Rolling out through the middle of March, v.116 continues to expand the reach of LM Cloud with monitoring additions and enhancements for AWS, Azure, and GCP. Other v.116 highlights include integration with ServiceNow CMDB, more robust integration with PagerDuty, Kubernetes monitoring improvements, and several UI updates.
NEW! NetFlow Widget
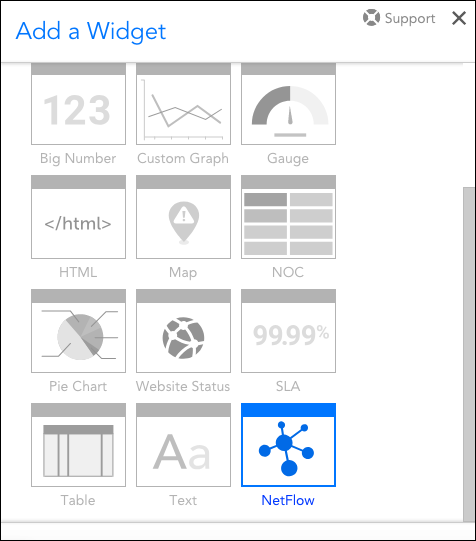
A configurable NetFlow widget is now available for your dashboards! Previously, NetFlow data could only be added to dashboards by manually adding the tables, graphs, and pie charts available from the Traffic tab found on the Resources page.
The new NetFlow widget is available as a new widget type from the Add a Widget dialog, with options to create any of the views currently visible under the Traffic tab. Users can update an existing NetFlow widget to point to a new resource at any time, and the Widget Title and Device fields both accept tokens, allowing for dashboard-wide changes and replication. Finally, NetFlow views added manually from a resource are automatically made configurable, and feature the same options as those added from a dashboard.
NEW! ServiceNow CMDB Integration
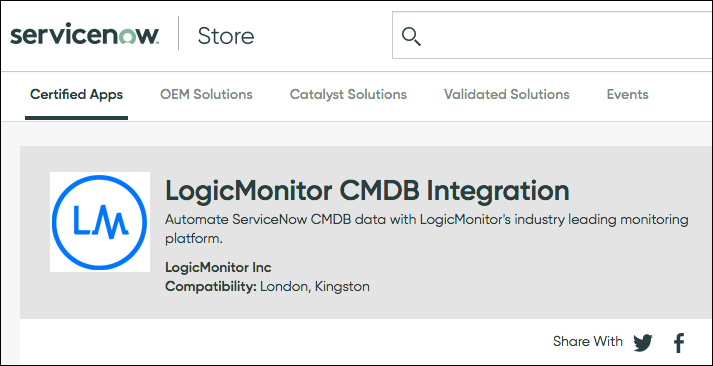
In addition to the existing ITSM integration, LogicMonitor now offers an out-of-the-box integration with ServiceNow CMDB (available as a premium, add-on feature). This new integration provides a robust baseline code that can easily be built upon to customize and fit the needs of any IT environment.
Key features of this new integration include bi-directional data synchronization to ensure a reliable and up-to-date CMDB, and enriched alerting data for quicker mean-time-to-resolution for incidents critically affecting business. By integrating LogicMonitor and ServiceNow CMDB, customers gain full visibility into their IT ecosystems, from infrastructure to applications. The certified LogicMonitor CMDB Integration app is available on the ServiceNow Store.
Other v.116 Enhancements
Dashboards
- Instance limits increased for several dashboard widgets. The Custom Graph, Big Number, and NOC widgets can now pull in up to 5000 instances each, increased from their previous maximums of 2000 instances. This is part of an ongoing effort to raise instance limits across all widgets and reports.
Integrations
- PagerDuty integration now incorporates machine learning and response automation features. Using LogicMonitor’s out-of-the-box PagerDuty integration, alerts can now generate PagerDuty events that take advantage of advanced PagerDuty capabilities such as intelligent real-time decisions and automated precision response. For more information on integrating with PagerDuty (or upgrading your existing PagerDuty integration to leverage these new features), see PagerDuty Integration.
LM Cloud
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) monitoring improvements:
- Added monitoring for two AWS regions. Added monitoring support for AWS Paris (eu-west-3) and Stockholm (eu-north-1) regions.
- Improved non-HTTP Route53 health check alerting. Added new properties for Route53 to include meaningful information for non-HTTP Route53 health checks (e.g. CloudWatch alarm name). These properties will be used to make alerts more meaningful for non-HTTP Route53 health checks.
- Spot instances filtered out of EC2 service limits collection. The AWS EC2 service limits DataSource was counting spot instances towards the on-demand limit. This has been corrected.
- Azure firewall monitoring. LogicMonitor now discovers and monitors metrics (application rules hit count, network rules hit count) for Azure firewalls.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) monitoring improvements:
- GCP VPN gateway monitoring. Added support for discovering and monitoring GCP VPN gateways. VPN tunnels are additionally discovered for each gateway, and metrics are collected at the tunnel level.
- GCP HTTPS load balancer monitoring. Added support for discovering and monitoring GCP HTTPS load balancers.
- Improved resiliency for GCP data collection. Previously, a configuration error in one datapoint for a GCP DataSource prevented successful data collection for all other datapoints, even if they were configured correctly. With v.116, LogicMonitor has made improvements to ensure that one misconfigured datapoint does not break data collection for other successfully configured datapoints in the DataSource.
- GCP filter validation. Errors will now display if datapoint filters for GCP (Stackdriver) data collection are not formatted correctly. This is helpful when modifying datapoints (e.g. tweaking a datapoint to get a different aggregation).
- Local Collector configuration removed for event data collection. Over the past few releases, all cloud event data collection (e.g. AWS, Azure, and GCP service disruptions) has been migrated to a LogicMonitor-maintained cloud Collector. As such, there is no longer a need for users to select local Collectors for event data collection and the configuration from the New Cloud Account wizard (and cloud account Manage dialog) that prompts a local Collector selection for event data collection has been removed.
LM Container
- Kubernetes node hostnames substituted for missing internal IPs. Kubernetes nodes are now added in by hostname if an internal IP is missing. Previously, a missing internal IP could cause errors.
- Kubernetes resource count broken out in resources tree. Kubernetes resource counts are now broken out from the standard device count that displays in the header of the resources tree. Along with cloud resources, Kubernetes resources now have their own category (e.g. “(261 devices / 211 cloud resources / 8 kubernetes resources)”). This provides visibility into Kubernetes resource counts for users that don’t have access to the Settings page.
LogicModules
- Hyphens no longer allowed in AppliesTo function names. User-defined AppliesTo functions can no longer be created with hyphens (-) in their names. Existing AppliesTo functions with hyphens in their names will continue to work in any AppliesTo fields in which they’ve previously been entered, but they cannot be newly entered without first being renamed. In a future release, any remaining AppliesTo functions containing hyphens in their names will be automatically migrated. This will help us optimize the backend code that evaluates AppliesTo and matches LogicModules with devices.
User Interface
- “Platform” column added to Collectors page. A new column titled “Platform” now displays on the Collectors page to denote Collector CPU architecture (e.g. Windows 64-bit, Linux 64-bit, etc.).
- SDT tab opens after a resource is put into scheduled downtime. After a resource is put into scheduled downtime using the Put in SDT button (found in the Resources page’s toolbar), the LogicMonitor UI will now automatically take users directly to the SDT tab for that resource.
- Improved Audit Log display. Lengthy descriptions for Audit Log entries are now truncated to provide a more friendly display. Truncated descriptions are indicated with a “Show more” hyperlink and can be expanded by clicking anywhere within the log entry.
LogicModule Releases
LogicModules that have been added or updated since the last release.
New Monitoring Coverage
- AWS Service Health – 1 DataSource
- Cisco NTP – 1 DataSource, 1 PropertySource
- EMC VNXe – 10 DataSources, 1 PropertySource
- Google Cloud Platform – HTTPS Load Balancer – 1 DataSource
- Kubernetes Topology – 3 PropertySources, 2 TopoSources
- Microsoft Azure Firewalls – 1 DataSource
Monitoring Improvements
- Citrix Application Trends – 1 DataSource
- Corrected issue with querying applications with large deployments
- GCP Service Health – 1 EventSource
- Data collection method change
- Kubernetes Pod – 1 DataSource
- Additional port compatibility
- Linux SSH CPU Cores – 1 DataSource
- Added support for Linux kernel versions 2.6.32 and older which did not support guest_nice stats
- VMware vCenter Datastore Performance – 1 DataSource
- Issue fixed in AD script that mismatched instance wildvalues, causing no data