Collector Capacity
Last updated - 09 September, 2025
The amount of data that a Collector can handle depends on the Collector’s configuration and resources. You can monitor the data collection load and performance of your Collector to minimize disruption and notify when a collector is down. See Monitoring your Collectors.
If you have a large environment, and are experiencing alerts on the Unavailable Task Rate datasource of your Collectors, you may need to tune your Collector to increase its monitoring capacity.
Device Capacity Limits
The following table describes the capacity of collectors in different sizes. It is measured in requests per second (RPS) (except for Syslog, which is measured in events per second (EPS).
Note:
- We have attached 50 instances to every device. Thus, to get the number of instances, multiply the number of devices by 50. For example, 50 x 211 (devices) = 10550 instances
- These measurements are estimates and the actual capacity may vary as per production environment.
| Protocol | Small Collector | Medium Collector | Large Collector | Extra Large (XL) Collector | Double Extra Large (XXL) Collector |
| CPU: 1 Intel Xeon Family System Memory: 2GiB JVM maximum memory: 1GiB | CPU: 2 Intel Xeon E5-2680v2 2.8GHz System Memory: 4GiB JVM maximum memory: 2GiB | CPU: 4 Intel Xeon E5-2680v2 2.8GHz System Memory: 8GiB JVM maximum memory: 4GiB | CPU: 8 System Memory: 16GiB JVM maximum memory: 8GiB | CPU: 16 System Memory: 32GiB JVM maximum memory: 16GiB | |
| SNMP v2c (Linux) | 300 standard devices 76 RPS | 1000 standard devices 256 RPS | 4000 standard devices 1024 RPS | 8000 standard devices 2048 RPS | 15000 standard devices 3840 RPS |
| SNMP v3 | 855 standard devices 220 RPS | 1087 standard devices 278 RPS | 1520 standard devices 390 RPS | 2660 standard devices 682 RPS | 4180 standard devices 1074 RPS |
| HTTP | 320 standard devices 160 RPS | 1400 standard devices 735 RPS | 2400 standard devices 1260 RPS | 4500 standard devices 2000 RPS | 7500 standard devices 3740 RPS |
| WMI | 211 standard devices 77 RPS | 287 standard devices 102 RPS | 760 standard devices 272 RPS | 1140 standard devices 409 RPS | 1330 standard devices 433 RPS |
| BatchScript | 94 standard devices 5 RPS | 124 standard devices 7 RPS | 180 standard devices 11 RPS | 295 standard devices 17 RPS | 540 standard devices 32 RPS |
| Perfmon | 200 standard devices 87 RPS | 400 standard devices 173 RPS | 800 standard devices 347 RPS | TBA | TBA |
| JMX | 1000 standard devices 416 RPS | 2500 standard devices 1041 RPS | 5000 standard devices 2083 RPS | TBA | TBA |
| Syslog | TBD | 500 EPS (assuming event size of 100-200 bytes) | 2500 EPS (assuming event size of 100-200 bytes) | 4000 EPS (assuming event size of 100-200 bytes) | 7000 EPS (assuming event size of 100-200 bytes) |
| SNMP v2 Trap | TBD | 17 standard devices | 87 standard devices | 140 standard devices | 245 standard devices |
| SNMP v3 Trap | TBD | 14 standard devices | 70 standard devices | 112 standard devices | 196 standard devices |
The capacity also depends on the number of instances that need to be discovered for each monitored device. For example, if each device is a load balancer with 10,000 instances, collector capacity will be lower. If each device is a switch with hundreds of interfaces, collector capacity may be lower because it is limited by discovery.
Note:
- For monitoring production critical applications and infrastructure, it is recommended to use medium and above size collector as per your requirements. You can use small size collector for testing purpose.
- If a collector runs on an Amazon EC2 instance, we recommend that you use a fixed performance instance type (such as M5 or C5) instead of a credit based instance type (such as T2).
- The nano collector size is not included in this table. The nano collector is used for testing and hence, no recommended device-count capacity has been assigned to it.
- Collectors using JDK 11 (supported by collector version 28.400 and later) will see roughly 10% more memory and CPU usage than the previous JDK 8 collectors on the same hardware.
- Incase of the estimated collector performance numbers for SNMP v2 and v3 Trap LogSource, we have assumed that each device generates 10 traps per second.
Collector Memory Requirements in a VM
Part of a Collector’s system memory allocation is devoted to Standalone Script Engine (SSE), which is enabled by default and used to execute script DataSources (Groovy scripts).
| Collector Size | SSE Memory Requirements |
| Small | 0.5GiB |
| Medium | 1GiB |
| Large | 2GiB |
| Extra Large | 4GiB |
| Double Extra Large | 8GiB |
In general, the SSE requires half of the amount of memory allotted to the JVM. The memory requirements are not shared, rather the SSE requirement is in addition to the JVM memory requirements. If the Collector does not have this memory available, the SSE will not start and you will see “Can’t find the SSE Collector Group” in the Collector Status dialog. The Collector will work without the SSE, but Groovy scripts will be executed from the Agent instead of the SSE.
If the Collector is executed in a VM, this safeguard can be overridden because the OS indicates there is free memory. This burst memory capacity in VMs can increase memory use above the system memory requirements listed previously. Although this can happen for Collector of any size, it is far more likely to happen to small Collectors.
To disable SSE and prevent additional memory use, edit the Collector’s agent.conf:
- If the configuration setting reads
groovy.script.runner=sse, change it togroovy.script.runner=agent. - If the previous setting is not present, update the following setting:
collector.script.asynchronous=false.
For more information, see Editing the Collector configuration files.
NetFlow Capacity
The following table describes the capacity of NetFlow collectors across different sizes and OS platforms. It is measured in flows per second (FPS).
Note:
- For optimum performance, we recommend that you use the NetFlow collector only for collecting and processing NetFlow data.
- All numbers mentioned below are captured in the in-house PSR lab under controlled conditions. Hence, collector’s actual capacity may vary based on the nature of the NetFlow traffic at the customer’s end.
- Processing NetFlow data is CPU intensive. In case of a CPU crunch, we recommend that you first increase the resources (CPU cores) on the Collector Host to support more number of flows. You can then switch to a bigger size collector if increasing the CPU capacity does not help.
| OS Platform | Metric | Small Collector | Medium Collector | Large Collector | Extra Large (XL) Collector | Double Extra Large (XXL) Collector |
| Windows 64 bit Linux 64 bit | Supported Flows/sec | 7800 | 13797 | 23166 | 37418 | 52817 |
Adjusting Collector Size
You can adjust the collector size from the LogicMonitor portal, especially for performance tuning and increasing the collector capacity after installing it.
- Navigate to Settings > Collectors.
- Under the Collectors tab, select the collector whose size you want to adjust.
- Select the More option and then select Collector Configuration.
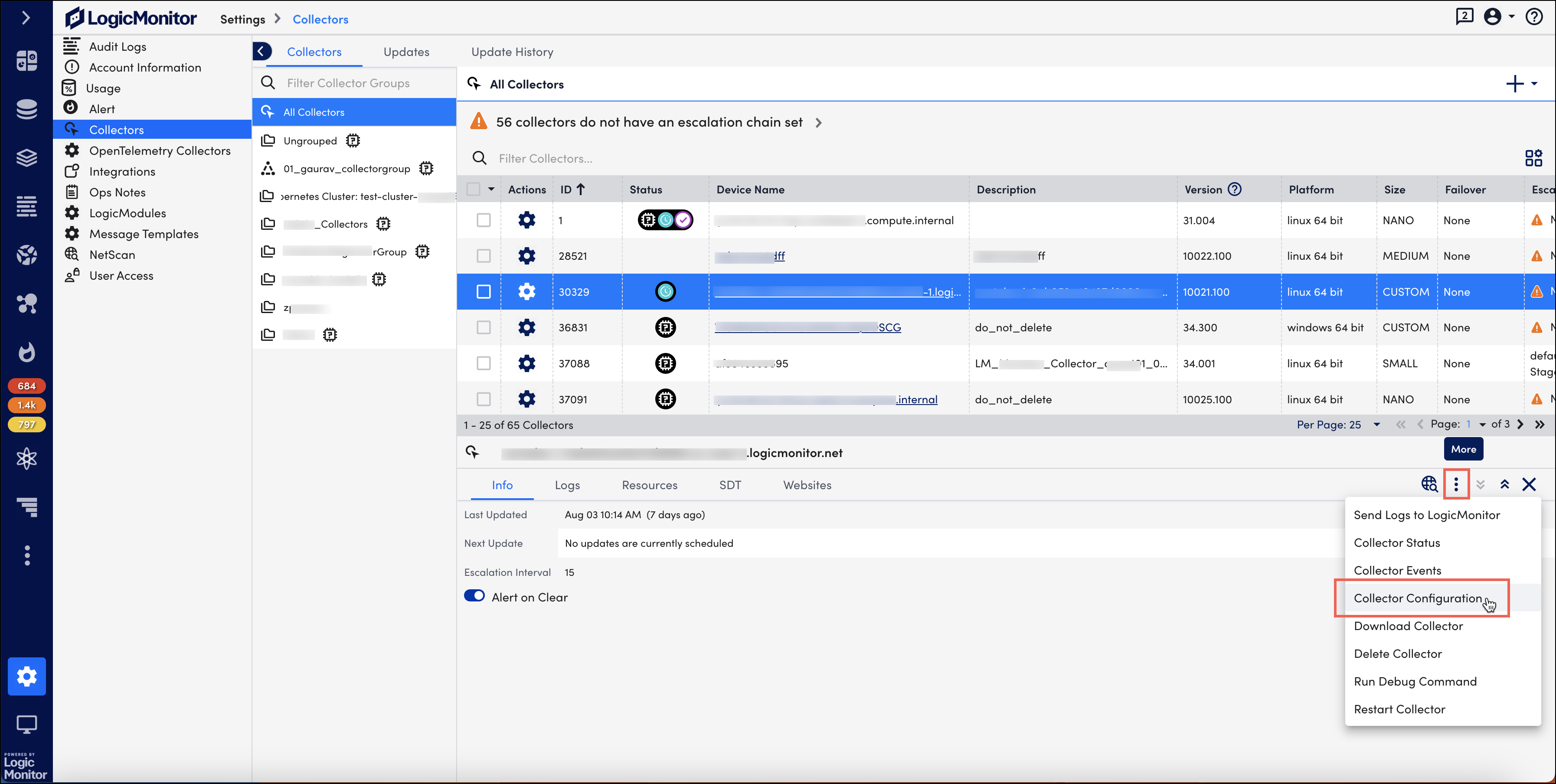
On the Collector Configuration page, the Agent Config settings are displayed. - Select the collector size from the dropdown menu.
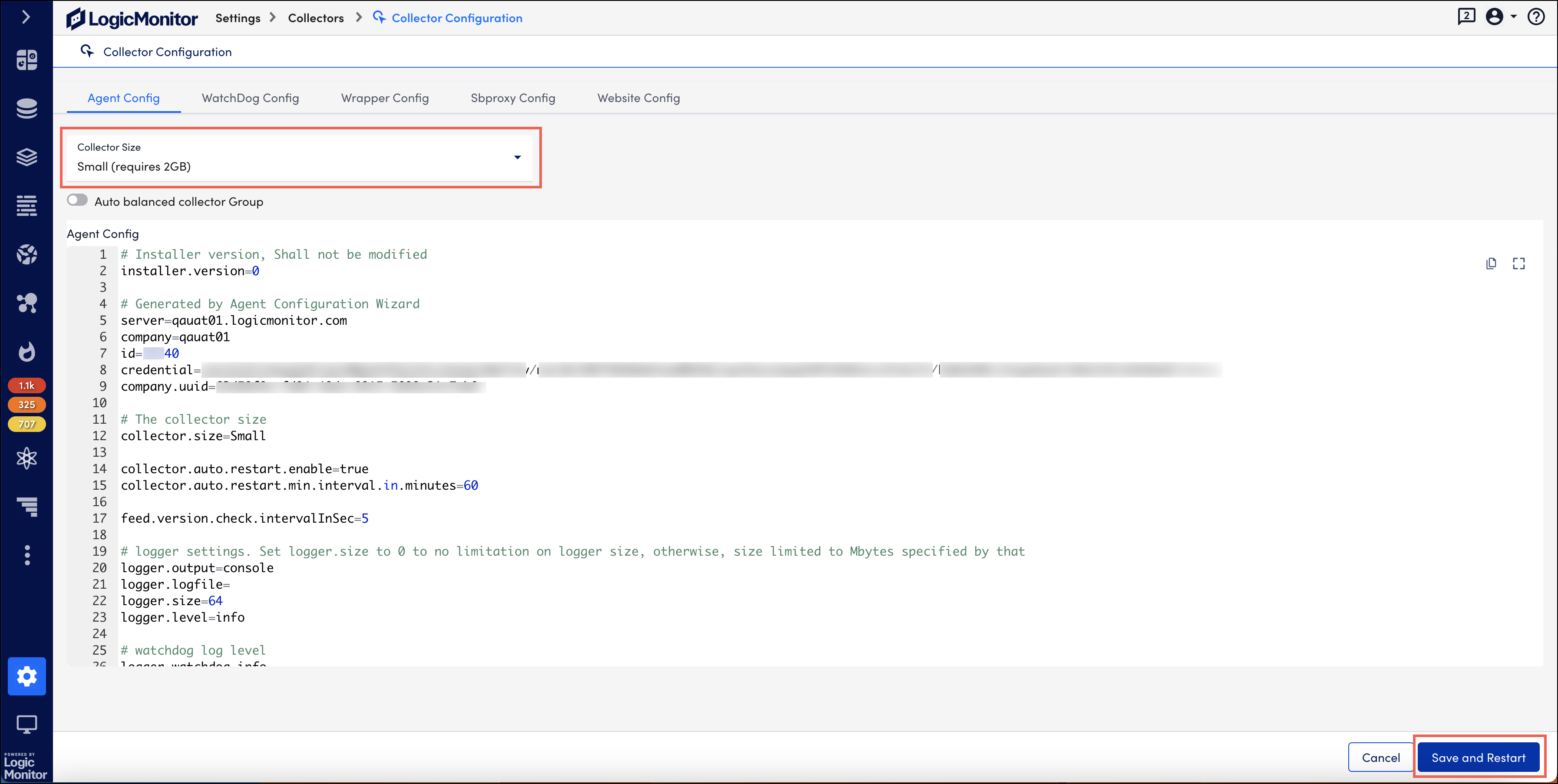
- Select Save and Restart. LogicMonitor automatically verifies if your host has enough memory to support the new collector size.
Note:
- Older Collectors will display their current size as “Custom (xGiB)” in the dropdown, even if no parameters have been modified since installing. This is because our definition of size has changed since the Collector was installed. If you want to ensure the Collector configuration is up to date, simply select the size you want (or had installed originally) and select Save and Restart.
- Changing a Collector’s size has no effect on parameters unrelated to its size. The parameters listed in the section below, Configuration Details, are the only ones impacted by a change in the Collector’s size.
If you are manually changing the collector’s config parameters, LogicMonitor runs a validity check after you select Save and Restart to ensure that no errors were made in the new configuration. If errors are detected, the missing/duplicated lines are displayed so that they can be corrected.
Small Collector
| Config File | Parameters | Description |
| wrapper.conf | wrapper.java.initmemory=128 | Minimum Java Heap Size(MiB) for Collector |
| wrapper.java.maxmemory=1024 | Maximum Java Heap Size(MiB) for Collector | |
| sbproxy.conf | wmi.stage.threadpool.maxsize=100 | The maximum size of threads to handle WMI query/fetch data in sbwinproxy.exe |
| wmi.connection.threadpool.maxsize=50 | The maximum size of threads for WMI to connect to remote machine in sbwinproxy.exe | |
| agent.conf | sbproxy.connector.capacity=8192 | The maximum number of requests that the Collector can send in parallel to sbwinproxy and sblinuxproxy |
| discover.workers=10 | Allocates resources to Active Discovery iterations | |
| autoprops.workers=10 | The thread pool size for AP | |
| reporter.persistent.queue.consume.rate=10 | The max count of data entries that will be reported for each API call. | |
| reporter.persistent.queue.consumer=10 | The thread count used to read from buffer and execute reporting. | |
| collector.script.threadpool=100 | The max thread count to run script tasks. | |
| website.conf | sse.max.spawn.process.count=3 | N/A |
Medium Collector
| Config File | Parameters | Description |
| wrapper.conf | wrapper.java.initmemory=512 | Minimum Java Heap Size(MiB) for Collector |
| wrapper.java.maxmemory=2048 | Maximum Java Heap Size(MiB) for Collector | |
| sbproxy.conf | wmi.stage.threadpool.maxsize=200 | The maximum size of threads to handle WMI query/fetch data in sbwinproxy.exe |
| wmi.connection.threadpool.maxsize=100 | The maximum size of threads for WMI to connect to remote machine in sbwinproxy.exe | |
| agent.conf | sbproxy.connector.capacity=8192 | The maximum number of requests that the Collector can send in parallel to sbwinproxy and sblinuxproxy |
| discover.workers=40 | Allocates resources to Active Discovery iterations | |
| autoprops.workers=10 | The thread pool size for AP | |
| reporter.persistent.queue.consume.rate=12 | The max count of data entries that will be reported for each API call. | |
| reporter.persistent.queue.consumer=10 | The thread count used to read from buffer and execute reporting. | |
| collector.script.threadpool=200 | The max thread count to run script tasks. | |
| website.conf | sse.max.spawn.process.count=5 | N/A |
Large Collector
| Config File | Parameters | Description |
| wrapper.conf | wrapper.java.initmemory=1024 | Minimum Java Heap Size(MiB) for Collector |
| wrapper.java.maxmemory=4096 | Maximum Java Heap Size(MiB) for Collector | |
| sbproxy.conf | wmi.stage.threadpool.maxsize=400 | The maximum size of threads to handle WMI query/fetch data in sbwinproxy.exe |
| wmi.connection.threadpool.maxsize=200 | The maximum size of threads for WMI to connect to remote machine in sbwinproxy.exe | |
| agent.conf | sbproxy.connector.capacity=16384 | The maximum number of requests that the Collector can send in parallel to sbwinproxy and sblinuxproxy |
| discover.workers=80 | Allocates resources to Active Discovery iterations | |
| autoprops.workers=15 | The thread pool size for AP | |
| reporter.persistent.queue.consume.rate=12 | The max count of data entries that will be reported for each API call. | |
| reporter.persistent.queue.consumer=15 | The thread count used to read from buffer and execute reporting. | |
| collector.script.threadpool=300 | The max thread count to run script tasks. | |
| website.conf | sse.max.spawn.process.count=5 | N/A |
XL Collector
| Config File | Parameters | Description |
| wrapper.conf | wrapper.java.initmemory=1024 | Minimum Java Heap Size(MiB) for Collector |
| wrapper.java.maxmemory=8192 | Maximum Java Heap Size(MiB) for Collector | |
| sbproxy.conf | wmi.stage.threadpool.maxsize=800 | The maximum size of threads to handle WMI query/fetch data in sbwinproxy.exe |
| wmi.connection.threadpool.maxsize=400 | The maximum size of threads for WMI to connect to remote machine in sbwinproxy.exe | |
| agent.conf | sbproxy.connector.capacity=32768 | The maximum number of requests that the Collector can send in parallel to sbwinproxy and sblinuxproxy |
| discover.workers=160 | Allocates resources to Active Discovery iterations | |
| autoprops.workers=20 | The thread pool size for AP | |
| reporter.persistent.queue.consume.rate=15 | The max count of data entries that will be reported for each API call. | |
| reporter.persistent.queue.consumer=20 | The thread count used to read from buffer and execute reporting. | |
| collector.script.threadpool=400 | The max thread count to run script tasks. | |
| website.conf | sse.max.spawn.process.count=10 | N/A |
XXL Collector
| Config File | Parameters | Description |
| wrapper.conf | wrapper.java.initmemory=2048 | Minimum Java Heap Size(MiB) for Collector |
| wrapper.java.maxmemory=16384 | Maximum Java Heap Size(MiB) for Collector | |
| sbproxy.conf | wmi.stage.threadpool.maxsize=1600 | The maximum size of threads to handle WMI query/fetch data in sbwinproxy.exe |
| wmi.connection.threadpool.maxsize=800 | The maximum size of threads for WMI to connect to remote machine in sbwinproxy.exe | |
| agent.conf | sbproxy.connector.capacity=65536 | The maximum number of requests that the Collector can send in parallel to sbwinproxy and sblinuxproxy |
| discover.workers=320 | Allocates resources to Active Discovery iterations | |
| autoprops.workers=30 | The thread pool size for AP | |
| reporter.persistent.queue.consume.rate=20 | The max count of data entries that will be reported for each API call. | |
| reporter.persistent.queue.consumer=30 | The thread count used to read from buffer and execute reporting. | |
| collector.script.threadpool=600 | The max thread count to run script tasks. | |
| website.conf | sse.max.spawn.process.count=15 | N/A |
Minimum Recommended Disk Space
Although the Collector operates in memory, operations such as caching require available disk space on its host. The exact amount of required storage varies and depends on factors such as Collector size, configuration, NetFlow usage, number of Collector logs, and so on.
These are examples of required disk space based on these factors:
- A brand new install Collector will use about 500MiB.
- At most, Collector logs will use 800MiB.
- Temporary files (ie. upgrade files) will use less than 1500MiB.
- Report cache data will use less than 500MiB by default (this figure represents 30 minutes of cached data for a Large Collector)
- If using NetFlow the disk usage is less than 30GiB.
In total, this means Collector disk usage will be less than 3.5GiB without NetFlow and up to 33.5GiB with NetFlow enabled.


