Webhook Events as Logs
Last updated - 13 October, 2025
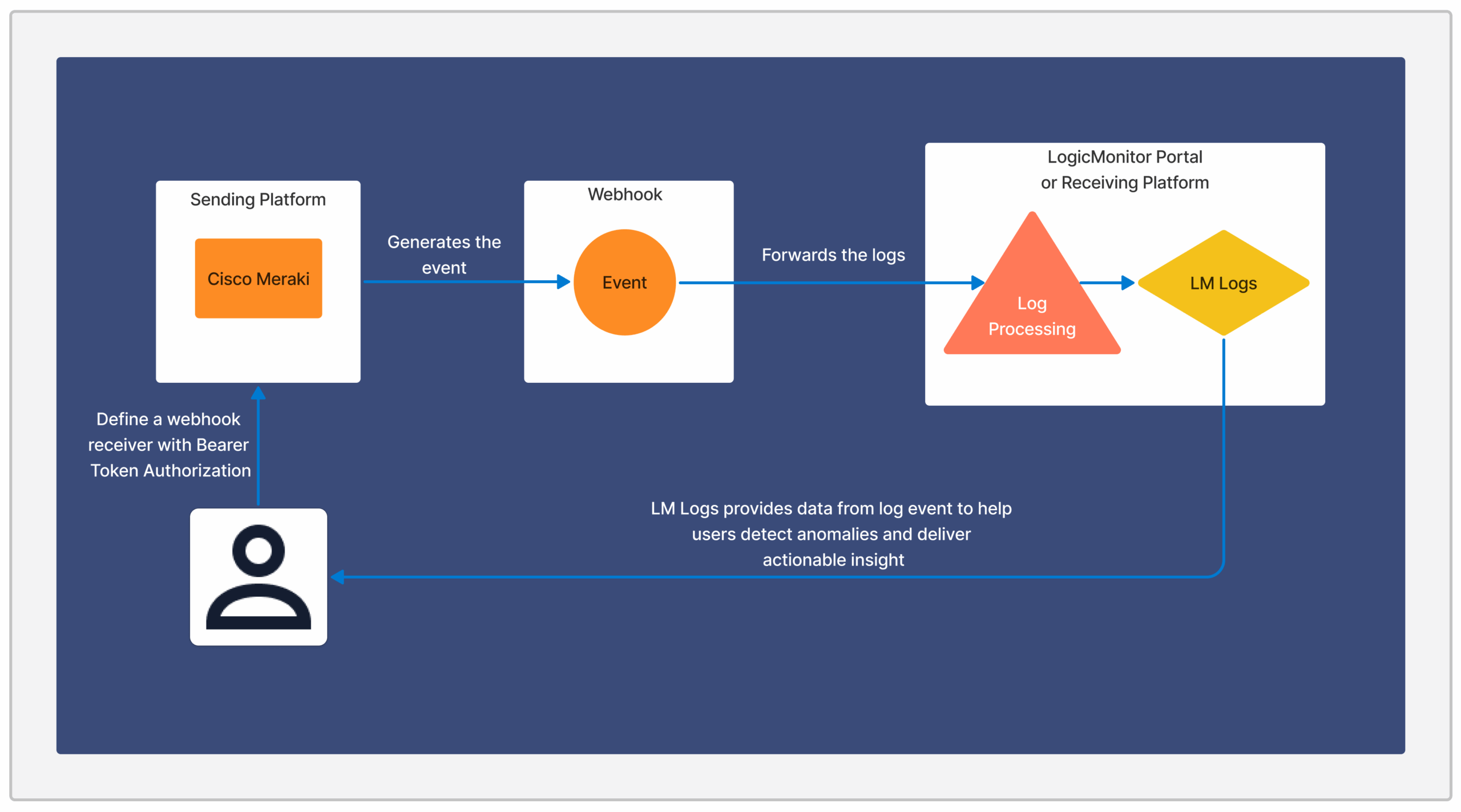
Webhooks provide a way for one system to send real-time data to another system as soon as an event occurs. In LogicMonitor, webhooks enable external platforms to send log events directly into the platform for ingestion using HTTP POST requests. This feature enables capturing of event-driven data such as metrics, alerts, notifications as logs in near real time, helping you centralize log collection.
Webhook Events as Logs provides the following benefits:
- Instant log delivery—Receive logs instantly from systems that support webhooks, without requiring custom Collectors or scheduled queries.
- Stronger correlation— Correlate external alerts with existing logs in LogicMonitor for deeper insights.
- Broader ingestion options—Ingest data from cloud services, SaaS platforms, and cloud-managed networking platforms.
- Prebuilt modules—Use prebuilt modules in LogicMonitor Exchange, such as those designed for Cisco Meraki.
Webhook LogSources further defines how inbound webhook data should be processed and stored.
The following steps occur when an external system sends a message to the webhook endpoint:
- The request is received by the LogicMonitor webhook listener.
- The associated LogSource configuration determines how the message is parsed and mapped.
- Logs are ingested into LogicMonitor, where they can be visualized, correlated, and used for alerting.
The following diagram illustrates the webhook workflow:
For more information, refer to Webhook LogSource Configuration.
Requirements for using a Webhook LogSource to Ingest Messages
To configure webhook events, you need the following:
- An API Only User in LogicMonitor with “Manage” permission for Logs & Traces
- An appropriate webhook name, for example,
Meraki_Webhook - A valid Receiver URL (Callback URL) to the LogicMonitor portal
For example:https://portalname.logicmonitor.com/rest/api/v1/webhook/ingest/sourceName
In this example,- The
sourceNameis included in webhook messages to identify the origin of the data. - You can also configure a LogSource to filter by
sourceName. - Each
sourceNameshould be unique (for example,Meraki+CustomerName).
- The
- Bearer Token assigned to the API Only User configured for authentication
Authorization
HTTP Header Value:Bearer <BearerTokenHere>
The word Bearer, followed by a single space, must precede the LogicMonitor Bearer Token.
For more information, see Adding a Bearer Token.


