BatchScript Data Collection
Last updated - 24 July, 2025
Overview
The BatchScript Data Collection method is ideal for DataSources that:
- Will be collecting data from a large number of instances via a script, or
- Will be collecting data from a device that doesn’t support requests for data from a single instance.
The Script Data Collection method can also be used to collect data via script, however data is polled for each discovered instance. For DataSources that collect across a large number of instances, this can be inefficient and create too much load on the device data is being collected from. For devices that don’t support requests for data from a single instance, unnecessary complication must be introduced to return data per instance. The BatchScript Data Collection method solves these issues by collecting data for multiple instances at once (instead of per instance).
Note:
- Datapoint interpretation methods are limited to multi-line key-value pairs and JSON for this collection method. For more information on datapoint interpretation methods, see Normal Datapoints.
- The instances’ WILDVALUE cannot contain the following characters:
:
#
\
spaceThese characters should be replaced with an underscore or dash in WILDVALUE in both Active Discovery and collection.
How the BatchScript Collector Works
Similar to when collecting data for a DataSource that uses the script collector, the batchscript collector will execute the designated script (embedded or uploaded) and capture its output from the program’s stdout. If the program finishes correctly (determined by checking if the exit status code is 0), the post-processing methods will be applied to the output to extract value for datapoints of this DataSource (the same as other collectors).
Output Format
The output of the script should be either JSON or line-based.
Line-based output needs to be in the following format:
JSON output needs to be in the following format:
{
data: {
instance1: {
values: {
"key1": value11,
"key2": value12
}
},
instance2: {
values: {
"key1": value21,
"key2": value22
}
}
}
}Since the BatchScript Data Collection method is collecting datapoint information for multiple instances at once, the ##WILDVALUE## token needs to be used in each datapoint definition to pass instance name. “NoData” will be returned if your WILDVALUE contains the invalid characters named earlier in this support article.
Using the line-based output above, the datapoint definitions should use the multi-line-key-value pairs post processing method, with the following Keys:
- ##WILDVALUE##.key1
- ##WILDVALUE##.key2
Using the JSON output above, the datapoint definitions should use the JSON/BSON object post processing method, with the following JSON paths:
- data.##WILDVALUE##.values.key1
- data.##WILDVALUE##.values.key2
BatchScript Data Collection Example
If a script generates the following output:
Then the IOPS datapoint definition may use the key-value pair post processing method like this:
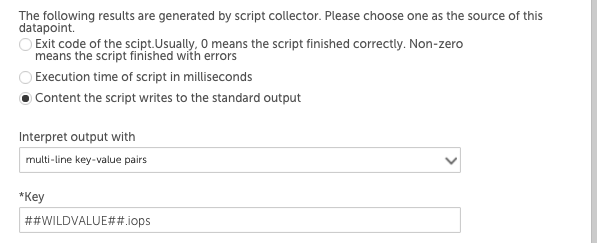
The ##WILDVALUE## token would be replaced with disk1 and then disk2, so this datapoint would return the IOPS values for each instance. The throughput datapoint definition would have ‘##WILDVALUE##.throughput’ in the Key field.
BatchScript Retrieve Wild Values Example
Wild values can be retrieved in the collection script:
def listOfWildValues = datasourceinstanceProps.values().collect { it.wildvalue }datasourceinstanceProps.each { instance, instanceProperties ->
instanceProperties.each
{ it -> def wildValue = it.wildvalue // Do something with wild value }
}

