Syslog LogSource Configuration
Last updated - 06 February, 2026
Recommendation: LogSource is the recommended method for ingesting syslog logs. For more information, see LogSource Overview.
You can ingest syslog logs using LogSource, a LogicModule that enables you to configure which syslog logs are ingested into LM Logs and how they are mapped to resources. You can configure a Syslog LogSource to apply to the Collector itself for broad control over syslog handling, or to individual resources for more specific control.
Every LM Collector includes a pre-configured default LogSource for syslog ingestion. This LogSource is the best out-of-the-box solution for ingesting syslogs because of its simple setup, searchable log views and alerts, ease of filtering, and no required licensing or agents from additional sources.
Collector Syslog Processing
While applying LogSource on a collector, the collector can process Syslog in the following ways:
- If the requirement is to ingest the Syslog events received by the collector, Collector’s agent.conf property “lmlogs.syslog.enabled” can be enabled. This property can also be enabled by turning on Enable log collection for Syslog and SNMP trap option on the Add collector page. With this property enabled, the collector will ingest all the Syslog events without any customization such as Filters, Resource Mapping, and others.
- If the requirement is to add some customisation such as filtering some Syslog events or adding a different method for resource mapping, a LogSource can be created and applied on the Syslog receiving collector using the Apply to Collector(s) option on the LogSource.
- If the requirement is to handle the Syslog events from a device using a specific LogSource definition, a usual LogSource can be applied on a device that is forwarding the Syslog events to the collector.
A usual LogSource that is applied on a device, will be preferred over the LogSource applied on a collector for processing the syslog.
A LogSource that is applied on a collector, will be preferred over collector’s agent.conf property “lmlogs.syslog.enabled” for processing the syslog.
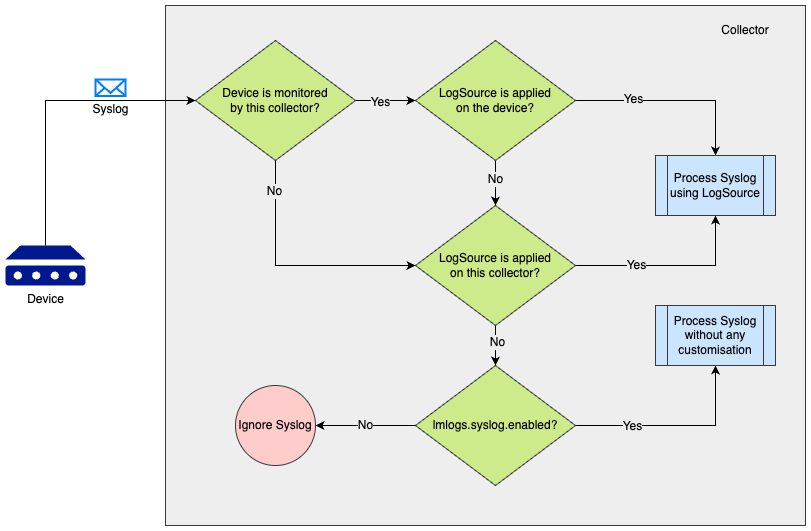
The following scenarios can be referred to understand the syslog processing preference by a collector which is receiving the syslog.
| Scenario | Is the device monitored by the collector* | Is a usual LogSource applied on the device | Is a LogSource applied on collector using the Apply to Collector(s) switch | Is collector’s agent.conf property lmlogs.syslog.enabled set to true | Outcome |
| 1 | Yes | Yes | Any (Yes/No) | Any (Yes/No) | Syslog will be processed using the usual LogSource applied on the device that forwards the Syslog. |
| 2 | Yes | No | Yes | Any (Yes/No) | Syslog will be processed using the LogSource which is applied to the collector that receives the Syslog. |
| 3 | No | Any (Yes/No) | Yes | Any (Yes/No) | Syslog will be processed using the LogSource which is applied to the collector that receives the Syslog. |
| 4 | No | Any (Yes/No) | No | Yes | Syslog will be processed using the agent.conf property (“lmlogs.syslog.enabled”) of the collector that receives the Syslog. |
*A device is said to be monitored by a collector if
- The collector is assigned as a Preferred Collector on Manage Resource page
-or- - The collector is assigned as Log Collector using Set LM Logs Collector option on Manage Resource page
For more information about applying a Collector to a LogSource to process Syslog logs, see Applying LogSource to Collectors.
Include Filters
You can add filters to include resources of certain types, such as an application. The output matching the filter criteria will be forwarded to the log ingestion process.
The following table details the available parameters:
| Attributes | Comparison operator | Value example | Description |
| Application | Equal, NotEqual, Contain, NotContain, Exist, NotExist, RegexMatch, RegexNotMatch. | nginx, apache | Used to filter syslog messages based on the application name that generated them. This filter relies on the presence of application metadata (for example, APP-NAME in syslog messages). Ensure that your syslog source includes this information, as it may not always be present depending on the syslog version or source configuration. |
| Facility | Equal, NotEqual, Contain, NotContain, RegexMatch, RegexNotMatch, Exist, NotExist, GreaterThan, GreaterEqual, LessThan, LessEqual. | Predefined options like “kernel messages”, “system daemons”, and “log alert” | A categorization tag used to specify the type or source of the system process generating the log message. |
| Message | Equal, NotEqual, Contain, NotContain, RegexMatch, RegexNotMatch, Exist, NotExist. | “Failed alert” | Include or exclude syslog logs based on the content of their messages. |
| Severity | Equal, MoreUrgentThan. | Emergency, Alert, Critical, Warning, Notice, Informational, Debug | Indicates the importance of the event, with levels ranging from 0 (Emergency) to 7 (Debug), as defined by the syslog protocol. |
Log Fields
You can configure Log Fields (tags) to send additional metadata with the logs. The following table details the available parameters:
| Method | Key example | Value example | Description |
| Static | “Customer” | “Customer_XYZ” | Attaches a fixed key-value pair to every log processed by the log source, ensuring consistent metadata tagging across all log entries. |
| Dynamic(REGEX) | “Host” | “host=*” | The query will run on the message field. |
| LM Property(Token) | “Device” | “##system.deviceId##” | The DeviceID value extracted from the existing device property in LogicMonitor. |
| Syslog Attribute | “Application, Facility, Log_Level” | Application, Facility, Severity. | Directly maps a specific syslog metadata field to a log field in LM Logs. |
| Dynamic Group Regex | “Scheme, Login” | “(https*):\/\/([]a-z]+)” | The query runs on the message field and captures the first group value from Regex. The keys for Dynamic Group Regex can be added as a comma separated list and values are read from same number of groups. For the Key and Value example provided in this table, the regex results in metadata for key and value, which is, Scheme and Login. For example: Scheme=https Login=<Actual username extracted from the message> Note: The Dynamic Group Regex method for log fields is available from the LM collector version 34.200 and later. |
Resource Mappings
Configure the LM log property to match a monitored resource. The following table details the available parameters:
| Method | Key example | Value example | Description |
| Static | “Customer_Id” | “1921” | Maps log messages to a specific monitored resource by matching a predetermined key-value pair corresponding to a resource property. |
| IP | “system.ips” | “10.20.30.40” | Use the syslog host field information and resolve it to IP (For example “10.20.30.40”). The Value field is disabled if you select this method, you can only enter a Key. |
| FQDN | “system.hostname” | “application.service.example.com” | Fully Qualified Domain Name, from DNS resolution of hostname received from syslog message or socket address. |
| HOSTNAME | “system.hostname” | “host1.example.com” | The Value field is disabled if you select this method, you can only enter a Key. |
| HOST WITHOUT DNS | “system.hostname” | “host1” | The Value field is disabled if you select this method, you can only enter a Key. |
| Dynamic(REGEX) | “system.ServiceName” | “service=*” | The query will run on the message field. |
| LM Property(Token) | “token.resourceMap” | “syslog_test_collector” | The DeviceID extracted from the existing device property in LogicMonitor. |
| Dynamic Group Regex | “Scheme, Login” | “(https*):\/\/([]a-z]+)” | The query runs on the message field and captures the first group value from Regex. The keys for Dynamic Group Regex can be added as a comma separated list and values are read from same number of groups. For the Key and Value example provided in this table, the regex results in metadata for key and value, which is, Scheme and Login. For example: Scheme=https Login=<Actual username extracted from the message> Note: The Dynamic Regex Group method for resource mapping is available from the LM collector version 35.200 and later. |
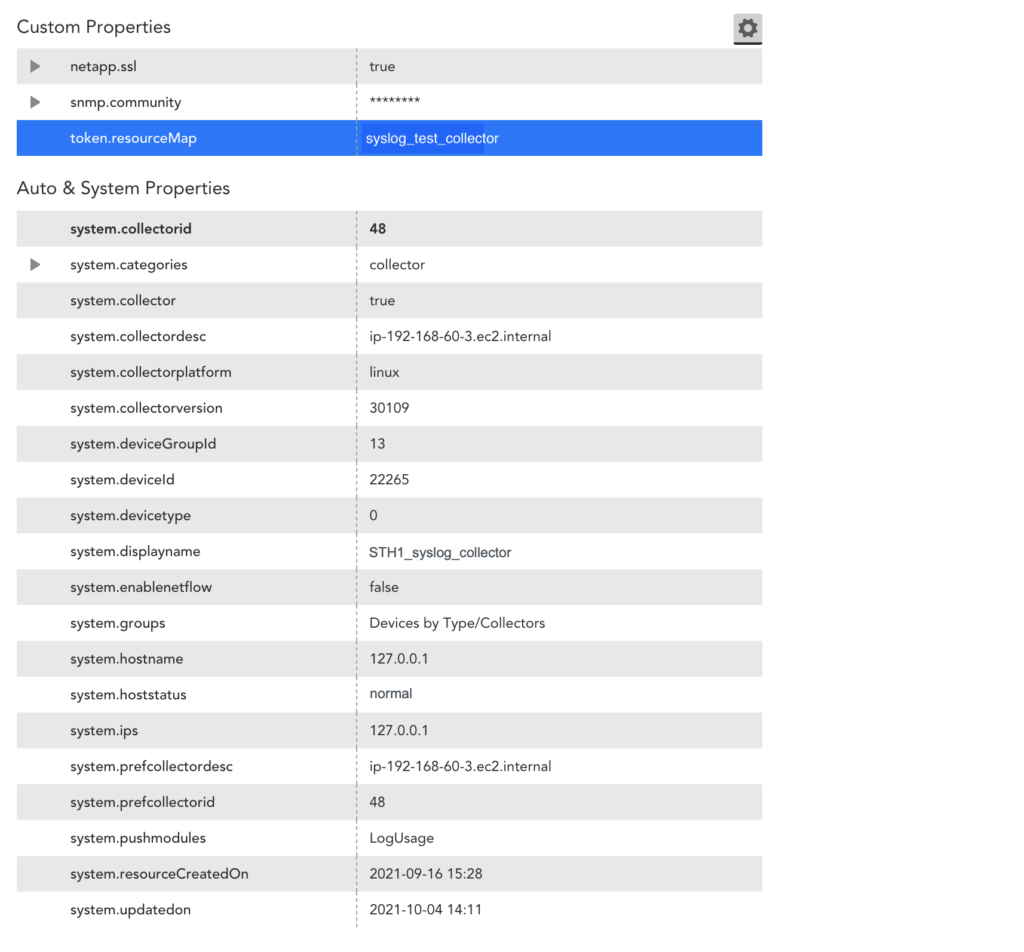
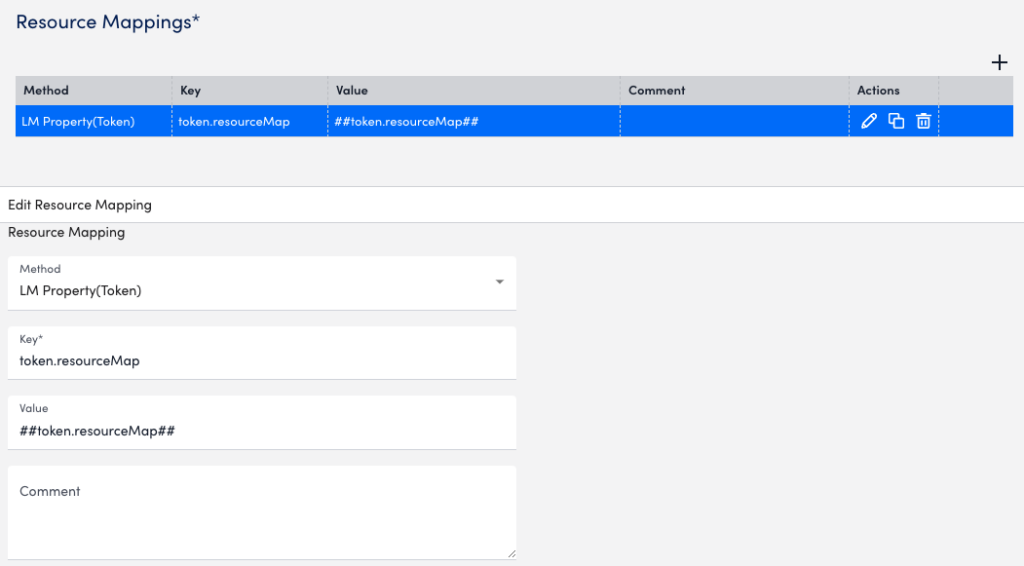
The following is an example of a resource mapping using the LM Property (Token) method. In this example, you provide a property to map to one of the monitored devices in the LM portal. The key for the LM Property is token.resourceMap and the value is syslog_test_collector.
When a LogSource is applied on the device, the resource mapping is processed with LM_property as token.resourceMap, the source as LM Property, the parse method as Token, and the value as any item starting with ##, such as ##token.resourceMap##.
The collector receives the hostEntry from the feed, and replaces the ##token.resourceMap## with the value received against the LM_property token.resourceMap for that particular host (for example, syslog_test_collector).
If there are multiple resources to which the log source is applied, the value for LM_property should be unique. Otherwise the Ingest API will not map it to the resource.
The following image is from the Resources information for the syslog_test_collector example.
The following image is from the resource mapping in LogSource for the syslog_test_collector example.
The resource mapping on the Collector side for this LogSource is as follows:
'{"metadata":{"logSource_id":"2249","logsource_name":"syslog_test_token"},"Severity":"3: Error","Host":"localhost","epochWhenAddedInQueue":1633501246808,"Facility":"1: user-level messages","message":"<11>Just a message with metadata test_md1 !!\u0000","_lm.resourceId":{"token.resourceMap":"syslog_test_collector"},"timestamp":1633501246808,"_lm.collectorId":"48"}', raw:'<11>Example message with metadata test_md1 !!'Requirements for Configuring a Syslog LogSource
You must have an LM Collector installed on the machine ingesting syslog logs. For more information, see About the LogicMonitor Collector.
Configuring a Syslog LogSource
- In LogicMonitor, navigate to Modules > My Module Toolbox.
- Select
 .
. - In the Add modal, select LogSource.
- In the Name field, enter a descriptive and unique name for the source of the syslog logs.
- In the Description field, enter a description of the source of the syslog logs. The description can provide additional context to help you and other users understand the purpose, function, or configuration details of the log source.
- In the Tags field, search for tags (also referred to as log fields) you want to assign to your log source.
Note: Tags are metadata fields used for filtering, grouping, and automation. For more information about tags, see the Log Fields table above. - In the Group field, select one or more groups that best categorize the log source. Groups typically reflect the function, location, or environment of the log origin.
- Use the Technical Notes field to provide detailed reference information that may assist with troubleshooting or maintenance.
- Toggle the Show preview of rendered technical notes switch to view how markdown-formatted content displays when rendered.
- Set the Type dropdown menu to LM Logs: SysLog.
- Toggle the Use received time instead of logstamp switch to use timestamps based on when LogicMonitor receives the syslog messages, rather than the timestamp embedded in the syslog message.
- Add Access Groups to enable who can view, manage, and interact with the logs.
- In the AppliesTo field, define which resources this LogSource should apply to. For example, you can apply the LogSource only to devices in a specified group, tag, or Collector, as seen below:
isInDeviceGroup("Network Devices") *Applies the logsource only to devices in the "Network Devices" group. system.env == "prod" *Applies to devices tagged with env:prod. collectorId == 27 *Applies only to devices using a specific Collector. - Add Filters using the available parameters listed above.
- Review the default Log Fields and edit as needed:
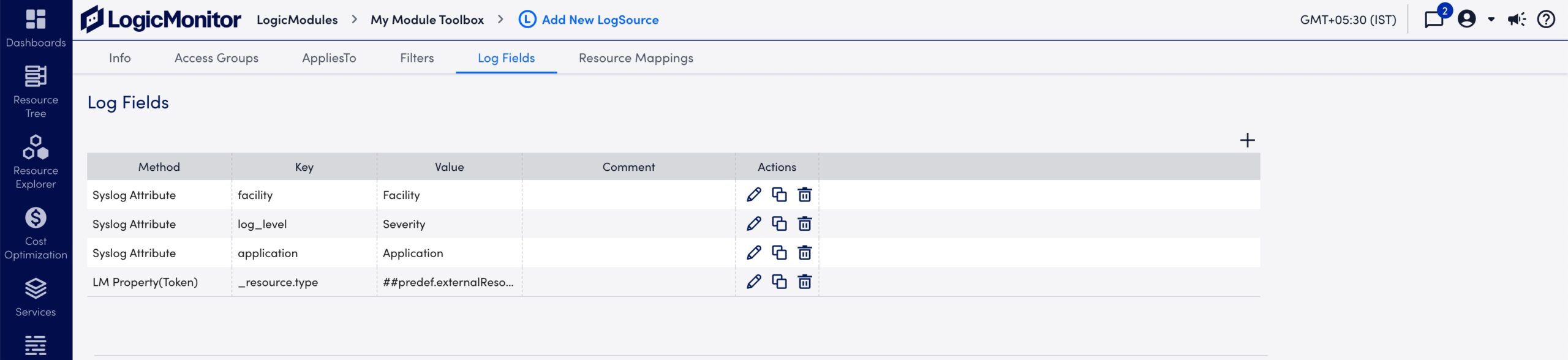
- Review the default Resource Mappings and edit as needed:
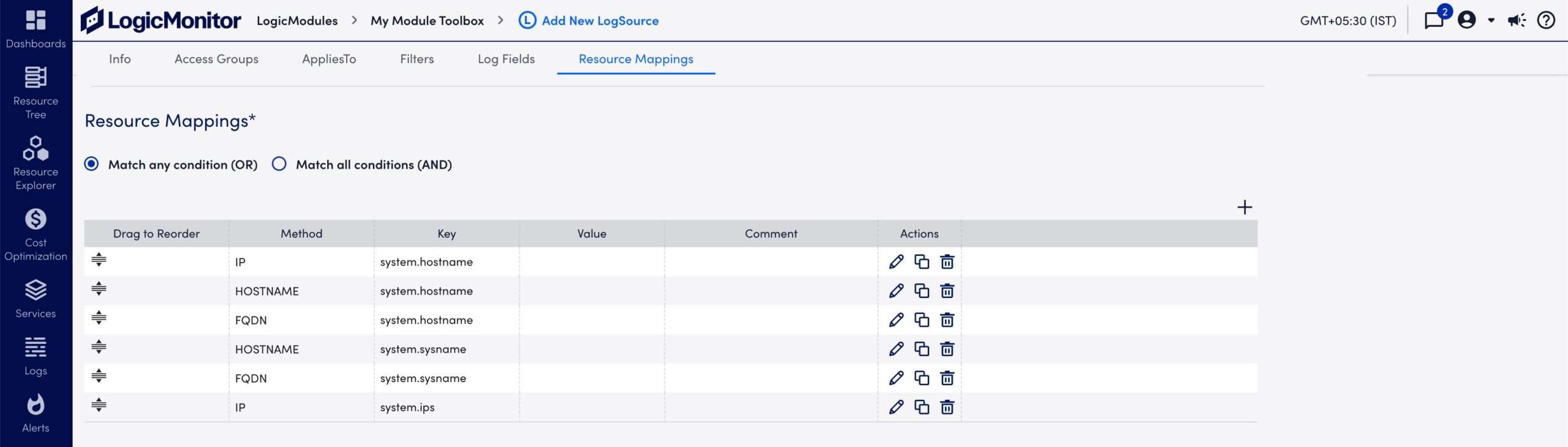
- Select Save.
Apply LogSource to Collectors
With collector version EA-35.200, you can apply LogSource to a collector directly using the Apply to Collector(s) option. The AppliesTo option is also available to apply LogSource to a device. But, if you are using a collector version prior to EA-35.200, you can only use AppliesTo to apply LogSource to a device.
Applying a LogSource to the collector is useful in the following scenarios:
- The device that is forwarding the Syslog to the collector is not monitored by the collector.
- The device that is forwarding the Syslog to the collector is not monitored in LogicMonitor at all.
To apply LogSource to collector:
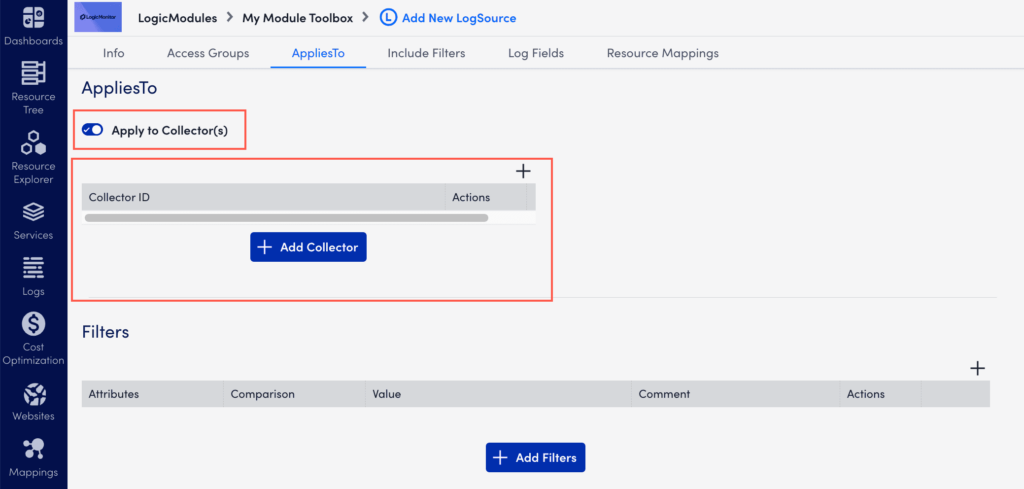
- While creating a LogSource, on the AppliesTo tab, toggle Apply to Collector(s) switch.
- Under Collector Mappings, select Add Collector.
Note:
- When you enable the Apply to Collector(s) switch, the AppliesTo field becomes unavailable. It is not possible to use both the options together.
- Only the self-monitoring collectors with a minimum version as EA-35.200 appear in the Collector Mapping field.
- Only one LogSource of type Syslog can be applied on a self-monitoring collector.
- If a device is monitored by a collector that is receiving the Syslog, then the LogSource that is applied on the device is preferred over the LogSource applied on the collector. To know more about it, refer Syslog Processing Preference.
- In a LogSource, where the ApplyTo Collector(s) switch is enabled, to ensure smooth functioning, you must select Collectors that are not part of an Auto-Balanced Collector Group (ABCG).


