Syslog LogSource Configuration
Last updated on 20 February, 2025LogSource is a LogicModule that provides templates to help you enable LM Logs and configure log data collection and forwarding. LogSource contains details about which logs to get, where to get them, and which fields should be considered for parsing. LogSource is available for common sources of log data.
Requirements for Configuring Syslog LogSources
The Syslog LogSource type uses the LM Collector. When using the LM Collector with LogSource, the LM Collectors installed in your infrastructure must be version EA 31.200 or later. For information on how to upgrade a collector, see Managing Collectors.
Configuration Options
The following describes configuration details specific to the Syslog type of LogSource. For general information on how to add a LogSource, see Configuring a LogSource.
Note: In cases with high volume of Linux syslog messages, some messages may not reach the collector. To prevent this, you can increase the rmem value on the Linux instance where the collector is installed. Do the following:
- Open the /etc/sysctl.conf file
- Add the line
net.core.rmem_max=15728640and save the file - Run the
sysctl --systemcommand
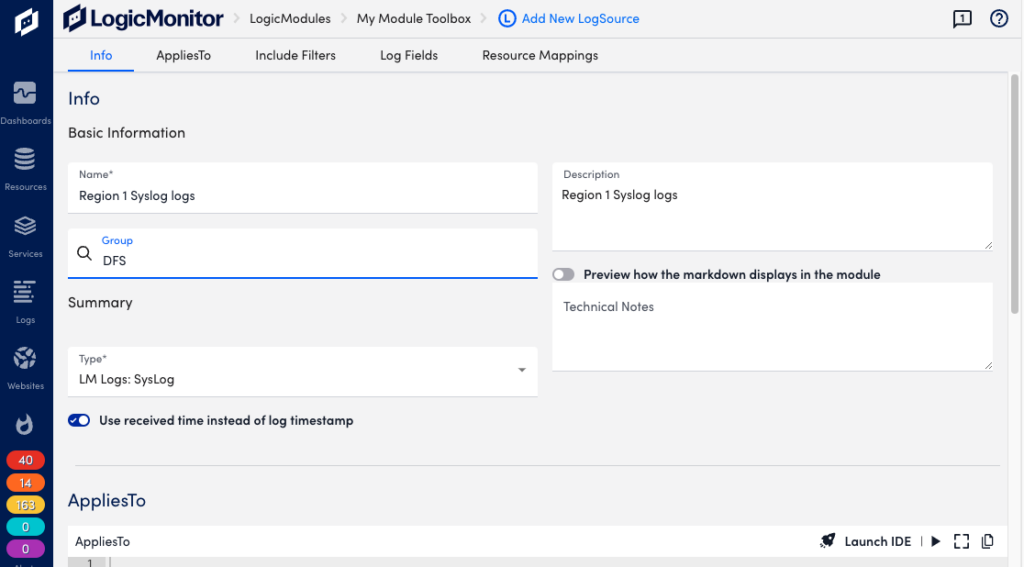
Basic Information
If you have Syslog events that do not include time information, toggle Use received time instead of log timestamp to use the timestamp for when the log was received by the Collector.
Important: If the Collector and device are off three hours or more, the logs are ignored. The Use received time instead of log timestamp setting mitigates timing issues between the Collector and device.
Apply LogSource to Collectors
With collector version EA-35.200, you can apply LogSource to a collector directly using the Apply to Collector(s) option. The AppliesTo option is also available to apply LogSource to a device. But, if you are using a collector version prior to EA-35.200, you can only use AppliesTo to apply LogSource to a device.
Applying a LogSource to the collector is useful in the following scenarios:
- The device that is forwarding the Syslog to the collector is not monitored by the collector.
- The device that is forwarding the Syslog to the collector is not monitored in LogicMonitor at all.
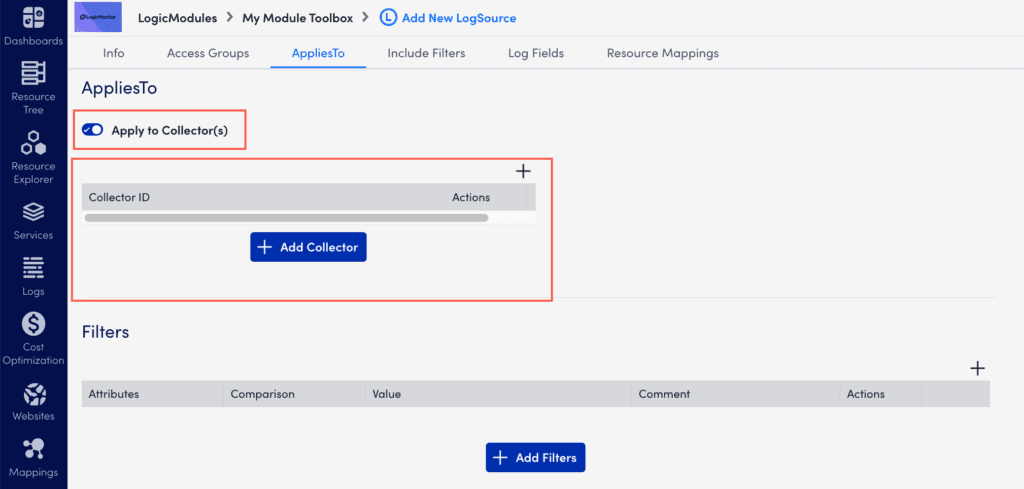
Applying LogSource on Collector
To apply LogSource to collector:
- While creating a LogSource, on the AppliesTo tab, toggle Apply to Collector(s) switch.
- Under Collector Mappings, select Add Collector.
Note:
- When you select Apply to Collector(s) toggle, the AppliesTo field becomes unavailable. It is not possible to use both the options together.
- Only the self-monitoring collectors with a minimum version as EA-35.200 appear in the Collector Mapping field.
- Only one LogSource of type Syslog can be applied on a self-monitoring collector.
- If a device is monitored by a collector that is receiving the Syslog, then the LogSource that is applied on the device is preferred over the LogSource applied on the collector. To know more about it, refer Syslog Processing Preference.
Syslog Processing Preference
While applying LogSource on a collector, the collector can process Syslog in the following ways:
- If the requirement is to ingest the Syslog events received by the collector, Collector’s agent.conf property “lmlogs.syslog.enabled” can be enabled. This property can also be enabled by turning on Enable log collection for Syslog and SNMP trap option on the Add collector page. With this property enabled, the collector will ingest all the Syslog events without any customization such as Filters, Resource Mapping, and others.
- If the requirement is to add some customisation such as filtering some Syslog events or adding a different method for resource mapping, a LogSource can be created and applied on the Syslog receiving collector using the Apply to Collector(s) option on the LogSource.
- If the requirement is to handle the Syslog events from a device using a specific LogSource definition, a usual LogSource can be applied on a device that is forwarding the Syslog events to the collector.
A usual LogSource that is applied on a device, will be preferred over the LogSource applied on a collector for processing the syslog.
A LogSource that is applied on a collector, will be preferred over collector’s agent.conf property “lmlogs.syslog.enabled” for processing the syslog.
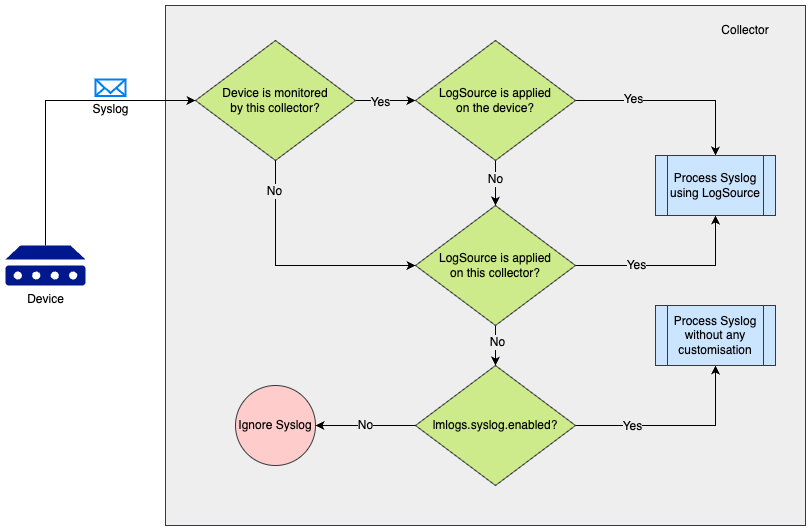
The following scenarios can be referred to understand the syslog processing preference by a collector which is receiving the syslog.
| Scenario | Is the device monitored by the collector* | Is a usual LogSource applied on the device | Is a LogSource applied on collector using the Apply to Collector(s) switch | Is collector’s agent.conf property lmlogs.syslog.enabled set to true | Outcome |
| 1 | Yes | Yes | Any (Yes/No) | Any (Yes/No) | Syslog will be processed using the usual LogSource applied on the device that forwards the Syslog. |
| 2 | Yes | No | Yes | Any (Yes/No) | Syslog will be processed using the LogSource which is applied to the collector that receives the Syslog. |
| 3 | No | Any (Yes/No) | Yes | Any (Yes/No) | Syslog will be processed using the LogSource which is applied to the collector that receives the Syslog. |
| 4 | No | Any (Yes/No) | No | Yes | Syslog will be processed using the agent.conf property (“lmlogs.syslog.enabled”) of the collector that receives the Syslog. |
*A device is said to be monitored by a collector if
- The collector is assigned as a Preferred Collector on Manage Resource page
-or- - The collector is assigned as Log Collector using Set LM Logs Collector option on Manage Resource page
Include Filters
You can add filters to include resources of certain types, for example an application. The output matching the filter criteria will be forwarded to the log ingestion process.
Available parameters
| Attributes | Comparison operator | Value example | Description |
| Application | Equal, NotEqual, Contain, NotContain, Exist, NotExist, RegexMatch, RegexNotMatch. | The Value field is disabled if you select “Exist” or “NotExist”. | |
| Facility | Equal, NotEqual, Contain, NotContain, RegexMatch, RegexNotMatch, Exist, NotExist, GreaterThan, GreaterEqual, LessThan, LessEqual. | Predefined options like “kernel messages”, “system daemons”, and “log alert”, are available. | The Value field is disabled if you select “Exist” or “NotExist”. |
| Message | Equal, NotEqual, Contain, NotContain, RegexMatch, RegexNotMatch, Exist, NotExist. | The Value field is disabled if you select “Exist” or “NotExist”. | |
| Severity | Equal, MoreUrgentThan. | Emergency, Alert, Critical, Warning, Notice, Informational, Debug. |
Log Fields
You can configure Log Fields (tags) to send additional metadata with the logs.
Available parameters
| Method | Key example | Value example | Description |
| Static | “Customer” | “Customer_XYZ” | |
| Dynamic(REGEX) | “Host” | “host=*” | The query will run on the message field. |
| LM Property(Token) | “Device” | “##system.deviceId##” | The DeviceID value extracted from the existing device property in LogicMonitor. |
| Syslog Attribute | Application, Facility, Severity. | ||
| Dynamic Group Regex | “Scheme, Login” | “(https*):\/\/([]a-z]+)” | The query runs on the message field and captures the first group value from Regex. The keys for Dynamic Group Regex can be added as a comma separated list and values are read from same number of groups. For the Key and Value example provided in this table, the regex results in metadata for key and value, which is, Scheme and Login. For example: Scheme=https Login=<Actual username extracted from the message> Note: The Dynamic Group Regex method for log fields is available from the LM collector version 34.200 and later. |
Resource Mappings
Configure the LM log property to match a monitored resource.
Available parameters
| Method | Key example | Value example | Description |
| Static | “Customer_Id” | “1921” | |
| IP | “system.ips” | “10.20.30.40” | Use the syslog host field information and resolve it to IP (For example “10.20.30.40”). The Value field is disabled if you select this method, you can only enter a Key. |
| FQDN | “system.hostname” | “application.service.example.com” | Fully Qualified Domain Name, from DNS resolution of hostname received from syslog message or socket address. |
| HOSTNAME | “system.hostname” | “host1.example.com” | The Value field is disabled if you select this method, you can only enter a Key. |
| HOST WITHOUT DNS | “system.hostname” | “host1” | The Value field is disabled if you select this method, you can only enter a Key. |
| Dynamic(REGEX) | “system.ServiceName” | “service=*” | The query will run on the message field. |
| LM Property(Token) | “token.resourceMap” | “syslog_test_collector” | The DeviceID extracted from the existing device property in LogicMonitor. |
| Dynamic Group Regex | “Scheme, Login” | “(https*):\/\/([]a-z]+)” | The query runs on the message field and captures the first group value from Regex. The keys for Dynamic Group Regex can be added as a comma separated list and values are read from same number of groups. For the Key and Value example provided in this table, the regex results in metadata for key and value, which is, Scheme and Login. For example: Scheme=https Login=<Actual username extracted from the message> Note: The Dynamic Regex Group method for resource mapping is available from the LM collector version 35.200 and later. |
Examples
General Setup
Basic Information
- Name: Syslog
- Description: Data collection template for data from monitored syslogs.
- AppliesTo (custom query): /*isLinux() || isNetwork()*/
- Type: LM Logs: Syslog
- Group: Syslog
Resource Mappings
| Method | Key | Value |
| Token | device | ##system.hostname## |
Resource Mapping
The following is an example of a resource mapping using the LM Property (Token) method. Say you provide a property to map to one of the monitored devices in the LM portal. The key for the LM Property is “token.resourceMap” and the value is “syslog_test_collector”.
When a LogSource is applied on the device, the resource mapping is done with LM_property as “token.resourceMap”, source as “LM Property”, parse method as “Token”, and value as anything starting with “##”, like “##token.resourceMap##”.
The collector receives the hostEntry from the feed, and replaces the ##token.resourceMap## with the value received against the LM_property “token.resourceMap” for that particular host (For example “syslog_test_collector”).
If there are multiple resources to which the log source is applied, the value for LM_property should be unique. Otherwise the Ingest API will not map it to the resource as there will be multiple resources having the same mapping.
The following image is from the Resources information for the example “syslog_test_collector”.
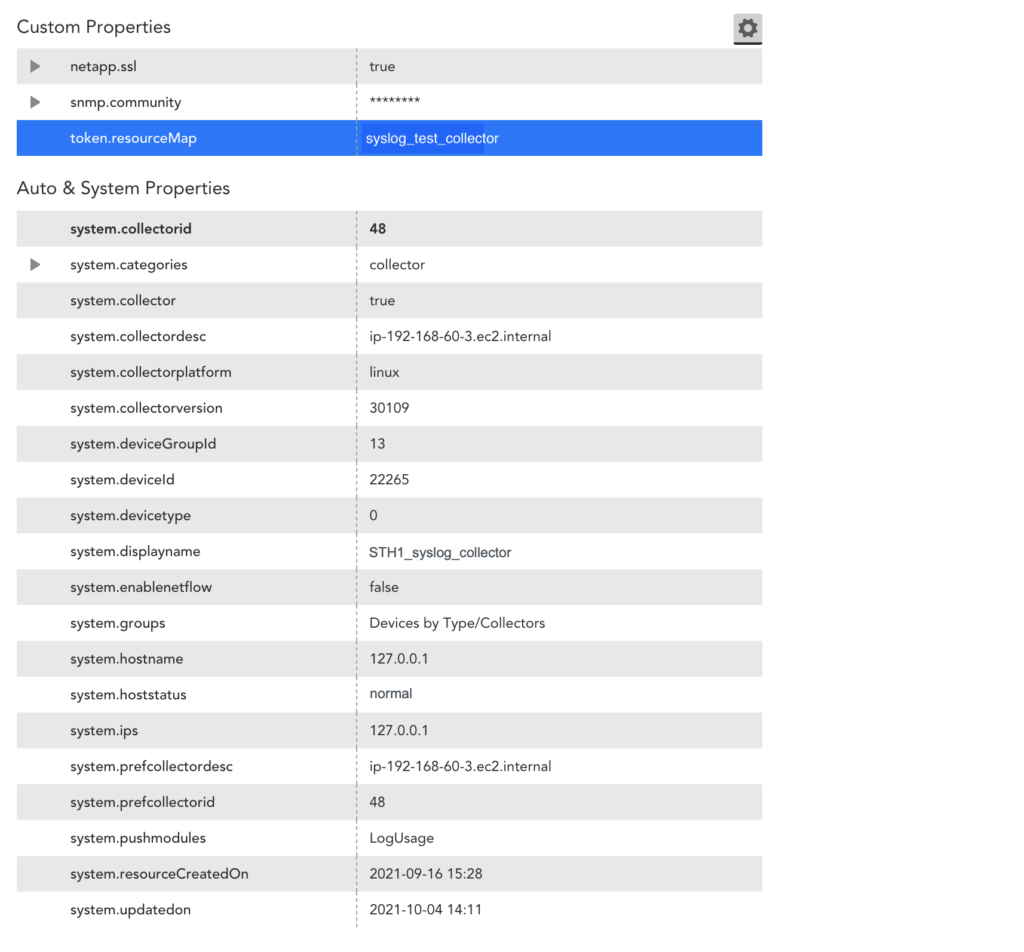
The following image is from the resource mapping in LogSource for the example “syslog_test_collector”.
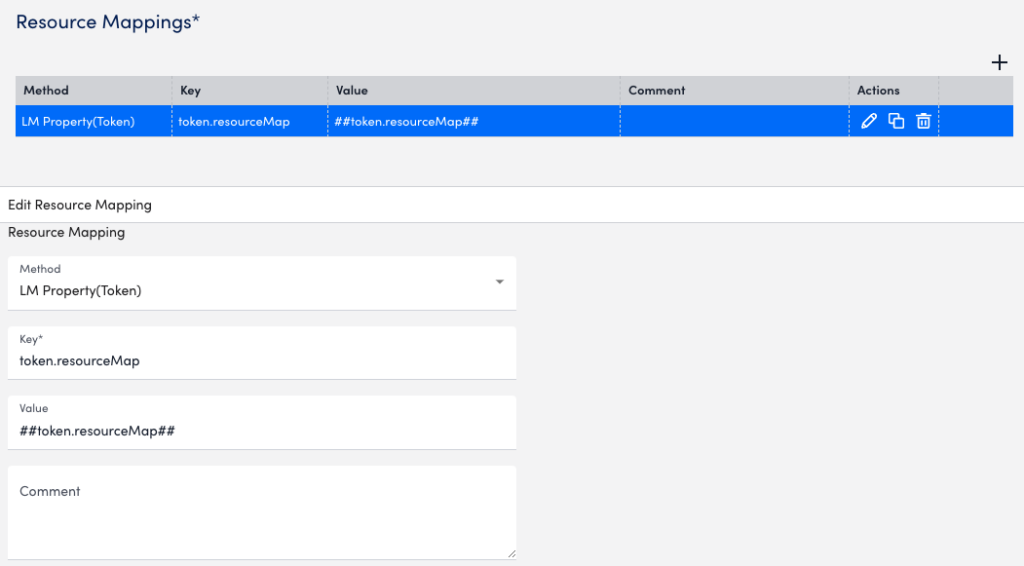
The resource mapping on the collector side for this LogSource is as follows:
'{"metadata":{"logSource_id":"2249","logsource_name":"syslog_test_token"},"Severity":"3: Error","Host":"localhost","epochWhenAddedInQueue":1633501246808,"Facility":"1: user-level messages","message":"<11>Just a message with metadata test_md1 !!\u0000","_lm.resourceId":{"token.resourceMap":"syslog_test_collector"},"timestamp":1633501246808,"_lm.collectorId":"48"}', raw:'<11>Example message with metadata test_md1 !!'