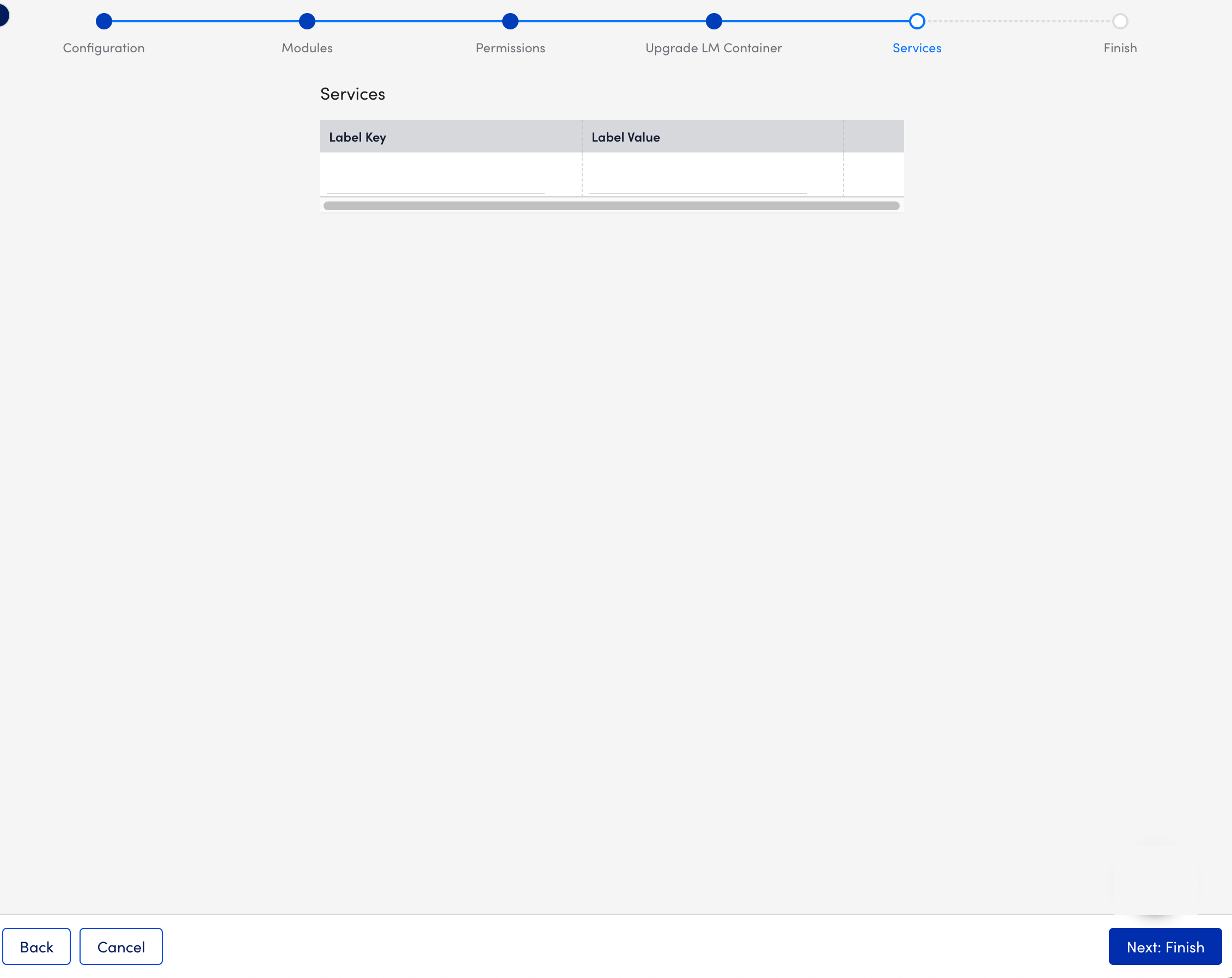
- Select Next: Finish.
Kubernetes Cluster is updated.
Upgrading LM Container Charts using Command-Line Interface
- Take a backup of
lm-container-configuration.yamlfile by performing the following:- Create
lm-container-configuration.yamlfile. - Run the following command:
helm get values lm-container -n logicmonitor - Copy and save the content into lm-container-configuration.yaml file.
- Create
- Open the command line interface window.
- In the terminal, update the repository with the latest Helm charts by using the following command:
helm repo update logicmonitor - Run the following command to update the existing Custom Resource Definition (CRD):
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/logicmonitor/helm-charts/main/charts/collectorset-controller/crds/collectorset.yaml - Run the following Helm upgrade command:
helm upgrade \
--reuse-values \
--namespace=<namespace> \
-f lm-container-configuration.yaml \
lm-container --version <Latest LM Container Chart Version Number> logicmonitor/lm-containerFor more information on the list of values and their descriptions used in the lm-container-configuration.yaml file, see Values Schema Reference from ArtifactHUB.
Note: Latest LM Container Chart Version Number refers to the LM Container Chart version number you want to upgrade to.
For more information on Installing the LM Container chart, see Installing LM Container Chart using CLI and Installing the LM Container Helm Chart.
Container security best practices recommend running Docker containers as non-root users with the minimum necessary privileges to perform their intended tasks. This helps to limit the impact of any security breaches and makes it easier to manage and secure your Docker environment.
Note: LM Container collectors are defaulted to non-root user installation for collector versions 35.100 or later.
By following the best practices, users can now run the LM Container collector as a non-root user (rootless mode). The following instructions help you get started.
Note: In the following Docker configuration examples, the “non-root user” is displayed as “logicmonitor”.
Requirement
- The collector version must be GD Collector 34.002 or later. See, GD Collector 34.002 Release Notes.
Non-root user: Running Docker Collector using LM Container Chart
- Install the LM Container Chart v3.0.0 or later.
- Edit the LM Container Chart to add the following configurations:
argus:
collector:
env:
COLLECTOR_NON_ROOT: "true" # explicitly double quote to avoid
type conversions to boolean and keep as string - Run the following Helm upgrade command to update the LM Container Chart configurations:
helm upgrade \
--install \
--debug \
--wait \
--create-namespace \
--namespace="logicmonitor" \
-f lm-container-configuration.yaml --version <version>
lm-container logicmonitor/lm-containerNon-root user: Running Docker Collector using Argus and Collectorset-Controller charts
If you have an earlier LM Container deployment, then you need to migrate to the following component versions:
- Collectorset controller helm chart to version 1.4.0 or later.
- Argus Helm chart to version 2.5.0 or later.
Collectorset-Controller
Run the following Helm command to update the version Collectorset-Controller to v1.4.0 or later.
helm repo update
helm upgrade \
--install \
--debug \
--wait \
--namespace="logicmonitor" \
-f collectorset-controller-configuration.yaml \
collectorset-controller logicmonitor/collectorset-controllerArgus
- Edit the Argus configuration file to add the following configurations:
collector:
env:
COLLECTOR_NON_ROOT: "true" # explicitly double quote to avoid
type conversions to boolean - Run the following Helm command to update cluster configurations and to Argus v2.5.0 or later.
helm repo update
helm upgrade \
--install \
--debug \
--wait \
--namespace="logicmonitor" \
-f argus-configuration.yaml \
argus logicmonitor/argusPost-Installation or Upgrade
Once you complete the install or upgrade procedure for the cluster configurations, ensure to complete the following for continuous monitoring of the resources:
- Verify if the collector pod is up and running. Also, check the collector status by navigating to Settings > Collectors on the LogicMonitor portal.
- Ensure all datasources are collecting metrics and there is no loss in any metric value.
Configuration Rollback
If you want to rollback the configurations, you can complete the steps from the following options sequentially.
Option 1
- Set the
COLLECTOR_NON_ROOTparameter value to “false” in the configuration file. - Apply updated configuration on the cluster by running the helm upgrade command. For more information, see the Argus configuration and upgrade section.
Option 2
- Set the Collector image tag to
v2.0.0.
- Apply updated configuration on the cluster by running the helm upgrade command. For more information, see the Argus configuration and upgrade section.
Option 3
- Set the Collector image tag to
v2.0.0. - Apply updated configuration on the cluster by running the helm upgrade command. For more information, see the Argus configuration and upgrade section.
- If you want to downgrade the collector version to the desired version, navigate to Settings > Collectors on the LogicMonitor portal.
What is Container Monitoring? What are the advantages of Container Monitoring?
LM Container provides organizations insight into the performance of applications running in containers and the health of the underlying container resources and orchestrating components.
To get the most out of deployment, LogicMonitor presents these insights alongside your organization’s existing monitored hybrid infrastructure in a single, unified platform.
Containers create a dynamic environment that is difficult to monitor because container resources are ephemeral. An effective monitoring solution has to be able to detect and monitor containers while they exist, understand when they disappear, and retain data about the performance of the service or application that is running in the container.
LogicMonitor addresses these challenges with Container Monitoring.
What is Kubernetes Monitoring?
LM Container monitors your Kubernetes-orchestrated container environment and the applications running within the hybrid infrastructure on a single pane of glass. LM Container provides automated monitoring and pre-configured alert thresholds for Kubernetes cluster components (containers, nodes, pods, and services), container health, and application performance.
How to monitor Kubernetes with LogicMonitor?
Kubernetes allows DevOps teams to deploy containerized applications faster and makes managing containers at a scale significantly easier. For more information, see Kubernetes documentation.
With LogicMonitor’s new Kubernetes Monitoring Integration, you can comprehensively monitor your Kubernetes clusters and the containerized applications running within them, alongside your
existing hybrid IT infrastructure on a single pane of glass.
LogicMonitor uses API to ensure that your monitoring is always up to date, even as the resources within the cluster change. Data is automatically collected for Kubernetes nodes, pods, containers, services, and master components (e.g. scheduler, api-server, controller-manager). Pre-configured alert thresholds provide meaningful alerts out of the box.
What does Kubernetes monitoring do and what are the advantages of LogicMonitor’s implementation of Kubernetes monitoring?
LogicMonitor’s event-based Kubernetes monitoring:
- Eliminates the need to have an agent on every node (unlike some other container monitoring tools).
- Automatically adds and removes cluster resources from monitoring (including nodes, pods, and services).
- Offers comprehensive performance and health metrics at both the cluster and application levels.
- Stores data for up to two years (unlike Prometheus, an open-source monitoring alternative).
- Provides insight on underutilized resources (including CPU and memory) for maximum optimization.
- Allows you to create intuitive out-of-the-box dashboards. For more information, see Kubernetes Dashboards.
How can I estimate the number of resources monitored by LogicMonitor?
LogicMonitor can detect and monitor several resources in your Kubernetes cluster such as Pods, Nodes, Services, etc.
Our billing model is based on the number of devices that you monitor, and LM Container treats each Kubernetes object instance as a device. To estimate the number of devices that incur charges, follow these steps:
- Check the various Kubernetes-supported objects for monitoring the required objects. For more information, see the Supported Resources section in the About LogicMonitor’s Kubernetes Monitoring article.
- Run the command to count the number of Kubernetes object instances present in your cluster:
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces --no-headers -o custom-columns=Type:kind,NS:metadata.namespace | sort | uniq -c
For example, the following screenshot shows the number of instances of services and pods present in the different namespaces in your cluster:
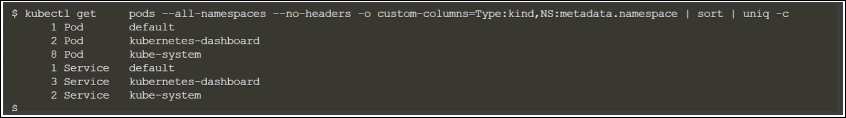
Optionally, aggregate the number of instances of the various objects, excluding the ones that you do not want to monitor to estimate the number of licenses that you need to monitor your cluster.
How are Kubernetes container resources counted?
Kubernetes resources, like cloud resources, are ephemeral resources, though Kubernetes nodes and services are more persistent or less ephemeral than pods. ‘Ephemeral’ means that a Kubernetes or cloud resource may only exist for a concise period, possibly only a few minutes. Count Kubernetes container resources the same way that LM cloud resources are counted:
- LogicMonitor polls the customer account several times a day at roughly 4-hour intervals. At each poll, a count of Kubernetes resources in the account is captured at that specific time. At the end of the day, a daily average from the polls is calculated.
- Based on the daily average, monthly billing is calculated. So pods that might spin up and down between polls in essence are complimentary. They are not counted, but LogicMonitor still retains the data for the resource that is mentioned in the customer’s SLA for the license.
When a poll is taken or whenever a user looks at their portal, the most current Kubernetes resource count is displayed in the Account Information table within LogicMonitor.
Following is the example of the count for the Kubernetes resources:
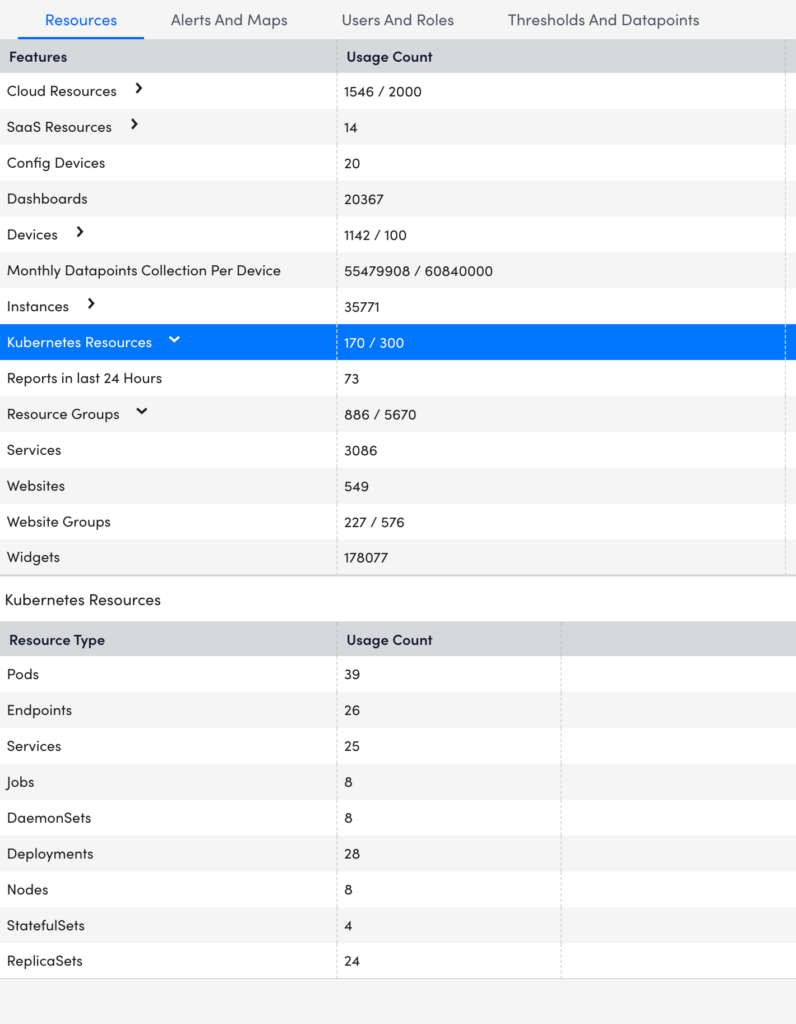
Where can I find the license information?
For license information, contact your Customer Success Manager (CSM).
What is the pricing for Kubernetes Container Monitoring?
Kubernetes monitoring capability is available as an add-on across all licenses (Starter, Enterprise, SP Enterprise). The add-on feature is called ‘LM Container’. Users are charged per Kubernetes Pod only. This makes it easier for you to count fewer resource types and calculate the number of licenses required to monitor your Kubernetes clusters. LogicMonitor can monitor a variety of Kubernetes objects. For more information on a comprehensive list, see Supported Resources.
Note: Users on legacy SKU will continue to be charged for individual Kubernetes objects, such as Services, Deployments, Pods, and Nodes, until you migrate to the new pricing structure.
- The number of licenses used is determined by the number of Pods monitored per day averaged over the month.
- We recommend contacting your Customer Success Manager with a license purchase request if your infrastructure exceeds your committed licenses. This ensures that your costs grow predictably.
Resource Units for Kubernetes
| Service | Category | Resource Unit | Billable As |
| LM Container | Compute | Kubernetes Pod | PaaS |
LogicMonitor’s Cisco Unified Contact Center Express (UCCX) monitoring package leverages the Unified CCX Configuration API, the CTI protocol, and the UCCX CLI to monitor a variety of UCCX system information and agent call statistics.
Compatibility
As of March 10th 2022, LogicMonitor’s UCCX package is known to be compatible with:
- Cisco Unified CCX Versions 11.6 through 12.5
Setup Requirements
- Cisco Unified CCX Configuration API service running
- Available port for CTI applications
Add Resources into Monitoring
Add your UCCX host into monitoring. For more information on adding resources into monitoring, see Adding Devices.
Obtain Credentials
LogicMonitor must provide the appropriate credentials to access the Cisco UCCX host’s data.
- UCCX CLI – UCCX Platform User/Administrator is required for SSH and API monitoring. This administration account is required due to being the only user that is able to remotely access various system statistics, such as system memory and backup status. The Platform User/Administrator account is configured during the UCCS installation and setup process.
Assign Properties to Resources
The following custom properties must be set on the UCCX resource within LogicMonitor. For more information on setting properties, see Resource and Instance Properties.
| Property | Value |
| uccx.user | (Required) UCCX Platform/Administrator user for both SSH and API based monitoring. This user is configured during the UCCS installation process. |
| uccx.pass | (Required) UCCX Platform/Administrator password for both SSH and API based monitoring |
| uccx.api.https | (Optional) Make API requests use HTTPS or HTTP. By default, HTTPS is used. To switch to HTTP, set the value of this property to false. |
| uccx.ssh.timeout | (Optional) Timeout in seconds for SSH connection. By default, the SSH timeout defined in collector settings is used. |
| uccx.ssh.port | (Optional) Port for SSH communication. By default, port 22 is used. |
| uccx.rmcm.port | (Optional) RmCm port for CTI applications. By default, UCCX uses port 12028. |
Import LogicModules
From the LogicMonitor public repository, import all UCCX LogicModules, which are listed in the LogicModules in Package section of this support article. If these LogicModules are already present, ensure you have the most recent versions. Data collection will start automatically once the LogicModules are imported.
Troubleshooting
- If you are not getting all of the data or receiving incorrect data for the Configuration API based modules, verify the permissions are set to the Platform Administrator account. Using an account with permission levels of less than administrator will only report on the data that the user has access to.
- If you are unable to collect information from the CLI-based modules, verify that the correct administrator account if being used. The Platform User/Administrator account must be used. This account is configured during installation of UCCX.
LogicModules in Package
LogicMonitor’s package for UCCX consists of the following LogicModules. For full coverage, make sure that all of these LogicModules are imported into your LogicMonitor platform.
| Display Name | Type | Description | Protocol |
| addCategory_Cisco_UCCX | PropertySource | Determines if target device will respond to CTI/API/SSH. | ALL |
| Cisco UCCX Agent Stats | DataSource | Monitors the current status of all UCCX agents currently logged in. | CTI |
| Cisco UCCX Daily Queue Statistics | DataSource | Provides information on call statistics for the current monitoring period. | CTI |
| Cisco UCCX Latest Backup | DataSource | Status of the most recent backup command performed. | SSH/CLI |
| Cisco UCCX Memory Usage | DataSource | Memory in use by Unified CCX Engine JVM Heap and Cisco Tomcat JVM. | SSH/CLI |
| Cisco UCCX Partitions | DataSource | Monitors the current amount of space in use and free for each disk partition. | SSH/CLI |
| Cisco UCCX Purge Config | DataSource | Status of the most recent purge config command performed. | API |
| Cisco UCCX Database File Storage | DataSource | Monitors the amount of space in use and free in the UCCX database. | API |
When setting static datapoint thresholds on the various metrics tracked by this package’s DataSources, LogicMonitor follows the technology owner’s best practice KPI recommendations. If needed, adjust these predefined thresholds to meet the unique needs of your environment. For more information on tuning datapoint thresholds, see Tuning Static Thresholds for Datapoints.
LogicMonitor’s Dell EMC PowerStore monitoring package leverages the PowerStore Management REST API to query the PowerStore cluster for a wide variety of health and performance metrics.
Compatibility
As of January 2022, LogicMonitor’s Dell EMC PowerStore package is known to be compatible with:
- Version 2.0.1.0 – 2.0.1.1
Dell EMC does not guarantee compatibility across minor releases, so later releases might render this suite unusable.
Setup Requirements
- Import the LogicMonitor_Collector_Snippets DataSource to ensure that your collector supports the code in this monitoring suite, or update to EA Collector 32.100 or later.
Add Resources into Monitoring
Add your Dell EMC PowerStore cluster into monitoring. For more information on adding resources into monitoring, see Adding Devices.
Obtain Credentials
LogicMonitor must provide the appropriate credentials in order to successfully access the PowerStore resource’s data. These credentials must belong to a user account that has been assigned the following minimum permissions:
| Role | Description |
| Read-only | The REST API Programmer’s Guide defines this role as “operator”. |
Assign Properties to Resources
The following custom properties must be set on the Dell EMC PowerStore resource within LogicMonitor. For more information on setting properties, see Resource and Instance Properties.
| Property | Value |
| dell.powerstore.user | REST API username |
| dell.powerstore.pass | REST API password |
| dell.powerstore.alert.levels | (Optional) Property to customize which alert levels from PowerStore are checked (None, Info, Minor, Major, Critical). Can be configured as single value or multiple values comma separated. Default value is “Major,Critical”. |
The modules in this suite support HTTP connections using a proxy server. You can configure this in the Collector settings, see Configuring your Collector for use with HTTP Proxies, or with the following device host properties. Device host properties take precedence over Collector settings for proxy configurations.
| Property | Value |
| proxy.enable | (Optional) This suite is written to use collector proxy settings for HTTP calls configured by the user. To enable, add this device property with the value set to true. Set to false to override the use of configured collector proxy settings and connect without a proxy. |
| proxy.host | (Optional) Configure a proxy host to connect through that is different from collector configuration. |
| proxy.port | (Optional) Configure a proxy port to connect through that is different from collector configuration. |
Import LogicModules
From the LogicMonitor public repository, import all Dell EMC PowerStore LogicModules, which are listed in the LogicModules in Package section of this support article. If these LogicModules are already present, ensure you have the most recent versions. Data collection will start automatically once the LogicModules are imported.
Troubleshooting
The modules in this package are designed with a debug mode embedded in the data collection scripts. If issues occur, turn on debug mode by setting the variable debug to “true” to get more information in the output when testing the script in the Collector Debug Facility. For more information on testing scripts in the Collector Debug Facility, see Script Troubleshooting.
LogicModules in Package
LogicMonitor’s package for Dell EMC PowerStore consists of the following LogicModules. For full coverage, make sure that all of these LogicModules are imported into your LogicMonitor platform.
| Display Name | Type | Description |
| addCategory_DellEMC_PowerStore | PropertySource | Collects the current PowerStore version, model and adds “DellEMC_PowerStore” to system.categories. |
| PowerStore Alerts | EventSource | Dell EMC PowerStore Alerts reported via API that have not been acknowledged or cleared. |
| PowerStore Cluster Capacity | DataSource | Storage capacity metrics for PowerStore clusters. |
| PowerStore Ethernet Port | DataSource | Frontend ethernet port performance metrics for PowerStore. |
| PowerStore Fibre Channel Port | DataSource | Frontend Fibre Channel port performance metrics for PowerStore. |
| PowerStore Nodes | DataSource | Node performance metrics for PowerStore. |
| PowerStore Volume Capacity | DataSource | Volume capacity and performance metrics for PowerStore volumes. |
The DataSources in this package do not include predefined datapoint thresholds (that is, no alerts will trigger based on collected data). This is because the technology owner has not provided KPIs that can be reliably extended to the majority of users. If needed, manually create custom thresholds to receive alerts for collected data, as discussed in Tuning Static Thresholds for Datapoints.
LogicMonitor’s Puppet monitoring package leverages the Puppet Server API and SNMP to monitor performance and state metrics and alert on the status of the Puppet Server and Puppet Agent availability.
Compatibility
As of March 2022 of package release, LogicMonitor’s Puppet package is known to be compatible with:
- Version 4 through 7 for Puppet Agent Process module
- Version 7 and up for the rest of the Puppet modules
Setup Requirements
- Collector version 30.000 or higher .
- SNMP must be enabled on the Puppet agent devices for process monitoring.
- The file last_run_summary.yaml must be given full read permissions for other users to gather last run metrics.
- Allow incoming calls to port 8140 from the Collector to monitor the Puppet Server.
Add Resources into Monitoring
Add your Puppet hosts into monitoring. For more information on adding resources into monitoring, see Adding Devices.
Assign Properties to Resources
The following custom properties must be set on the Puppet Agent resource within LogicMonitor. For more information on setting properties, see Resource and Instance Properties.
| Property | Value |
| ssh.user | SSH Username |
| ssh.pass | (Optional, depending on SSH configuration) SSH Password |
| ssh.publickey | (Optional, depending on SSH configuration) SSH Public Key and Private Key file path |
| system.category | Add “Puppet Server” or “Puppet Agent”. This value is populated by addCategory_puppet. You can also add this value manually as a category for the system.category property (such as in the case when Puppet Agent also runs on Puppet Server, but is incorrectly identified). |
| puppetmaster.port | (Optional) Puppet Server uses port 8140 by default. Modifications can be made in puppetmaster.port host or group property based on the service configuration. |
Import LogicModules
From the LogicMonitor public repository, import all Puppet LogicModules, which are listed in the LogicModules in Package section of this support article. If these LogicModules are already present, make sure you have the most recent versions. Data collection will start automatically once the LogicModules are imported.
Considerations and Warnings
- (Recommended) Set up proper read permissions for last_run_summary.yaml in the puppet public folder to make sure the Puppet Agent Last Run Metrics module runs properly. The permissions might reset to original settings if “puppet agent -t” is manually run on the system. If possible it’s best to automate the permissions to make sure the script always has read-only access to the file.
Troubleshooting
- “No Data” may be returned to raw data if the firewall is blocking port 8140 from the Collector to the Puppet Server or if the last_run_summary.yaml file is not given proper read permissions on the Puppet Agents.
- In case of errors, debug can be enabled within the script by setting the debug=true to gain more insight into the script errors
LogicModules in Package
LogicMonitor’s package for Puppet consists of the following LogicModules. For full coverage, make sure that all of these LogicModules are imported into your LogicMonitor platform.
| Display Name | Type | Description |
| addCategory_Puppet | PropertySource | Determines if Puppet Server or Puppet Agent is running on your device and adds corresponding category. |
| Puppet Server Routes Statistics | DataSource | Returns details from Puppet Server containing information about the routes that agents use to connect to this server. |
| Puppet Server JVM Resources | DataSource | Returns details from JVM metrics about resource utilization of Puppet Server. |
| Puppet Server JVM NIO Buffer Pools | DataSource | Returns Puppet Server JVM NIO Buffer Pool metrics. |
| Puppet Server JVM Memory Pools | DataSource | Returns Puppet Server JVM Memory Pools metrics. |
| Puppet Server JVM Garbage Collection | DataSource | Returns Puppet Server JVM Garbage Collection metrics. |
| Puppet Server JRuby Statistics | DataSource | Returns details from Puppet Server containing information about the JRuby pools from which Puppet Server fulfills agent requests. |
| Puppet Profiler Statistics | DataSource | Returns details from Puppet Profiler containing statistics about catalog compilation. Discover which functions or resources are consuming the most resources or are most frequently used. |
| Puppet Agent Process | DataSource | Tracks status of Puppet Agent processes. |
| Puppet Agent Last Run Metrics | DataSource | Gets metrics and event details regarding the last Puppet run on a puppet agent. |
The DataSources in this package do not include predefined datapoint thresholds (that is, no alerts will trigger based on collected data). This is because the technology owner has not provided KPIs that can be reliably extended to the majority of users. Manually create custom thresholds to receive alerts for collected data, as discussed in Tuning Static Thresholds for Datapoints.
Disclaimer: This content applies only to legacy Cisco Meraki modules (for Cisco Meraki Networks). For more information about the latest monitoring solution for Cisco Meraki, see Cisco Meraki Monitoring.
Use the LogicMonitor Cisco Meraki suite to monitor Meraki devices on a per-network level using a hybrid API/SNMP data collection approach. You can monitor API usage and device counts on a per-organization level.
Requirements
- Import the
LogicMonitor_Collector_SnippetsDataSource and apply it to your monitored collector resource to ensure that your collector supports the code in this monitoring suite, or update to EA Collector 32.100 or later. - Enable access to the Meraki Dashboard API.
- In your Meraki environment, navigate to Organization > Settings > Dashboard API access.
- Select Enable access to the Cisco Meraki Dashboard API.
- Generate an API key from the My Profile page. The API key will be assigned to a property within LogicMonitor. Copy the API key in a secure location once it is generated. For more information, see Cisco Meraki Dashboard API.
- Enable SNMP v2c or v3 on the Meraki Cloud Controller. For more information, see SNMP Overview and Configuration.
Creating a Meraki Device Group
From the LogicMonitor Resources page, create a Meraki device group with the following properties. For more information, see Adding Device Groups.
| Property | Description |
| meraki.api.key | Meraki API key (key must be generated and API must be enabled as discussed in previous section) |
| snmp.port | 16100 |
| snmp.version | Because LogicMonitor is not querying the devices themselves, but rather the Cloud Controller, it is not able to automatically assign the SNMP version to this property as it typically does for other monitoring operations that leverage SNMP. Be sure to manually assign the corresponding SNMP version (either “v2c” or “v3”) to this property. |
| snmp.community (v2c only) snmp.security (v3 only) | These values are generated by Meraki and start with “o/”. |
| Other SNMP credentials | The properties required to establish the remaining SNMP credentials vary depending on the SNMP version being used. For more information, see Defining Authentication Credentials. |
Adding Resources to Monitoring
Use an Advanced NetScan to automatically add all relevant devices into monitoring (and auto-assign several required device properties). Or, you can manually add the devices into monitoring.
Adding Resources Using NetScan
To create an Advanced NetScan, see Creating an Advanced NetScan. Apply the following settings to the Advanced NetScan:
- Select Upload a script or csv to discover devices as the Method.
- Select Embed a Groovy script as the scripting option.
- Copy the following Groovy script and paste it into the field provided.
- Insert your API token into the line:
def token = ""
/*******************************************************************************
* © 2007-2024 - LogicMonitor, Inc. All rights reserved.
******************************************************************************/
import com.santaba.agent.groovy.utils.GroovyScriptHelper as GSH
import com.logicmonitor.mod.Snippets
modLoader = GSH.getInstance(GroovySystem.version).getScript("Snippets", Snippets.getLoader()).withBinding(getBinding())
meraki = modLoader.load("cisco.meraki", "0")
// Set this variable to meraki API token.
def token = ''
def urlList = [['https://api.meraki.com/api/v1', 'snmp.meraki.com'], ['https://api.meraki.cn/api/v1', 'snmp.meraki.cn']]
def serviceUrl, snmpUrl
// Optionally, create a list of organizations (e.g. [1243,2343,3564,4355])
// Setting this variable will only discover networks on those orgs.
List<Long> orgsAllowed = null
orgsAllowed = orgsAllowed?.collect{ it.toLong() }
Boolean debug = false
def orgs
urlList.find{ urls ->
try {
orgs = meraki.cachedHttpGet(token, "/organizations", [:], urls[0])
serviceUrl = urls[0]
snmpUrl = urls[1]
}
catch(java.net.ProtocolException ignored){ } //service url didn't work, trying next one
}
orgs.each { org ->
def orgId = org.id
// Filter in only allowed orgs if it's defined.
if (orgsAllowed != null) {
if (!orgsAllowed.contains(orgId.toLong())) {
return
}
}
def orgName = org.name
def networks = []
def devices = []
try {
networks = meraki.cachedHttpGet(token, "/organizations/${orgId}/networks", [:], serviceUrl)
devices = meraki.cachedHttpGet(token, "/organizations/${orgId}/devices", [:], serviceUrl)
} catch (Exception error) {
if (debug) println error.message
return
}
networks.each { network ->
def networkId = network.id
// Check if this network has any devices and avoid reporting deviceless networks.
def networkDevices = devices.findAll{it.networkId == networkId}
if (networkDevices.size() == 0) {
return
}
def networkName = network.name
def networkTags = network.tags.join(",")
def hostName = "${orgName.replaceAll('\\W', '')}.${networkName.replaceAll('\\W', '')}.invalid"
def displayName = "Meraki Network: ${networkName}"
println "${hostName}##${displayName}##meraki.org.name=${orgName}##meraki.org.id=${orgId}##meraki.api.key=${token}##meraki.network.id=${networkId}##meraki.network.name=${networkName}##meraki.network.tags=${networkTags}##meraki.service.url=${serviceUrl}##meraki.snmp.url=${snmpUrl}"
}
// Only add orgs if they have networks.
if (networks.size() > 0) {
println "${orgName.replaceAll('\\W', '')}.invalid##Meraki Org: ${orgName}##meraki.org.name=${orgName}##meraki.org.id=${orgId}##meraki.api.key=${token}##meraki.service.url=${serviceUrl}##meraki.snmp.url=${snmpUrl}"
}
}
def domain = (serviceUrl.split(/\/+/) as List<String>)?.get(1)
apiDevice = [domain, domain, "meraki.api.key=${token}", "meraki.service.url=${serviceUrl}", "meraki.snmp.url=${snmpUrl}"].join("##")
println apiDevice
return 0- In the Default Group field, enter the Cisco Meraki device group you created.
Note: Your SNMP credentials and Meraki key must be set as properties on this group before running the NetScan. For more information, see Create a Meraki Device Group.
- Select Save or Save & Run.
Manually Add Devices into Monitoring
You can manually add your Meraki devices into monitoring. There are three types of Meraki devices that can be added:
- Network device
- Organization device
- Meraki API device
When adding these devices, assign them to the device group you created previously. For instructions on manually adding resources into monitoring, see Adding Devices.
Network Device
The network device reports per-device and per-interface data for a specific network.
- The network device’s hostname (as entered into the IP Address/DNS name field) must end with
.invalid. - Network-specific properties must be assigned to the device. For more information, see Assign Properties to Resources.
Organization Device
The organization device reports per-network device counts and API Usage statistics for a specific organization.
- The organization device’s hostname (as entered into the IP Address/DNS name field) must end with
.invalid. - Organization-specific properties must be assigned to the device. For more information, see Assign Properties to Resources.
Meraki API Device
The Meraki API device reports per-network device counts and API Usage statistics for all organizations on the account.
- The Meraki API device’s hostname (as entered into the IP Address/DNS name field) must be
api.meraki.com.
Assign Properties to Resources
In addition to the group-level properties you configured, you must also set the following device-level properties in LogicMonitor. If you used a NetScan to add these resources into monitoring, the properties are assigned automatically.
| Property | Description |
| meraki.org.id | Set this property on organization devices only. For a list of organizations and their respective IDs, visit https://developer.cisco.com/meraki/api-v1/#!get-organizations. |
| meraki.network.id | Set this property on network devices only. Enter the organization ID for the organization for which you want to see networks. For a list of networks and their respective IDs, visit https://developer.cisco.com/meraki/api-v1/#!get-organization-networks. |
| meraki.service.url | The service URL https://api.meraki.com/api/v1 is used by default. An alternative service url such as https://api.meraki.cn/api/v1 can be specified. |
| meraki.snmp.url | The SNMP URL snmp.meraki.com is used by default. An alternative SNMP URL such as snmp.meraki.cn can be specified. |
Note: Set the X-Cisco-Meraki-API-Key header to your API key when running any API requests from https://developer.cisco.com/meraki/api.
Multiple Organizations
Some Meraki configurations can encompass multiple organizations with different SNMP credentials. In such instances, resources belonging to an organization can be grouped by creating a dynamic group for each organization and assigning the specific properties there.
Importing LogicModules
From the LogicMonitor public repository, import all Cisco Meraki LogicModules, which are listed in the LogicModules in Package section of this support article. If these LogicModules are already present, ensure you have the most recent versions.
Once the LogicModules are imported (assuming all previous setup requirements have been met), the suite of Meraki DataSources will automatically begin collecting data.
LogicModules in Package
LogicMonitor’s package for Cisco Meraki consists of the following LogicModules. For full coverage, please ensure that all of these LogicModules are imported into your LogicMonitor platform.
| Display Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Access Point Interfaces | DataSource | Monitors Meraki Access Point interface data throughput and packet transmission on a per-network level. |
| Access Points | DataSource | Monitors Meraki Access Point client connections and operating status. |
| Gateway Interfaces | DataSource | Monitors Meraki Teleworker Gateway interface data throughput and packet transmission on a per-network level. |
| Gateways | DataSource | Monitors Meraki Teleworker Gateway client connections and operating status. |
| Meraki API Usage | DataSource | Counts Meraki API Usage on a per-org basis. |
| Meraki Device Count | DataSource | Count of Meraki devices by organization on a per-network level as well as a total count. |
| Meraki Device Count | DataSource | Count of Meraki devices by organization. |
| Meraki License Status | DataSource | Reports licensing status of a given organization, of type “co-term”, in Meraki. |
| Meraki Licenses | DataSource | Reports licensing status of a given organization in Meraki using the v1 API. This version supports per-device licensing. |
| Meraki Troubleshooter | DataSource | Validates configuration of Cisco Meraki devices. |
| Meraki_Cloud_Topology | TopologySource | Map Meraki Cloud topologies |
| Meraki_Org_Topology | TopologySource | Map Meraki Org topologies |
| Security Appliance Interfaces | DataSource | Monitors Meraki Security Appliance interface data throughput and packet transmission on a per-network level. |
| Security Appliances | DataSource | Monitors Meraki Security Appliance client connections and operating status. |
| Switches | DataSource | Monitors Meraki Switch client connections and operating status. |
| Uplink Appliance Status | DataSource | Lists the uplink status of every Meraki MX and Z series appliances in the organization. |
| Uplink Loss And Latency | DataSource | Returns the uplink loss and latency for every MX in the organization. |
| addCategory_Meraki_API | PropertySource | Identifies if the host is configured for Meraki API access, adds various system auto properties and appropriate system category of based on whether it is an organization or network device. See Cisco Meraki Monitoring for more information. |
| addERI_Meraki | PropertySource | Adds ERI’s for Meraki hosts. See Cisco Meraki Monitoring for more information. Requires collector version 30.000 or greater. |
| addERI_Meraki_Device | PropertySource | Discover and add meraki specific ERI’s for meraki resources |
| addERI_Meraki_Org | PropertySource | Adds ERI’s for Meraki orgs. See Cisco Meraki Monitoring for more information. Requires collector version 30.000 or greater. |
When setting static datapoint thresholds on the various metrics tracked by this package’s DataSources, LogicMonitor follows the technology owner’s best practice KPI recommendations. If necessary, we encourage you to adjust these predefined thresholds to meet the unique needs of your environment. For more information on tuning datapoint thresholds, see Tuning Static Thresholds for Datapoints.
Migration from Legacy DataSources
In June 2022, LogicMonitor updated the Cisco Meraki suite to use the Meraki API v1 and expand topology support for identifying Meraki devices. As part of this update, the Cisco_Meraki_Switch_Interfaces DataSource was deprecated. You can still monitor switch connection status and client count using the Cisco_Meraki_Switches DataSource. For more information, see Deprecated LogicModules.
In June 2020, LogicMonitor released a new suite of Cisco Meraki DataSources to expand monitoring coverage and improve efficiency for future scalability and support. The release of these new DataSources serves to deprecate the following legacy Meraki DataSources:
- Meraki_CloudController_DeviceInventory
- Meraki_MR_Interfaces
- Meraki_MR_Stats
- Meraki_MS_Stats
- Meraki_MX_Interfaces
- Meraki_MX_Stats
- Meraki_Z_Interfaces
- Meraki_Z_Stats
If you are currently monitoring Meraki devices using any of these legacy DataSources, you will not experience data loss upon importing the new DataSources. This is because DataSource names have been changed to eliminate module overwriting.
However, you will collect duplicate data and receive duplicate alerts for as long as both sets of DataSources are active. For this reason, we recommend that you disable the above-listed DataSources after importing the new set of DataSources and confirming that they are working as intended in your environment.
When a DataSource is disabled, it stops querying the host and generating alerts, but maintains all historical data. At some point in time, you may want to delete the legacy DataSources altogether, but consider this move carefully as all historical data will be lost upon deletion. For more information on disabling DataSources, see Disabling Monitoring for a DataSource or Instance.
The LogicMonitor monitoring suite for the Dell PowerSwitch N-Series switches uses SNMP to query the PowerSwitch N-Series switches for health and performance metrics.
Compatibility
As of March 2022, LogicMonitor’s Dell PowerSwitch N-Series package is known to be compatible with:
- PowerSwitch N-Series 2000 and 3000 models.
Setup Requirements
- Collector version 30 or higher is required.
- SNMP must be enabled on the device.
Assign Properties to Resources
The following custom properties must be set on the PowerSwitch N-Series resource within LogicMonitor. For more information on setting properties, see Resource and Instance Properties.
| Property | Value |
| SNMP credentials | The properties required to establish SNMP credentials vary depending on the SNMP version being used. See Defining Authentication Credentials for details. |
| system.category | Add “PowerSwitchNSeries”. This value is automatically added by the property source addCategory_PowerSwitchNSeries. |
Import LogicModules
From the LogicMonitor public repository, import all PowerSwitch N-Series LogicModules, which are listed in the LogicModules in Package section of this support article. If these LogicModules are already present, ensure you have the most recent versions. Data collection will start automatically once the LogicModules are imported.
LogicModules in Package
LogicMonitor’s package for PowerSwitch N-Series consists of the following LogicModules. For full coverage, please ensure that all of these LogicModules are imported into your LogicMonitor platform.
| Display Name | Type | Description |
| addCategory_PowerSwitchNSeries | PropertySource | Identifies if the host is a PowerSwitch N-Series device and sets system category of ‘PowerSwitchNSeries’. |
| PowerSwitch N Series Temperature | DataSource | Temperature measured in degrees in celsius for all the sensors in the switch. |
| PowerSwitch N Series Resource Metrics | DataSource | Gathers resource metrics from the switch, including Memory, and CPU utilization. |
| PowerSwitch N Series Global Statistics | DataSource | Monitors the uptime and global status of the switch. |
| PowerSwitch N Series CPU Process Utilization | DataSource | Collects the CPU utilization for all the processes running on the switch. |
When setting static datapoint thresholds on the various metrics tracked by this package’s DataSources, LogicMonitor follows the technology owner’s best practice KPI recommendations. If necessary, we encourage you to adjust these predefined thresholds to meet the unique needs of your environment. For more information on tuning datapoint thresholds, see Tuning Static Thresholds for Datapoints.
LogicMonitor’s Linux PSI monitoring package leverages SSH to monitor the CPU, Memory and IO load of your Linux resource.
Compatibility
As of March 2022, LogicMonitor’s Linux PSI package is known to be compatible with:
- Linux Kernel version 4.20 and higher.
Setup Requirements
- SSH must be configured to detect the Linux system and its kernel version. This is required for the addCategory_LinuxPSI PropertySource.
- The Linux_SSH_Info PropertySource must run before addCategory_LinuxPSI PropertySource can verify Linux Kernel version and apply the “LinuxPSI” system.categories property. Dependencies are in the following order: addCategory_Linux_SSH -> Linux_SSH_Info -> addCategory_LinuxPSI.
- The Linux bootloader must have Linux PSI enabled for the module to run successfully.
- Collector version 30.000 and greater is required.
Add Resources into Monitoring
Add your Linux hosts into monitoring. For more information on adding resources into monitoring, see Adding Devices.
Assign Properties to Resources
The following custom properties must be set on the Linux PSI resource within LogicMonitor. For more information on setting properties, see Resource and Instance Properties.
| Property | Value |
| ssh.user | (Required) Secure Shell username. |
| ssh.pass | Secure Shell password. (Optional if public key is used.) |
| ssh.cert | Secure Shell public and private key. (Optional if password is used.) |
| ssh.port | Secure Shell port to use to access the resources data. Defaults to 22 (SSH). |
| system.category | Add “LinuxPSI”. This value is set automatically by the addCategory_LinuxPSI PropertySource. |
Import LogicModules
From the LogicMonitor public repository, import all Linux PSI LogicModules, which are listed in the LogicModules in Package section of this support article. If these LogicModules are already present, ensure you have the most recent versions. Data collection will start once the LogicModules are imported.
Troubleshooting
The module may not report all datapoints based on system configuration. For example, a single-core processor or 1 vCPU VM will only show “some CPU” metrics, while a dual-core or 2 vCPU VM will show “full CPU” metrics.
LogicModules in Package
LogicMonitor’s package for Linux PSI consists of the following LogicModules. For full coverage, make sure that all of these LogicModules are imported into your LogicMonitor platform.
| Display Name | Type | Description |
| addCategory_LinuxPSI | PropertySource | Adds property system.categories = LinuxPSI if running the running Kernel on the Linux system is running a version higher than 4.20. |
| Linux PSI | DataSource | Linux Pressure Stall Information monitors CPU, Memory and IO load. |
The DataSources in this package do not include predefined datapoint thresholds (that is, no alerts will trigger based on collected data). This is because the technology owner has not provided KPIs that can be reliably extended to the majority of users. To receive alerts for collected data, you need to manually create custom thresholds. For more information, see Tuning Static Thresholds for Datapoints.


