What is IT automation?


IT automation uses software and technology to handle repetitive IT tasks automatically, reducing the need for manual work and accelerating processes like infrastructure management and application deployment. This transformation is essential for IT teams needing to scale efficiently, as seen in the case of Sogeti, a Managed Service Provider (MSP) that provides tech and engineering resources worldwide.
Sogeti had a crucial IT challenge to solve. The MSP operates in more than 100 locations globally and uses six different monitoring tools to monitor its customers’ environments. It was a classic example of tool sprawl and needing to scale where multiple teams of engineers relied on too many disparate tools to manage their customers’ environments. It soon became too arduous for the service provider to collect, integrate, and analyze the data from those tools.
Sogeti had teams of technicians managing different technologies, and they all existed in silos. But what if there was a way to combine those resources?
IT automation provided a solution.
After working with LogicMonitor, Sogeti replaced the bulk of its repeatable internal processes with automated systems and sequences. The result? Now, they could continue to scale their business with a view of those processes from a single pane of glass.
Conundrum cracked.
That’s just one example of how IT automation tools completely revolutionizes how an IT services company like an MSP or DevOps vendor can better execute its day-to-day responsibilities.
By automating repeatable, manual processes, IT enterprises streamline even the most complicated workflows, tasks, and batch processes. No human intervention is required. All it takes is the right tech to do it so IT teams can focus on more strategic, high-priority efforts.
But what exactly is IT automation? How does it work? What are the different types? Why should IT companies even care?
IT automation is the creation of repeated software processes to reduce or eliminate manual or human-initiated IT tasks. It allows IT companies with MSPs, DevOps teams, and ITOps teams to automate jobs, save time, and free up resources.
IT automation takes many forms but almost always involves software that triggers a repeated sequence of events to solve common business problems—for example, automating a file transfer. It moves from one system to another without human intervention or autogenerates network performance reports.
Almost all medium and large-sized IT-focused organizations use some automation to facilitate system and software processes, and smaller companies benefit from this tech, too. The most successful ones invest heavily in the latest tools and tech to automate an incredible range of tasks and processes to scale their business.
The production, agricultural, and manufacturing sectors were the first industries to adopt IT automation. However, this technology has since extended to niches such as healthcare, finance, retail, marketing, services, and more. Now, IT-orientated companies like MSPs and enterprise vendors can incorporate automation into their workflows and grow their businesses exponentially.
IT automation software empowers teams to handle complex tasks effortlessly, allowing them to focus on strategic priorities.
The software does all the hard work. Clever programs automate tasks that humans lack the time or resources to complete themselves.
Developers code these programs to execute a sequence of instructions that trigger specific events from specific operating systems at specific times. For example, programming software so customer data from a customer relationship management system (CRM) generates a report every morning at 9 a.m. Users of those programs can then customize instructions based on their business requirements.
With so many benefits of IT automation, it’s no wonder that two-thirds of CFOs plan to accelerate the automation of repetitive tasks within their companies.
IT-focused businesses use automation for various reasons:
IT automation delivers many advantages that extend beyond simple task delegation. Let’s look at a few benefits your organization will see.
With the complexity of modern IT infrastructure, modern environments may handle thousands of requests daily—everything from password resets to system failures. Automation can help reduce the time it takes to handle many of those requests. For example, look at an IT telecommunications company with a lot of infrastructure. They can automate their network configuration process, cutting the deployment time from a few weeks to less than a day.
Human error in IT environments can be costly. Errors can lead to unexpected system downtime, security breaches, and data entry errors—all of which you can avoid by standardizing consistency and standards through automation. Automation helps your team eliminate routine data entry and other tasks and greatly reduces the chance of human error. For example, your team may decide to create backup scripts for more complicated setups to ensure you always have reliable backups.
Automation helps speed up responses to common IT requests. If your IT team is stuck needing to perform every task manually, it increases incident response time and the length of time your customer waits on the other end of the line for a fix. Automation speeds up common tasks—setting up VPN access, account resets, report creation, and security scans—allowing your team to focus on finding the root cause of problems, deploying resources, and bringing systems back online.
Your organization’s IT needs may fluctuate depending on how many users you have and their activities. A strict guide for resource usage may result in some users being unable to work efficiently because of slow systems. Automation can help by automating resource allocation. For cloud services, you can scale your servers based on demand, and for network traffic, you can dynamically adjust traffic routes based on usage.
Automated systems can help your team maintain detailed audit trails and enforce consistent security policies. They can also help with continuous monitoring, allowing your team to get alerts immediately when your solution detects suspicious activity. Additionally, your IT systems can automatically generate compliance reports, such as SOC 2, for review, helping your team find potential problems and comply with audit requests.
With the right technology, IT automation can turn time-consuming processes into streamlined, efficient workflow
IT companies benefit from various types of IT automation.
A branch of computer science concerned with developing machines that automate repeatable processes across industries. In an IT-specific context, artificial intelligence (AI) automates repetitive jobs for engineers and IT staff, reduces the human error associated with manual labor, and allows companies to carry out tasks 24 hours a day.
Machine learning (ML) is a type of AI that uses algorithms and statistics to find real-time trends in data. This intelligence proves valuable for MSPs, DevOps, and ITOps companies. Employees can stay agile and discover context-specific patterns over a wide range of IT environments while significantly reducing the need for case-by-case investigations.
Robot Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that instructs ‘robots’ (machines) to emulate various human actions. Although less common in IT environments than in AI and ML, RPA still provides value for MSPs and other professionals. For example, enterprises can use RPA to manage servers, data centers, and other physical infrastructure.
IT infrastructure automation involves using tools and scripts to manage computing resource provisioning with manual intervention. This includes tasks like server provisioning, bandwidth management, and storage allocation. This allows for dynamic resource usage, with the most resources going to the users and applications with the most need.
A proper automation strategy is critical for IT companies. CIOs and executives should decide how to achieve automation within their organizations and then choose the right tools and technologies that facilitate these objectives.
Doing so will benefit your business in many ways.
Here are some examples of how IT companies use automation:
Companies can automate templates and blueprints, promoting the successful rollout of services such as network security and data center administration.
Automation allows companies to integrate technology with workflows. As a result, CIOs and executives complete day-to-day tasks more effectively with the latest hardware and software. For example, automating server management to improve service level management workflows proves useful if clients expect a particular amount of uptime from an MSP.
AI and ML might be hard for some companies to grasp at first. However, teams can learn these technologies over time and eventually combine them for even more effective automation within their organizations.
Automated applications like the LogicMonitor Collector, which runs on Linux or Windows servers within an organization’s infrastructure, use monitoring protocols to track processes without manual configuration. Users discover network changes and network asset changes automatically.
IT companies can monitor components like device clusters or a VM in a public cloud and scale resources up or down as necessary.
Hardware and software can provide companies like MSPs with all kinds of problems (downtime, system errors, security vulnerabilities, alert storms, etc.). Automation, however, identifies and resolves infrastructure and system issues with little or no human effort.
Automation can automatically generate regular performance reports, SLA reports, compliance reports, and capacity planning forecasts. It can also generate automated alerting systems in case of problems and report trends to help your business with capacity planning.
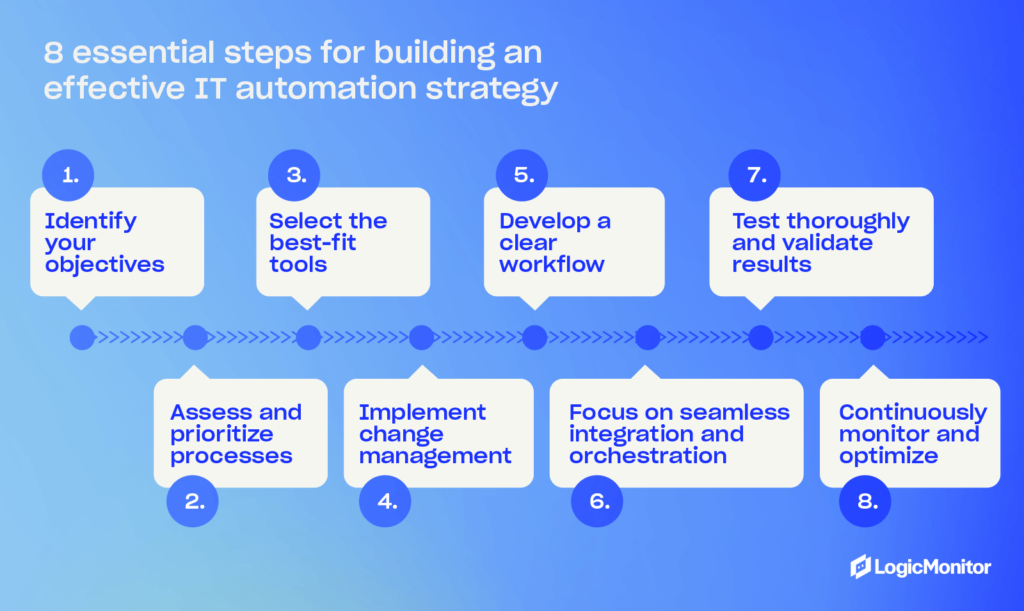
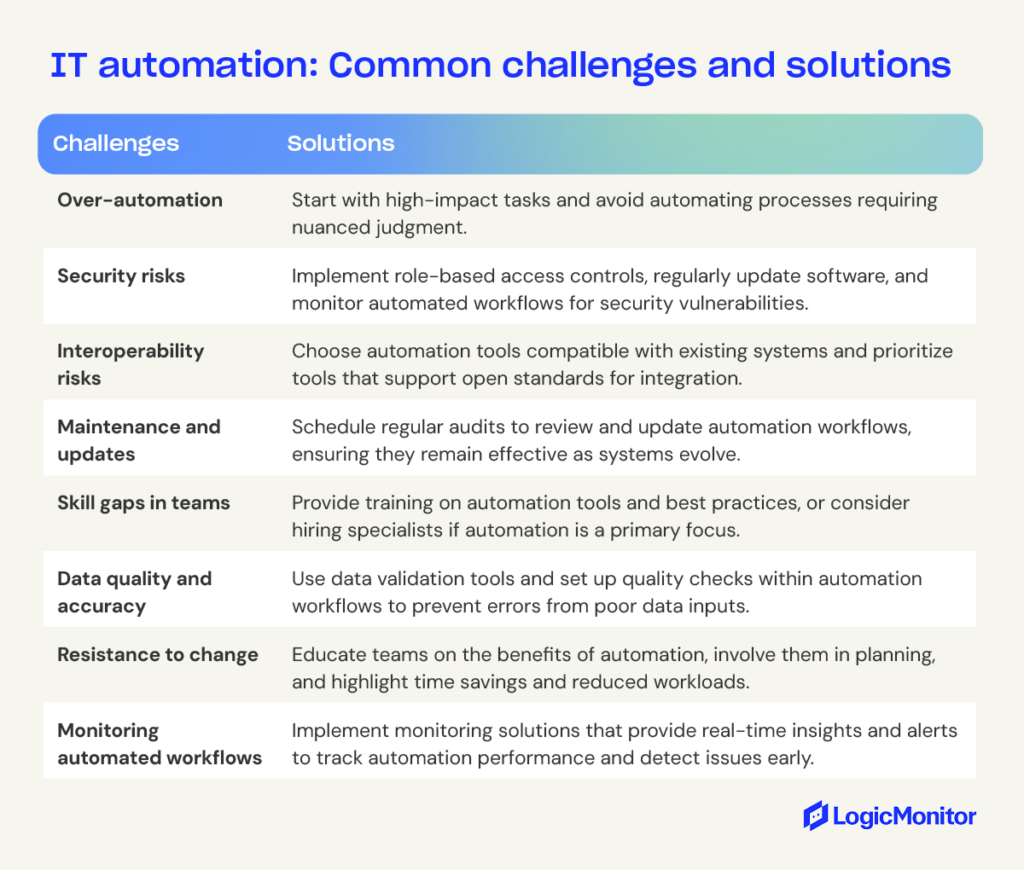
Successfully automating IT in business requires careful planning and thoughtful execution. Follow these best practices to avoid the common mistakes and maximize efficiency:
Automating routine IT tasks frees teams from manual work, paving the way for innovation and growth
Here are some pros and cons of automation for those working in IT:
Read more: The Leading Hybrid Observability Powered by AI Platform for MSPs
There’s a misconception that IT automation will cause job losses. While this might prove true for some sectors, such as manufacturing, IT-focused companies have little to worry about. That’s because automation tools don’t work in silos. Skilled IT professionals need to customize automation tools based on organizational requirements and client demands. MSPs that use ML, for example, need to define and determine the algorithms that identify real-time trends in data. ML models might generate data trends automatically, but MSPs still need to select the data sets that feed those models.
Even if automation takes over the responsibilities of a specific team member within an IT organization, executives can upskill or reskill that employee instead of replacing them. According to LogicMonitor’s Future of the MSP Industry Research Report, 95% of MSP leaders agree that automation is the key to helping businesses achieve strategic goals and innovation. By training employees who currently carry out manual tasks, executives can develop a stronger, higher-skilled workforce that still benefits from IT automation.
AI, machine learning, and cloud computing advancements are significantly altering how businesses manage their IT infrastructure. As these technologies continue to evolve, how you manage your business will change along with them.
Here’s what to expect in the future of IT automation:
Traditional automation tools use a rules-based approach: a certain event (e.g., time of day, hardware failure, log events) triggers an action through the automation systems.
Advanced AI operations tools are changing that with their ability to predict future events based on data. That leads to more intelligent automation that doesn’t require a rules-based system. These systems understand natural language, recognize patterns, and make decisions based on real-time data. They allow for more responsive IT systems that anticipate and fix problems.
The growing adoption of cloud environments—which include private, public, and on-prem resources—requires your business to adopt new strategies to manage infrastructure and automate tasks. You need tools that seamlessly integrate with all environments to ensure performance and compliance where the data resides.
Hybrid environments also allow for more flexibility and scalability for IT infrastructure. Instead of being limited by physical constraints, your business can use the cloud to scale computing resources as much as needed. Automated provisioning and deployment means you can do this at scale with minimal IT resources.
As workforces and companies become more distributed, your business needs a way to provide resources to customers and employees in different regions. This may mean a web service for customers or a way for employees to access business services.
Edge devices can help supply resources. Automation will help your business manage edge devices, process data on the edge, and ensure you offer performant applications to customers and employees who need them.
Successful data-driven IT teams require technology that scales as their business does, providing CIOs and executives with ongoing value. LogicMonitor is the world’s only cloud-based hybrid infrastructure monitoring platform that automates tasks for IT service companies like MSPs.
LogicMonitor features include:
IT automation has revolutionized the IT sector, reducing the manual responsibilities that, for years, have plagued this industry. MSPs no longer need to enter network performance data into multiple systems, physically inspect servers, manage and provision networks manually, analyze performance reports, or perform other redundant tasks manually. Automation does a lot of the hard work so that these IT professionals can focus on far more critical tasks. By incorporating cloud-based infrastructure monitoring, AI, machine learning, and other new technologies, your IT executives improve productivity, enhance workflows, reduce IT resources, promote better client outcomes, and reduce costs over time.
By automating routine processes, IT automation speeds up incident response, account setup, report creation, and other common tasks. This leads to faster fixes and better customer satisfaction.
Popular types include infrastructure automation (server provisioning and resource management), AI/ML-based automation (pattern recognition and trend analysis), and robot process automation for handling repetitive admin tasks.
Automation helps enforce security policies, maintain audit trails, and generate compliance reports. It can also trigger alerts for suspicious activity, supporting better governance.
No. IT automation handles repetitive tasks, but skilled professionals are still needed to design, manage, and improve automated systems. Automation often leads to upskilling rather than job loss.
LogicMonitor provides a cloud-based platform that automates monitoring, reporting, and problem detection across hybrid environments. It helps you to scale without extra hardware or maintenance.
© LogicMonitor 2026 | All rights reserved. | All trademarks, trade names, service marks, and logos referenced herein belong to their respective companies.
